Abstract
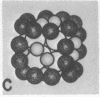
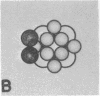
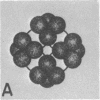
The binding of pyruvate dehydrogenase and dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase (flavoprotein) to dihydrolipoyl transacetylase, the core enzyme of the E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex [EC 1.2.4.1:pyruvate:lipoate oxidoreductase (decaryboxylating and acceptor-acetylating)], has been studied using sedimentation equilibrium analysis and radioactive enzymes in conjunction with gel filtration chromatography. The results show that the transacetylase, which consists of 24 apparently identical polypeptide chains organized into a cube-like structure, has the potential to bind 24 pyruvate dehydrogenase dimers in the absence of flavoprotein and 24 flavoprotein dimers in the absence of pyruvate dehydrogenase. The results of reconstitution experiments, utilizing binding and activity measurements, indicate that the transacetylase can accommodate a total of only about 12 pyruvate dehydrogenase dimers and six flavoprotein dimers and that this stoichiometry, which is the same as that of the native pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, produces maximum activity. It appears that steric hindrance between the relatively bulky pyruvate dehydrogenase and flavoprotein molecules prevents the transacetylase from binding 24 molecules of each ligand. A structural model for the native and reconstituted pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes is proposed in which the 12 pyruvate dehydrogenase dimers are distributed symmetrically on the 12 edges of the transacetylase cube and the six flavoprotein dimers are distributed in the six faces of the cube.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEINERT H., PAGE E. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. V. Oxidation-reductions of the flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):479–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Perham R. N. An amino acid sequence in the active site of lipoamide dehydrogenase from the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex of E. coli (Crookes strain). FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derosier D. J., Oliver R. M., Reed L. J. Crystallization and preliminary structural analysis of dihydrolipoyl transsuccinylase, the core of the 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1135–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eley M. H., Namihira G., Hamilton L., Munk P., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. 18. Subunit composition of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):655–669. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R., Creaghan I. T. Gene-protein relationships of the alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli K12: isolation and characterization of lipoamide dehydrogenase mutants. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):197–210. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning U., Dennert G., Hertel R., Shipp W. S. Translation of the structural genes of the E. coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:227–234. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOIKE M., REED L. J., CARROLL W. R. alpha-Keto acid dehydrogenation complexes. IV. Resolution and reconstitution of the Escherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenation complex. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:30–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. C., Pelley J. W., Pettit F. H., Hucho F., Randall D. D., Reed L. J. -Keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XV. Purification and properties of the component enzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes from bovine kidney and heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):327–342. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe O. A., Jr, Hammes G. G. A study of the binding of thiamine diphosphate and thiochrome diphosphate to the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2547–2552. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk P., Cox D. J. Sedimentation equilibrium of protein solutions in concentrated guanidinium chloride. Thermodynamic nonideality and protein heterogeneity. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):687–697. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Hamilton L., Munk P., Namihira G., Eley M. H., Willms C. R., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. XIX. Subunit structure of the Escherichia coli alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5282–5290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. 8. Comparison of dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenases from pyruvate and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1126–1130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed L. J., Oliver R. M. The multienzyme alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1968 Jun;21(2):397–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speckhard D. C., Frey P. A. Esherichia coli pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: improved purification and the flavin content. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90443-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel O., Hoehn B., Henning U. Molecular structure of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1615–1619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]