Abstract
This article is a primer on the pathophysiology and clinical evaluation of peripheral neuropathy for the radiologist. Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) has utility in the diagnosis of many focal peripheral nerve lesions. When combined with history, examination, electrophysiology, and laboratory data, future advancements in high-field MRN may play an increasingly important role in the evaluation of patients with peripheral neuropathy.
Keywords: neuroimaging, peripheral neuropathy, electromyography, nerve conduction study, entrapment neuropathy, hereditary neuropathy
Introduction
Although neuroimaging has been used routinely to help diagnose focal nerve lesions such as trauma and tumors for years, the utility of high-resolution MR Neurography in evaluation of multifocal and systemic polyneuropathies is just being investigated[1]. For the neurologist, the anatomic distribution, temporal progression, and electrophysiological properties of neuropathies guide the differential diagnosis, workup, and management of most forms of peripheral neuropathy; and, at present, MR Neurography is not part of the standard workup for patients with peripheral neuropathy. For example, both Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and amyloid neuropathy may show diffuse nerve enlargements that may not be readily distinguishable from one another on MR Neurography[2], whereas a nerve conduction study (NCS) will reveal dramatic reduction of conduction velocity in Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A, but normal velocity in amyloid neuropathy. As neuroimaging technology improves, novel MR imaging techniques such as molecular imaging may make MR Neurography more useful in the evaluation of patients with neuropathy.
In the first part of this article, we will review how neurologists approach peripheral nerve lesions, based on the anatomical, pathophysiological, and electrophysiological properties of peripheral nerves. Later in this chapter, characteristics of various peripheral nerve lesions will be summarized.
Basic Structure of Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system refers to the part of the nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord. Functionally, peripheral nerves are categorized into motor, sensory, and autonomic nerves. The cell bodies (soma) of motor neurons reside in the ventral gray matter of the spinal cord and are called anterior horn cells. Motor fibers often have very long axons that extend all the way to the neuromuscular junction. A motor unit consists of an anterior horn cell, its motor axon and all the muscle fibers it innervates, forming a synapse at the neuromuscular junction. Sensory neurons are bipolar with an afferent axon receiving sensory input from the periphery and an efferent axon entering the central nervous system via the dorsal root. The cell body of the sensory neuron resides in the dorsal root ganglion or one of the sensory ganglia of sensory cranial nerves. The autonomic nervous system is classified into sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves. The neurons of sympathetic nerves are located in the lateral horn of the spinal cord from T1 to L2, whereas the neurons of parasympathetic nerves are located in the brain stem and sacral spinal cord (S2, S3, and S4).
Peripheral nerves have multiple layers of connective tissue surrounding axons; epineurium contains blood vessels and other connective tissues that surround multiple fascicles of nerves (Figure 1A). Each fascicle is encased in perineurial connective tissue. Inside of each fascicle; individual myelinated and/or unmyelinated axons are surrounded by endoneurial connective tissue. Blood vessels (vasa vasorum) and nerves (nervi nervorum) are also contained within the nerve.
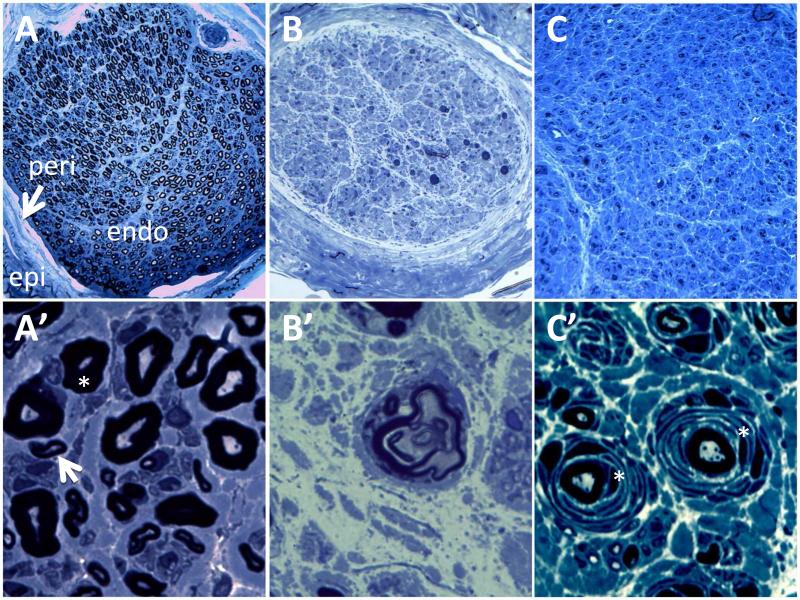
Figure 1.
Plastic sections of sural nerves stained with Toluidine Blue at 10X (A-C) and 100X (A’-C’). (A) Normal nerve showing normal density of myelinated nerve fibers. “endo” is endoneurium, “peri” (arrow) is perineurium surrounding fascicles, “epi” is epineurium. At high magnification (A’), large, thickly myelinated fibers (*) can be distinguished from smaller, thinly myelinated fibers (arrow). (B) Sural nerve from a patient with axonal neuropathy showing a fascicle with markedly reduced nerve fiber density. (B’) shows a fiber with a “myelin ovoid”, which can be seen in Wallerian degeneration. (C) Sural nerve from a patient with Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease type 1A. The nerve is diffusely enlarged (C), and at high magnification (C’), shows nerve fibers undergoing cycles of demyelination and remyelination, resulting in the typical “onionbulb” appearance (*).
Pathophysiology of Peripheral Nerve Injury
Regardless of its cause and nature of injury, peripheral nerve reaction to injury is limited to certain types of physiologic changes, depending on the extent of injury (Table 1). Minor, local insult to a peripheral nerve will result in a transient, focal conduction block, whereas intermediate insult may cause focal demyelination that requires a longer period of time for recovery. If the extent of nerve injury is severe enough to disrupt its axonal contents, a series of physiologic changes known as Wallerian degeneration follow to ensure removal and reformation of the nerve's damaged portion. The distal, degenerating portion of the axon undergoes stereotyped morphological changes and is subsequently digested by Schwann cells to pave the way for regenerating axons from the proximal portion.
Table 1.
Peripheral Nerve Reaction To Injury
| Insult | Physiologic Status | Etiology | Electrophysiology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal | Conduction block, rapidly reversible | Focal ischemia, mild compression | Focal conduction block |
| Intermediate | Conduction block, prolonged | Focal demyelination | Focal conduction block and slowing |
| Severe | Wallerian degeneration | Loss of axon and myelin sheath | Absent response |
Immediately after nerve transection, there are micro-structural changes in the distal portion of the axon without any gross light microscopic abnormalities until 48 hours. During this period, a nerve conduction study of the distal portion will show only a mild decrease in amplitude and nearly normal conduction velocity[3, 4]. At about 48-72 hours, the axons begin to fragment and form spiral or hook-like segments; in a cross section of a nerve biopsy, this fragmentation will appear as “myelin ovoids” (figure 1B’). At 7 days, there is a complete absence of axon organelles. By this time, there is significant reduction or absence of motor/sensory responses in nerve conduction studies. Considering the length of the entire axon, how these reactions occur in a concerted way within a relatively short period of time, it remains unknown. In the case of toxic or metabolic neuropathy where the entire nerve fiber – from cell body to neuromuscular junction – is affected, retrograde degeneration appears to take place, possibly due to insufficient supply of energy or other resource from the soma. This phenomenon is also called “dying-back” neuropathy and typically affects longest nerves first, thus causing symptoms initially in the feet.
Peripheral nerve injury is often classified into three basic categories based on its etiology, histological features, and clinical manifestations: neuropraxia, axonotmesis, and neurotmesis[5] (Table 2). Prognosis following trauma is poor if there is loss of continuity of the endoneurial tube.
Table 2.
Classification of Nerve Injury
| Classification | Physiology | Histology | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropraxia | Focal conduction block | Local myelin injury; no axonal injury | Recovery in weeks to months |
| Axonotmesis | Loss of nerve conduction at injury site and distally | Loss of continuity of axon, but endoneurial tube, perineurium and epineurium are intact | Good |
| Loss of continuity of axon and endoneurial tube, but perineurium and epineurium are intact | Poor | ||
| Neurotmesis | Loss of nerve conduction at injury site and distally | Severance of entire nerve | Regeneration only possible if distal stump reconnected |
Following nerve transection, the regeneration process begins at the distal end of the proximal stump. By 3-8 days after injury, small club-like branches will appear at the terminal axon. This distal extension is called a “growth cone”. By 48 hours, only a few of these collaterals reach the zone of injury. In optimal situations, it may take 8-15 days for growing axons to reach the distal portion. However, the closer to the cell body the site of injury is, the faster the rate of growth. The ability of nerves to regenerate depends upon maintenance of endoneurial tube, which practically speaking, depends upon the severity of nerve injury and length that the axon needs to regenerate. After approximately 9-20 days, the regenerating axon remyelinates; however, it should be noted that the myelination of the regenerating axon is often incomplete and has shorter inter-nodal distances compared to the pre-injured axon, delaying the propagation of action potentials.
Electrophysiology in peripheral neuropathy
Nerve conduction study: Peripheral neuropathy can be divided into those that primarily affect axons and those that primarily affect the myelin sheath. Axon loss may be seen after trauma to the nerve or as a result of toxic, ischemic, metabolic or genetic conditions. Demyelination may be seen in compressive neuropathies, hereditary neuropathies, and acquired immune-mediated neuropathies like Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). Nerve conduction studies provide information to differentiate primary axon loss lesion from a primary demyelinating lesion.
Axon loss: Amplitude of compound muscle action potential (CMAP) correlates with the number of motor nerve axons, and similarly, the amplitude of the sensory nerve action potential (SNAP) reflects the number of sensory nerve axons. Lesions causing axon loss generally result in reduced CMAP and SNAP amplitudes. It's important to keep in mind, however, that secondary axonal loss often occurs in severe or chronic demyelinating lesions. Furthermore, in axonal neuropathies, mild slowing of conduction velocity and prolongation of the distal latency (measure of distal conduction velocity) may occur if the fastest and largest axons are lost.
Demyelination: Loss of myelin is associated with slowing of conduction velocity (slower than 75% of the lower limit of normal), marked prolongation of distal latency (longer than 130% of the upper limit of normal), or both. Amplitude changes can also occur with demyelination due to secondary axonal loss. Reduced motor amplitude may also occur in demyelination if there is conduction block. In conduction block, the amplitude will be low when the nerve is stimulated proximal to the site of demyelination, but will be normal when stimulated below the block (Figure 2). Any drop in CMAP amplitude or area of more than 20% implies conduction block and any increase in the CMAP duration of more than 15% signifies temporal dispersion; both are hallmarks of demyelination. In patients with demyelinating polyneuropathies, conduction block at non-entrapment sites helps to differentiate acquired (GBS and CIDP) from inherited neuropathies (CMT).
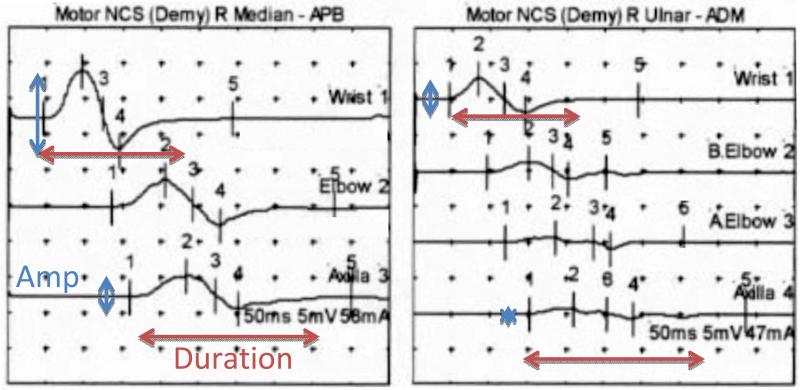
Figure 2.
Median and ulnar motor nerve conduction study showing partial motor conduction block in the forearm segment in a patient with acquired demyelinating polyneuropathy. Note that with stimulation above the elbow, the amplitiude (vertical blue lines) of the motor response is diminished (due to conduction block) when compared with the response at the wrist. Also, the duration of the response (horizontal red lines) is prolonged with stimulation above the elbow due to temporal dispersion, a common feature of demyelination.
Another useful measurement obtained in nerve conduction studies is the “F-wave” response, which is derived by antidromic travel of the action potential up the nerve to the anterior horn cell which then backfires in a small proportion of anterior horn cells, leading to orthodromic travel back down the nerve, past the stimulation site, to the muscle. The F response measures conduction along the entire length of a nerve and is typically markedly prolonged in demyelinating lesions.
In patients with entrapment neuropathy, the exact entrapment site can be obtained by finding evidence of focal demyelination, either by slowing or conduction block across the lesion site. Recovery from entrapment may occur quickly over several weeks if the compression is reversible and causes only focal demyelination. In contrast, entrapment causing significant axonal loss, evidenced by marked decrease in motor and sensory amplitudes, will have a longer and less complete recovery.
Electromyography: (EMG) is the recording of muscle electrical activity at rest (spontaneous) and with exertion (voluntary motor units) with an insertional electrode. The presence of abnormal spontaneous activity (positive sharp waves and fibrillation potentials) suggests active denervation. Analysis of motor unit potentials (MUAPs) on needle EMG helps determine the acuity and severity of nerve injury. Long duration, large amplitude and polyphasic motor unit potentials are seen in chronic axonal neuropathies, due to uninjured motor axons innervating denervated muscle fibers. During muscle contraction, there are two ways to increase muscle force: either motor units can increase their firing rate or additional motor units can start firing. Recruitment refers to the ability to add motor units as the firing rate increases. In neuropathic diseases, recruitment is reduced, and may be the earliest physiological sign of nerve injury. Thus, several weeks following a focal traumatic nerve injury, EMG will show abnormal sponanteous activity and reduced recruitment of normal-appearing motor units, whereas several months following later, the spontaneous activity will be normal, recruitment will remain reduced, and now the motor units will have prolonged duration and enlarged amplitude. In this way, EMG can not only help localize nerve lesions, but can also determine the chronicity of the neuropathic process.
Clinical Assessment of Peripheral Nerve Injury
When evaluating patients with neuropathy or nerve injury, it is very important to assess the physiologic status of peripheral nerves with nerve conduction studies in order to correlate their physiology with their clinical symptoms. Once the physiologic status of the nerve injury is assessed, its temporal progression, severity, and anatomic distribution should be carefully determined to reach an accurate diagnosis.
Anatomical Distribution: Localization of nerve lesions is the most important aspect of the neurological examination. A careful history and examination in conjunction with a thorough understanding of the anatomy of the peripheral nervous system should allow one to localize the lesion. Additionally, EMG/nerve conduction study can further localize the lesion and aid in understanding the pathophysiology. Table 3 summarizes common types of neuropathies that should be considered according to their characteristic patterns of neurologic findings.
Nerve Fiber Type: Motor, Sensory, and/or Autonomic; Large and/or Small Fibers
Table 3.
Pattern of neurologic symptoms
| Pattern | Neuropathies that should be considered |
|---|---|
| Symmetric, length-dependent distal weakness with sensory loss (Most Common type) | Metabolic neuropathies (e.g. diabetes), toxic neuropathies, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease |
| Symmetric proximal and distal weakness with sensory loss and areflexia | Inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathies (CIDP and GBS) |
| Multiple mononeuropathies | Vasculitic neuropathy, hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies (HNPP) |
| Asymmetric weakness with intact sensory exam and SNAPs | Motor neuron disease, multifocal motor neuropathy |
| Asymmetric weakness with pain in a dermatomal distribution | Radiculopathy |
| Sensory ataxia with or without weakness | Sensory neuronopathies from paraneoplastic syndrome, Sjogren's syndrome. |
| Significant autonomic involvement | Amyloidosis, diabetic neuropathy |
Careful attention to patients’ symptomatology and clinical exam often reveals the type of fibers that are involved in disease. Typically, the involvement of motor fibers can cause weakness, fasciculations, or muscle atrophy, whereas sensory involvement causes numbness, tingling, and/or altered perception of pain. Also, the damage of large fibers causes imbalance and reduced vibratory and proprioceptive sensation, while small fiber dysfunction causes decreased pinprick and temperature sensations. Autonomic involvement can result in altered sweating, orthostasis, constipation, urinary retention, or palpitations. Nerve conduction studies can only evaluate large motor and sensory nerve fibers; whereas if there is selective damage to small fibers, other tests, such as a skin biopsy, are required to evaluate these small unmyelinated nerve fibers.
• Pathophysiology: Demyelinating or Axonal
A nerve conduction study is necessary to determine whether a nerve injury is primarily demyelinating, axonal, or both, and is essential in the assessment of peripheral nerve injury. Demyelinating neuropathy characteristically shows a reduction in conduction velocity and prolongation of distal and F-wave latencies, whereas axonal neuropathy shows a reduction in amplitude. In some situations, a nerve biopsy may be considered to evaluate the cause of neuropathy, and is most useful in diagnosing vasculitic or amyloid neuropathy and infiltrative neuropathies due to tumor. When possible, the sural or superficial radial sensory nerves are typically resected for pathologic analysis so as to leave minimal neurologic deficit. When other nerves are considered for biopsy, MR Neurography is often helpful in determining the optimal biopsy site. While diagnosis of demyelinating neuropathies (e.g. CIDP or CMT) can be aided by biopsy, nerve biopsy is rarely needed for diagnosis.
• Severity
In addition to the examination, EMG/NCS is extremely helpful in determining severity of nerve injury. The amplitude of motor and sensory responses is a good measure of degree of axonal loss and correlates with disability. EMG can assess whether muscles are denervated, and if so, can also determine the acuity and severity of denervation. There are different quantitative methods for measuring severity of nerve injury, often using simple tools such as the Rydel-Seiffer tuning fork, Von Frey monofilaments, and hand-held dynamometer. Various measurement formulas have also been suggested, using a combination of the above quantitative testing results. Among them, Total Neuropathy Score (TNS) is widely used for many systemic neuropathies; its inter-and intra-reliability are well established[6, 7], and is particularly useful in assessing therapeutic responses.
• Clinical Course
Careful evaluation of the temporal progression of the patients’ symptoms, when correlated with the exam and physiology, can provide crucial information about the disease process. For example, a toxic or nutritional neuropathy might present with a monophasic course when adequately treated, whereas chronic inflammatory neuropathy can present with a relapsing and remitting course.
Entrapment mononeuropathies
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common mononeuropathy and is caused by entrapment of the median nerve as it runs in the carpal tunnel at the wrist. Other common entrapment neuropathies include ulnar neuropathy at the elbow (cubital tunnel syndrome), radial neuropathy at the spiral groove, and peroneal neuropathy at the fibular head. Conditions that predispose to carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel syndrome include occupations that undergo repetitive flexion/contraction of the wrists and elbows, diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism, arthritis, and underlying peripheral neuropathies leading to nerve hypertrophy. Examination shows sensory with or without motor deficits in the distribution of the peripheral nerve and may show a “positive Tinel's sign” in which percussion over the site of nerve injury reproduces the patient's sensory symptoms. Diagnosis is typically made with EMG/NCS, but imaging modalities such as ultrasound and MR Neurography are increasingly being used to help surgeons determine etiology, severity, prognosis, and treatment of entrapment mononeuropathies.
Neuropathies associated with metabolic disease typically present with a slowly progressive, distal (length-dependent) symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy (DSPN) with physiologic features of axonal loss.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy in the United States and Europe. The risk of developing peripheral neuropathy correlates with the duration of DM, glycemic control, and presence of retinopathy and nephropathy[8]. Distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy (DSPN) is by far the most common form of diabetic neuropathy; however, multiple forms of neuropathy are associated with diabetes. Nerve conduction studies typically show length-dependent, mixed demyelinating and axonal polyneuropathy, and this correlates with the nerve biopsy findings of axonal degeneration, regenerative clusters, and segmental demyelination. Autonomic and sensory nerve fibers are prominently involved in diabetic DSPN. Some diabetic patients develop “diabetic amyotrophy”, also known as “diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexopathy” which presents with relatively abrupt-onset, severe, asymmetric pain in the proximal thighs, often lasting months. Muscle weakness and atrophy in proximal thigh muscles often develops, though, the course of diabetic amyotrophy is monophasic, and patients will usually improve without treatment. Some pathological studies revealed infiltration of inflammatory cells in various locations in roots and peripheral nerves in patients with diabetic amyotrophy, suggesting an autoimmune etiology[9, 10]. However, efficacy of immunotherapy with IVIG or prednisone is questionable due to its favorable outcome even without any treatment. (Table 4)
Hypothyroidism most commonly predisposes patients to entrapment neuropathies, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, but rarely can cause generalized sensory neuropathy, characterized by painful paresthesias and numbness in distal limbs[11].
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Deficiency causes peripheral neuropathy in addition to the classic presentation of “subacute combined degeneration”, referring to loss of dorsal columns and corticospinal tracts within the spinal cord, leading to loss of proprioception and vibratory sensation in addition to hyperreflexia. Vitamin B12 deficiency-related neuropathy can be seen in patients who undergo bariatric surgery in addition to strict vegetarians.
Other Vitamin deficiencies. Vitamin B1 (thiamine) and vitamin E deficiency are rare causes of peripheral neuropathy. Thiamine deficiency can occur in patients with chronic alcoholic consumption. Of note, both deficiency and overdose of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) can both cause peripheral neuropathy.
Uremic Neuropathy refers to neuropathy associated with renal failure. Approximately 60% of patients with chronic renal failure (usually when glomerular filtration rate is less than 12 mL/min) develop DSPN[12]. Mononeuropathies, especially carpal tunnel syndrome, are common and thought to be related to accumulation of beta2-microglobulin during hemodialysis.
Chronic Liver Disease is another cause of neuropathy. In one study, DSPN was found in 71% and autonomic neuropathy was found in 48% of patients[13].
Table 4.
Neuropathy associated with diabetes
| Distal symmetric sensory motor polyneuropathy |
|---|
| Autonomic neuropathy |
| Diabetic polyradiculoneuropathy |
| • Asymmetric, painful lumbosacral radiculoplexopathy (diabetic amyotrophy) |
| • Symmetric, painless, polyradiculopathy |
| • Cervical or thoracic radiculopathy |
| Focal mononeuropathies |
| • Cranial neuropathy |
| • Entrapment mononeuropathy |
| Diabetic small fiber neuropathy |
Inflammatory and immune-mediated neuropathy
The immune-mediated neuropathies are a heterogeneous group of disorders wherein the immunologic process may be directed to either peripheral nerves or the supporting blood vessels. Peripheral nerve myelin is the usual target in demyelinating neuropathy. In vasculitic neuropathy, the pathologic process originates in the blood vessels and leads to nerve ischemia, resulting in a neuropathy characterized by multifocal sensory and motor axonal loss.
- Guillain Barré Syndrome (GBS) is the most frequent cause of acute flaccid paralysis worldwide[14]. GBS is not a single disorder, but rather encompasses several types of acute immune-mediated polyneuropathies (table 5).
- Antecedent illness: About two-thirds of patients with GBS have an illness during the preceding few weeks, usually a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection. Cytomegalovirus is the most commonly associated viral infection. Campylobacter jejuni, which causes gastroenteritis, is the most frequently associated bacterial infection. Vaccination may increase GBS risk.
- AIDP Clinical features: GBS usually initially presents with numbness and tingling in the feet and hands. Even at an early stage, the muscle stretch reflexes are usually lost or diminished. Progressive weakness accompanies the sensory disturbance, classically in an ascending pattern. However, in some patients, weakness from the onset involves proximal or axial muscles, and facial weakness is often apparent in at least half of the patients during the course of the illness. Ophthalmoparesis and bulbar paralysis may develop in some patients, and the most concerning feature is respiratory insufficiency due to diaphragm weakness.
- Axonal GBS is uncommon in United States and Europe, but is common in Asia[15]. AMAN has exclusively motor findings with weakness typically beginning in legs. Tendon reflexes are preserved until weakness is severe. Respiratory insufficiency may occur. AMSAN is clinically and physiologically similar, but with detectable sensory involvement.
- Miller Fisher Syndrome (MFS) is characterized by ataxia, areflexia, and ophthalmoplegia. There is a spectrum between MFS and Bickerstaff encephalitis which is characterized by ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, abnormalities in consciousness and pyramidal tract dysfunction associated with brain MRI showing gadolinium-enhancing brainstem lesions. These syndromes typically are preceded by C.jejuni or Mycoplasma infection, and are associated with anti-GQ1b antibodies[16].
- Electrophysiology: NCS in AIDP shows typical features of demyelination including prolonged distal latencies, slow conduction velocities, temporal dispersion, conduction block, and prolonged F-wave latencies. In axonal GBS, NCS reveals low amplitude or unobtainable CMAPS and/or SNAPs, and EMG shows acute and chronic denervation. In Miller Fisher syndrome, NCS reveals reduced amplitudes of SNAPs out of proportion to any prolongation of the distal latencies or slowing of sensory conduction velocities. CMAPs in the upper and lower limbs are usually normal.
- Investigations: CSF shows albuminocytologic dissociation (elevated CSF protein levels accompanied by few mononuclear cells) in over 80% of GBS patients after 2 weeks. Enhancement of nerve roots may be seen on spine MRI in AIDP. Antiganglioside antibodies, particularly GM1 IgG antibodies, are found in some patients with AIDP and correlates with recent C. jejuni infection. Serologic evidence of recent C. jejuni infection with GM1 or GD1a antibodies are demonstrated in the majority of patients with AMAN; GM1 antibodies are found in the majority of patients with AMSAN[17] and GQ1b antibodies are evident in many patients with Miller Fisher syndrome[16]. Molecular mimicry between gangliosides expressed on nerve fibres and glycolipids present on C. jejuni may account for their association and may play a role in the pathogenesis of the disorder.
- Prognosis: The rate of progression in GBS is variable; in over 90% of patients, the nadir is reached within 1 month. The severity of involvement varies from minimal weakness to complete quadriplegia and need for mechanical ventilation. Autonomic dysfunction can occur in many patients. The progression phase is followed by a plateau phase followed by recovery. Poor prognostic predictors include advanced age, fast rate of progression, axonal loss on NCS, and severe weakness at the nadir. Immunotherapy is believed to hasten recovery, but does not alter ultimate prognosis[18-20]. Recovery may take many months and may be incomplete. Approximately 15% of GBS patients have functionally significant residual deficits[21].
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an acquired immune-mediated peripheral neuropathy that presents either as a chronic progressive or relapsingremitting disorder[22].
- Clinical features: In typical CIDP, motor and sensory deficits develop insidiously over months (minimum of 8 weeks), often leading to significant disability. Most patients manifest with progressive, symmetric, proximal and distal weakness of the upper and lower limbs with numbness and paresthesias in extremities. As in AIDP, reflexes are usually absent or markedly attenuated, and examination reveals loss of large fiber sensory modalities (vibration and proprioception). Involvement of cranial nerves (ophthalmoparesis, facial or bulbar weakness) may be observed in approximately 15% of cases. Patients with long standing CIDP can have symptoms typical of lumbar stenosis and cauda equina dysfunction. In some cases, hypertrophy of nerve roots may cause crowding and entrapment of the roots in the lumbar thecal sac and lumbar spinal canal, including the neural foramina[23].
- Investigations: As in AIDP, diagnosis of CIDP is supported by findings of cytoalbuminergic dissociation and electrodiagnostic evidence of demyelination in multiple motor nerves. Nerve biopsy is performed in unusual cases, such as those patients with asymmetrical presentations and pain, in whom there is concern about other pathologies such as a vasculitis. Biopsies typically show inflammation and demyelination in addition to mild axonal degeneration. Laboratory testing should include a quantitative assessment of serum immunoglobulins and screening for monoclonal gammopathies in serum and urine with immunoelectrophoresis and immunofixation. If kappa or lambda light chains are detected, follow up with hematology consultation and bone marrow biopsy is often necessary to rule out a lymphoproliferative disorder or malignant plasma cell dyscrasia. A radiologic skeletal survey should be performed to search for either osteosclerotic or osteolytic myeloma.
- Prognosis: The course of CIDP may be continuous or stepwise progressive or relapsing. Most patients respond to immunotherapy (steroids, plasmapheresis, or intravenous gammaglobulin), and clinical response may aid in diagnosis. In patients who do not respond well to immunotherapy, variants of CIDP should be considered (table 6).
- Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is an acquired, immune-mediated asymmetrical motor neuropathy with focal motor conduction block on electrophysiologic testing.
- Clinical features. Generally, MMN has onset between the ages of 20 and 50, and men are affected three times more frequently than women. As it's name suggests, MMN is an asymmetric motor neuropathy that has a predilection for the upper limbs, particularly the nerves innervating the forearm and the intrinsic hand muscles leading to wrist drop. Sensory involvement is minimal. Fasciculations and cramps may be seen, often raising a concern for a diagnosis of motor neuron disease. Most of the cases follow a slow progressive course.
- Electrophysiology: Focal conduction block of motor fibers outside common entrapment sites is the hallmark of MMN. Sensory conduction studies obtained across the same sites of motor block are normal. Conduction block is defined as a significant reduction of the evoked compound muscle action potential (CMAP) amplitude, or area between distal and proximal sites of stimulation along a focal nerve segment, in the absence of abnormal temporal dispersion.
- Investigations: IgM anti-GM1 antibodies are present in ~ 50% of cases[24].
- Paraproteinemic Neuropathy. Monoclonal gammopathy (or paraprotein) identified on serum or urine electrophoresis is often found in patients with neuropathy[25]. IgG is the most common paraprotein, followed by IgM and IgA. Monoclonal gammopathy can be associated with hematological disorders like multiple myeloma, lymphoma, plasmacytoma, Waldenstrom globulinemia, amyloidosis, cryoglobulinemia, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. If a detailed hematologic evaluation is negative, the term monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance is used. Even if the initial evaluation is negative, these patients should be followed periodically. The association between paraprotein and neuropathy is strongest with IgM. Some paraproteinemic neuropathies may be caused by immunoreactivity of the paraprotein, whereas in patients with known hematological disease, pathogenic mechanisms such as nerve infiltration, cryoglobulinemia, amyloidosis, or hyperviscosity may play a role. In others, the paraprotein may not be the cause of neuropathy.
- IgM gammopathy: Most neuropathies seen in association with IgM gammopathy are demyelinating. About 50% of patients with peripheral neuropathy and IgM gammopathy have IgM antibodies that bind to myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG). These patients present with slowly progressive distal limb paresthesias, sensory loss, gait ataxia, and tremor, with mild or no weakness. This condition has also been called distal acquired demyelinating symmetric (DADS) neuropathy. Nerve conduction study often shows markedly prolonged distal latency with only mildly reduced conduction velocities.
- POEMS syndrome (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, and skin changes) is a rare paraneoplastic disorder that usually occurs in patients with osteosclerotic myeloma, but may occur is association with Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia or plasmacytoma. The most common paraprotein is IgG or IgA lambda chain. The clinical and electrophysiological features of neuropathy are similar to CIDP, but are usually refractory to immunosuppressive treatment. Serum VEGF levels are often markedly elevated.
Table 5.
The Guillain-Barré Syndromes
| Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (AIDP) |
| Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS): ataxia, areflexia, and ophthalmoplegia |
| Axonal forms |
| Acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN) |
| Acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN) |
Table 6.
CIDP with concurrent disease
| HIV infection |
| Lymphoma |
| Osteosclerotic myeloma, POEMS (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal proteinand skin changes) |
| Monoclonal gammopathy |
| Chronic active hepatitis, hepatitis C |
| Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Connective tissue disease |
| Bone marrow and organ transplants |
| Central nervous system demyelination |
| Nephrotic syndrome |
| Diabetes mellitus |
| Hereditary neuropathy |
| Thyrotoxicosis |
Vasculitic neuropathy
Vasculitic neuropathy is an immune-mediated disorder directed against blood vessels, resulting in ischemia and infarction to the peripheral nervous system.[26] Vasculitic involvement of the peripheral nerves typically causes multiple, focal areas of ischemic injury. The clinical presentation is typically initially one of multiple mononeuropathies (also called mononeuritis multiplex), but over time, may develop into a distal symmetric polyneuropathy. Patients typically present with an acute onset of pain and progressive sensory and motor deficits in the distribution of specific nerves. The clinical course may be step-wise or progressive. (Table 7)
Diagnosis: Electrodiagnostic testing often shows a mononeuritis multiplex pattern. Laboratory evaluations are performed to evaluated for systemic forms of vasculitis (table 7), including complete blood count, ESR, C-reactive protein, renal and liver functions, electrolytes, urinalysis, glycated hemoglobin, serum immunofixation electrophoresis, complement levels, cryoglobulins, hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis C antibody, HIV antibody, antinuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, SSA and SSB antibodies, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. The definitive diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy is made with biopsy of a clinically or electrophysiologically involved nerve, preferably the sural or superficial radial sensory nerve. The pathological features of vasculitic neuropathy includes vessel wall changes of transmural inflammation, fibrinoid necrosis, endothelial damage and hemorrhage, thrombosis, endothelial hyperplasia, fibrosis of vessel wall, fragmentation of the elastic membrane, narrowing or occlusion of the lumen, recanalization, wedge shaped axon loss, centrafascicular degeneration, subperineural edema, and fascicle-to-fascicle variability (Figure 2). A combined nerve and muscle biopsy increase the diagnostic sensitivity.
Table 7.
Vasculitis associated with neuropathy
| Primary systemic vasculitis |
| Large vessels |
| Giant cell arteritis |
| Medium vessels |
| Polyarteritis nodosa |
| Small vessels |
| Microscopic polyangiitis |
| Churg-Strauss syndrome |
| Wegener's granulomatosis |
| Secondary systemic vasculitis |
| Connective tissue diseases |
| Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Sjogren's syndrome |
| Dermatomyositis |
| Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Behcet disease |
| Sarcoidosis |
| Infection |
| Hepatitis B and C, HIV |
| Malignancy |
| Nonsystemic vasculitis |
Hereditary Neuropathy
Also known as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), the hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies (HMSN) encompass the largest group of inherited neuropathies. These diseases are commonly classified based on clinical presentation (age of onset and inheritance pattern) and pathology/electrophysiology (axonal: CMT1 vs. demyelinating: CMT2)[27, 28].
Clinical features. Most patients with CMT develop slowly progressive weakness and atrophy in their feet beginning in childhood or early adulthood. Pain or sensory loss is variable, but is usually not a chief complaint. Foot deformities (pes cavus, or high arches, and hammertoes) are common and may lead to disability. Due to the insidious nature of this disease, most patients do not complain of motor or sensory symptoms until late in the course of the disease, and most patients remain ambulatory. On examination, patients typically have distal weakness and atrophy in the feet, areflexia, and length-dependent sensory loss of both large and small-fiber sensory modalities. More severely affected patients will develop sensory ataxia or tremor (Roussey-Levey syndrome), palpably enlarged nerves (CMT1), and weakness, atrophy, and sensory loss of the hands. Patients without evidence of sensory involvement on examination or electrodiagnostic testing are classified as having hereditary motor neuropathy, whereas patients without evidence of motor involvement are classified as hereditary sensory or hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy.
Electrophysiology. When CMT is clinically suspected, the most useful test is nerve conduction study. Nerve conduction studies usually can classify the disease as primarily axonal or demyelinating. For example, the most common form of CMT, CMT1A, typically shows marked and uniform reduction of motor and sensory conduction velocities (typically 10-30 m/sec). Hereditary Neuropathy with Liability for Pressure Palsies (HNPP) shows milder slowing of conduction velocities, but frequently shows focal slowing or conduction block at common sites of entrapment. Classification of the disease as axonal or demyelinating can frequently limit the genetic testing required, as the common mutations causing CMT1 (demyelinating) are in general, different than those causing CMT2 (axonal).
Diagnosis. CMT is usually suspected when there is a family history of peripheral neuropathy, as most forms of CMT are autosomal dominant. Less commonly, CMT can be X-linked, autosomal recessive, or sporadic. Approximately 2/3 of CMT is type 1, and ~ 2/3 CMT1 is CMT1A, caused by duplication of the Peripheral Myelin Protein 22 (PMP22) gene. The most common cause of axonal CMT (CMT2A) is caused by mutations in the mitofusin2 (MFN2) gene; as its name implies, mitofusion regulates fusion of mitochondria, a process thought to be important in the maintenance of axonal health. Though treatments are not yet available for specific forms of CMT, genetic testing can potentially give a definitive diagnosis not available by any other means, and can obviate invasive testing (eg nerve biopsy) and unnecessary treatment (eg intravenous gamma globulin). Genetic testing also has important implications for other family members and family planning, and should be performed along with genetic counseling. When nerve biopsy is performed in CMT1 patients, they typically show the classic appearance of “onion bulbs” (Figure 1C’), caused by severe, chronic demyelination and remyelination.
Neuropathies associated with amyloid protein
Amyloids are insoluble aggregates of various proteins that share common three-dimensional structure of β-pleated sheets and are resistant to proteolytic decomposition. Amyloidosis refers to a variety of conditions where amyloid protein accumulates in any organ, including peripheral nerves, leading to dysfunction. Amyloid deposits have characteristic apple-green birefringence when stained with Congo red and seen under a polarizing microscope, and may be detected on nerve biopsy (figure 3). Amyloidosis can be either acquired or hereditary. Acquired amyloidosis can be due to abnormal protein accumulation in the setting of multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, lymphoma, or lymphoproliferative disorders. Polyneuropathy develops in about 30% of patients with acquired primary amyloidosis, which can be a presenting symptom[29]. There is a predilection for small fiber neuropathy causing painful burning sensation in the distal limbs. Nerve conduction study typically shows a symmetric, length-dependent sensorimotor polyneuropathy; however, some patients present with asymmetric, multiple mononeuropathies. In the case of primary amyloidosis, carpal tunnel syndrome is also very common. Familial amyloidosis is most commonly caused by mutations in the transthyretin (TTR) gene, but rarely can be caused by mutations in apolipoprotein A1 or gelsolin.
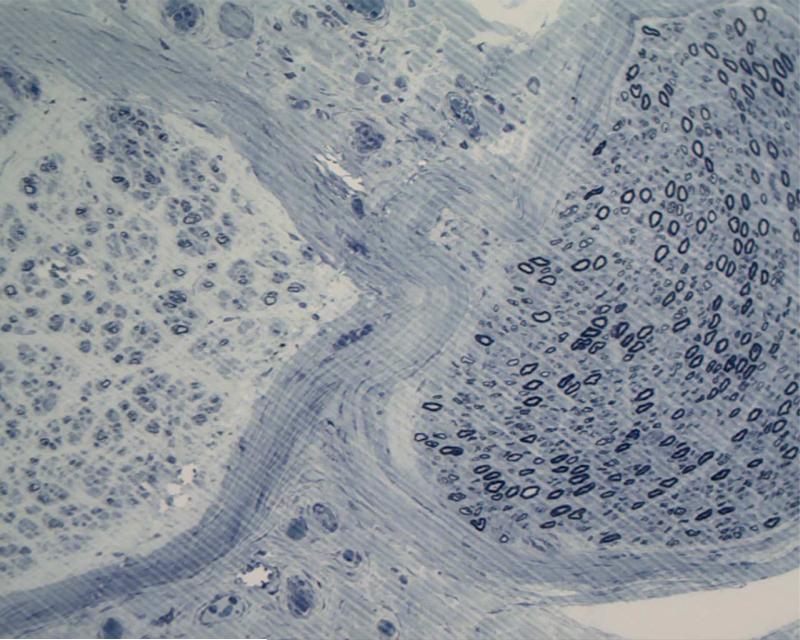
Figure 3.
Vasculitic neuropathy: the plastic section with toluidine blue staining shows a striking fascicle-to-fascicle variation of fiber density in the two adjacent fascicles. Mild subperineurial edema can also be appreciated in this section.
Toxic Neuropathy
From a practical perspective, it is often difficult to prove causality when a toxic neuropathy is suspected[30]. However, finding the cause should not be neglected, as toxic neuropathy is one of those conditions where treatments are available, if diagnosed timely. Although many clinicians regard toxic neuropathy as a diagnosis of exclusion, we found it very helpful to use quantitative measurement tools, such as the Total Neuropathy Score (TNS) to better appreciate the temporal relation of disease's severity and a suspected toxin. In some chemotherapy-induced neuropathies, TNS is shown to correlate with the dose of chemotherapeutic agents, validating its use to establish causality[7].
Most toxic neuropathies cause distal, length-dependent peripheral neuropathy, regardless of toxin. As briefly mentioned in the previous section, neurotoxins affect entire length of nerve, from its cell body to terminal axon, affecting more severely in the distal portion. This “dying-back” neuropathy is very common in most forms of neuropathy, making toxic neuropathy difficult to diagnose. Hence, other systemic features can be a clue to diagnose certain toxic neuropathies. For example, toxic neuropathy due to arsenic poisoning can show not only typical length-dependent neuropathy, but also systemic symptoms, such as GI symptoms, psychosis, and/or Mee's line in finger nails. Toxins that can cause neuropathy and its pathophysiologic characteristics are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8.
Common toxins that can cause neuropathy
| Toxins | Clinical Features | Pathophysiology |
|---|---|---|
| Vinca alkaloids | Symmetric, sensorimotor, large and small fiber polyneuropathy | Mixed axonal degeneration and demyelination |
| Cisplatin | Predominantly large fiber sensory neuronopathy | Sensory neuronopathy |
| Taxanes | Symmetric, predominantly sensory polyneuropathy | Axonal degeneration |
| Amiodarone | Severe proximal and distal weakness, affecting legs more than arms | Demyelinating |
| Colchicine | Proximal weakness from concomitant myopathy and loss of touch/vibratory sensation | Axonal degeneration |
| Lead | Insidious-onset, progressive weakness in upper extremities, with minimal sensory involvement; GI symptoms, bluish-black line coloration of gums (“lead line”) | Axonal degeneration |
| Alcohol | Slowly progressive parasthesia, numbness, and burning pain, more severe in legs; autonomic dysfunction is common | Generalized sensorimotor, primarily axonal polyneuropathy |
Neuropathies Associated With Autoimmune Disease
Sjogren Syndrome. Peripheral neuropathy is present in 10 to 22% of all patients with Sjogren's syndrome[31, 32]. Common forms of neuropathy include length-dependent axonal sensorimotor neuropathy, small fiber neuropathy, and sensory neuronopathy.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). About 50% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis are reported to have neuropathy, most frequently due to entrapment[33]. Vasculitic neuropathy can also develop patients with RA, making it the third most common cause of vasculitic neuropathy in one case series[34], after polyarteritis nodosa and isolated peripheral nervous system vasculitis. It is also important to rule out toxic neuropathy related to disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.
Systemic Sclerosis. Although sensory complaints are common and reported in up to 50% of scleroderma patients, the prevalence of polyneuropathy is thought to be low[35, 36]. Multiple mononeuropathies have been described in patients with CREST syndrome.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). SLE is a relatively common multisystem disease, often affecting the nervous system. Although SLE more frequently affects the central nervous system, about a quarter of patients with SLE are reported to have peripheral neuropathy[37]. Patients typically complain of slowly progressive distal sensory loss. Multiple mononeuropathies are reported, but appear to be less common.
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease. A mild distal axonal sensorimotor polyneuropathy reportedly occur in about 10% of patients[38].
Sarcoidosis. Central and peripheral nervous system can be affected in sarcoidosis. Characteristically, cranial nerves are frequently involved, mostly commonly the facial nerve. In one study, clinical features of 57 patients with sarcoid neuropathy were analyzed; the most common pattern was monophasic, asymmetric, and non-length dependent[39].
Celiac Disease. About 10% of patients with celiac disease have neurologic complications, with ataxia and peripheral neuropathy being most common. The peripheral neuropathy associated with celiac disease manifest as distal sensory[40]. Generalized sensorimotor polyneuropathy, motor neuropathy, multiple mononeuropaties, autonomic neuropathy and neuromyotonia are also reported.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease are inflammatory disorders of the bowel associated with various neurologic complications including peripheral neuropathy. AIDP, CIDP, sensory neuropathy, sensorimotor neuropathy, small fiber neuropathy, brachial plexopathy, multiple mononeuropathies, and cranial neuropathy have been reported[41].
Primary Biliary Sclerosis. Peripheral neuropathy associated with primary biliary sclerosis is characterized by distal numbness and tingling. Large fiber sensory modalities are predominantly affected by primary biliary sclerosis[42].
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome. A generalized peripheral neuropathy of multiple mononeuropathies occurs in 6-14% of patients with hypereosinophiic syndrome[43].
Neuropathies associated with infection
Leprosy is caused by the acid-fast bacteria Mycobacterium leprae and is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy in the developing world including Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America. A slowly progressive sensorimotor polyneuropathy gradually develops due to widespread invasion of the bacilli into the nerve fibers[44].
Lyme disease is caused by infection with Borrelia burgdorferi, which is transmitted by ticks. There are three stages of Lyme disease, first stage being early infection with erythema migrans, second stage being disseminated infection, and third stage being late infection. Neurologic complications may develop during the second and third stages of infection. Various neuropathies can occur with Lyme disease, facial neuropathy being most common. Mononeuropathies, polyradiculopathy, and plexopathy are also be associated with Lyme disease[45]. The presentation of polyradiculopathy may resemble Guillian-Barre Syndrome. It is also important to note that false-positive results of Lyme serology tests are common, and therefore, Western blot must be performed to confirm the results.
Diphtheritic Neuropathy is caused by a toxin released by the bacteria. Corynebacterium diphtheria. Cranial nerves can be affected 3-4 weeks after the infection. Generalized polyneuropathy may develop 2-3 months following the initial symptom presentation.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection can cause various neurological complications including peripheral neuropathy. About 20% of patients with HIV infection develop neuropathy as a result of virus infection itself, opportunistic infections, such as cytomegalovirus infection, or neurotoxicity from antiviral medications. The most common forms of HIV-related peripheral neuropathies include distal symmetric polyneuropathy, inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (either acute or chronic), multiple mononeuropathies, polyradiculopathy, autonomic neuropathy, and sensory ganglinitis[46]. Among them, distal symmetric polyneuropathy is the most common form and is usually seen in patients with AIDS. Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy can occur at the time of seroconversion.
Human T-lymphocyte Type 1 virus (HTLV-1) is associated with an axonal, length-dependent, sensorimotor polyneuropathy, which can be seen in the absence of myelopathy[47].
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) can cause acute lumbosacral polyradiculopathy and multiple mononeuropathies in immunocompromised patients.
Ebstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with acute inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy, cranial neuropathy, multiple mononeuropathies, brachial plexopathy, lumbosacral radiculoplexopathy, and sensory neuronopathies.
Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) can cause neuropathy due to reactivation of latent virus or a primary infection. Primary infection causes “chicken pox” and reactivation of the virus later in life results in dermal zoster. Most adult patients develop severe pain and parasethesias in a dermatomal region with a vesicular rash. Some patients also develop muscle weakness in the same myotomal area. Rarely, patients with VZV develop acute inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy.
Hepatitis B and C viruses can cause vasculitic neuropathy, often associated with cryoglobulinemia.
Neuropathies associated with malignancy
Paraneoplastic neuropathy is relatively rare and most commonly associated with lung cancer. In particular, paraneoplastic sensory neuronopathy/ganglinopathy most commonly occurs with small cell lung cancer (often associated with anti-Hu antibody) and can precede the diagnosis of cancer by 4-12 months[48-50]. The causes of sensory neuronopathy are limited, and upon recognition, should prompt and thorough evaluation for malignancy. In addition, symmetric, sensorimotor polyneuropathy and paraneoplastic autonomic neuropathy can develop in patients with underlying cancer.
Neuropathy secondary to tumor infiltration. Direct infiltration of tumor cells into leptomeninges, cranial nerves, and nerve roots can cause peripheral nervous system dysfunction. This is particularly common with leukemia and lymphoma, resulting in mononeuropathy, multiple mononeuropathies, polyradiculopathy, plexopathy, and generalized symmetric distal or proximal polyneuropathy. Polyradiculopathies are especially common, and MRI may show compression of multiple nerve roots by the tumor.
Peripheral neuropathies associated with lymphoproliferative disorders. There is an increased incidence of peripheral neuropathy in patients with monoclonal gammopathies, and there is a well-established causal relationship between IgM monoclonal gammopathy and demyelinating sensorimotor polyneuropathy[51]. Antibodies against myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) are found in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders or plasmacytomas, whereas IgA and IgG monoclonal gammopathies are much less common. Multiple myeloma is commonly related to distal axonal, sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Osteosclerotic myeloma is rare, but commonly associated with polyneuropathy, sometimes simultaneously presenting with hepatosplenomegaly, cutaneous pigmentation, hypertrichosis, edema, pericardial and pleural effusions, so-called POEMS syndrome (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, M protein, and skin abnormalities). POEMS syndrome is also known to be associated with Castleman disease (angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia).
Graft-vs.-host disease (GvHD) can cause various immune-mediated disorders, including the one against peripheral nervous system. Guillain-Barre syndrome, multiple mononeuropathies, and cranial neuropathy have been reported in patients with GVHD[52].
Summary
Peripheral nerves are affected by a broad spectrum of disorders. With technical advances that permit high-resolution MR, peripheral neuroimaging is gaining utility in evaluation of peripheral nerve disorders. MR Neurography is especially useful in evaluating proximal nerve lesions that are not easily assessable with nerve conduction study; for example, MR Neurography will not only provide better diagnosis of a tumor compressing the brachial plexus than an electrophysiological study, but will also aid neurosurgeons in their plan for treatment. However, it is important for radiologists to have an understanding of the various peripheral nervous disorders and communicate the findings to the referring physicians including neurologists and neurosurgeons for optimal patient management.
Key points.
Distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy (DSPN) due to “dying back” axonal degeneration is the most common form of polyneuropathy and is typically caused by a toxic/metabolic conditions, such as diabetes.
Electromyography and Nerve conduction study (EMG/NCS) is an extremely useful test in determining the localization (anatomic and nerve fiber type), pathophysiology (axonal or demyelinating), acuity, and severity of neuropathies.
Axonal neuropathies typically demonstrate decreased amplitude action potentials on NCS and neurogenic motor units on EMG.
Demyelinating neuropathies show decreased conduction velocity, temporal dispersion, and prolonged distal and F-wave latencies.
MR Neurography plays an important role in evaluation of proximal, focal nerve lesions that are difficult to evaluate by EMG/NCS.
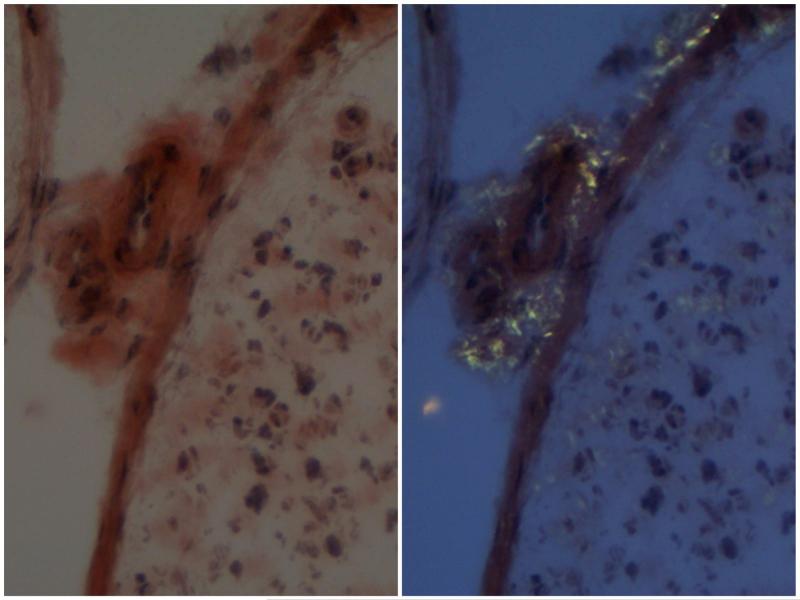
Figure 4.
Congo Red stain shows apple green birefringence under polarizing microscope. Note that the amorphous birefringent material invades into the vessel wall.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Chhabra A, Andreisek G, Soldatos T, Wang KC, Flammang AJ, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA. MR neurography: past, present, and future. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:583–91. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.6012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Thawait SK, Chaudhry V, Thawait GK, Wang KC, Belzberg A, Carrino JA, Chhabra A. High-resolution MR neurography of diffuse peripheral nerve lesions. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:1365–72. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Williams IR, Gilliatt RW. Regeneration distal to a prolonged conduction block. J Neurol Sci. 1977;33:267–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gutmann E, Holubar J. The degeneration of peripheral nerve fibers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1950;13:89–105. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.13.2.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Seddon HJ, Medawar PB, Smith H. Rate of regeneration of peripheral nerves in man. J Physiol. 1943;102:191–215. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cornblath DR, Chaudhry V, Carter K, Lee D, Seysedadr M, Miernicki M, Joh T. Total neuropathy score: validation and reliability study. Neurology. 1999;53:1660–4. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.8.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, Piatti M, Rota S, Briani C, Zara G, Plasmati R, Pastorelli F, Caraceni A, Pace A, Manicone M, Lissoni A, Colombo N, Bianchi G, Zanna C. The Total Neuropathy Score as an assessment tool for grading the course of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: comparison with the National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Scale. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2007;12:210–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1529-8027.2007.00141.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dyck PJ, Kratz KM, Karnes JL, Litchy WJ, Klein R, Pach JM, Wilson DM, O'Brien PC, Melton LJ, 3rd, Service FJ. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology. 1993;43:817–24. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.4.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dyck PJ, Norell JE. Microvasculitis and ischemia in diabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy. Neurology. 1999;53:2113–21. doi: 10.1212/wnl.53.9.2113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Said G, Elgrably F, Lacroix C, Plante V, Talamon C, Adams D, Tager M, Slama G. Painful proximal diabetic neuropathy: inflammatory nerve lesions and spontaneous favorable outcome. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:762–70. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nemni R, Bottacchi E, Fazio R, Mamoli A, Corbo M, Camerlingo M, Galardi G, Erenbourg L, Canal N. Polyneuropathy in hypothyroidism: clinical, electrophysiological and morphological findings in four cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987;50:1454–60. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.11.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ogura T, Makinodan A, Kubo T, Hayashida T, Hirasawa Y. Electrophysiological course of uraemic neuropathy in haemodialysis patients. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77:451–4. doi: 10.1136/pmj.77.909.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chaudhry V, Corse AM, O'Brien R, Cornblath DR, Klein AS, Thuluvath PJ. Autonomic and peripheral (sensorimotor) neuropathy in chronic liver disease: a clinical and electrophysiologic study. Hepatology. 1999;29:1698–703. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yuki N, Hartung HP. Guillain-Barre syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2294–304. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1114525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Griffin JW, Li CY, Ho TW, Xue P, Macko C, Gao CY, Yang C, Tian M, Mishu B, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barre syndrome in northern China. The spectrum of neuropathological changes in clinically defined cases. Brain. 1995;118(Pt 3):577–95. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Paparounas K. Anti-GQ1b ganglioside antibody in peripheral nervous system disorders: pathophysiologic role and clinical relevance. Arch Neurol. 2004;61:1013–6. doi: 10.1001/archneur.61.7.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ogawara K, Kuwabara S, Mori M, Hattori T, Koga M, Yuki N. Axonal Guillain-Barre syndrome: relation to anti-ganglioside antibodies and Campylobacter jejuni infection in Japan. Ann Neurol. 2000;48:624–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lawn ND, Fletcher DD, Henderson RD, Wolter TD, Wijdicks EF. Anticipating mechanical ventilation in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:893–8. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.6.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cornblath DR, Mellits ED, Griffin JW, McKhann GM, Albers JW, Miller RG, Feasby TE, Quaskey SA. Motor conduction studies in Guillain-Barre syndrome: description and prognostic value. Ann Neurol. 1988;23:354–9. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McKhann GM, Griffin JW, Cornblath DR, Mellits ED, Fisher RS, Quaskey SA. Plasmapheresis and Guillain-Barre syndrome: analysis of prognostic factors and the effect of plasmapheresis. Ann Neurol. 1988;23:347–53. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fletcher DD, Lawn ND, Wolter TD, Wijdicks EF. Long-term outcome in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome requiring mechanical ventilation. Neurology. 2000;54:2311–5. doi: 10.1212/wnl.54.12.2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Koller H, Kieseier BC, Jander S, Hartung HP. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1343–56. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ginsberg L, Platts AD, Thomas PK. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy mimicking a lumbar spinal stenosis syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995;59:189–91. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.59.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Adams D, Kuntzer T, Burger D, Chofflon M, Magistris MR, Regli F, Steck AJ. Predictive value of anti-GM1 ganglioside antibodies in neuromuscular diseases: a study of 180 sera. J Neuroimmunol. 1991;32:223–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90192-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Latov N. Pathogenesis and therapy of neuropathies associated with monoclonal gammopathies. Ann Neurol. 1995;37(Suppl 1):S32–42. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Burns TM, Schaublin GA, Dyck PJ. Vasculitic neuropathies. Neurol Clin. 2007;25:89–113. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2006.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lloyd TE, Chaudhry V. Treatment and Management of Hereditary Neuropathies. In: Bertorini T, editor. Neuromuscular Disorders: Treatment and Management. Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2011. pp. 191–213. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Patzko A, Shy ME. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related genetic neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2012;18:39–59. doi: 10.1212/01.CON.0000411567.34085.da. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kelly JJ, Jr., Kyle RA, O'Brien PC, Dyck PJ. The natural history of peripheral neuropathy in primary systemic amyloidosis. Ann Neurol. 1979;6:1–7. doi: 10.1002/ana.410060102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Morrison B, Chaudhry V. Medication, toxic, and vitamin-related neuropathies. Continuum (Minneap Minn) 2012;18:139–60. doi: 10.1212/01.CON.0000411565.49332.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gemignani F, Marbini A, Pavesi G, Di Vittorio S, Manganelli P, Cenacchi G, Mancia D. Peripheral neuropathy associated with primary Sjogren's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994;57:983–6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.8.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lopate G, Pestronk A, Al-Lozi M, Lynch T, Florence J, Miller T, Levine T, Rampy T, Beson B, Ramneantu I. Peripheral neuropathy in an outpatient cohort of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2006;33:672–6. doi: 10.1002/mus.20514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chamberlain MA, Bruckner FE. Rheumatoid neuropathy. Clinical and electrophysiological features. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970;29:609–16. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.6.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Scott DG, Bacon PA, Tribe CR. Systemic rheumatoid vasculitis: a clinical and laboratory study of 50 cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 1981;60:288–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Averbuch-Heller L, Steiner I, Abramsky O. Neurologic manifestations of progressive systemic sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1992;49:1292–5. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530360094024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Poncelet AN, Connolly MK. Peripheral neuropathy in scleroderma. Muscle Nerve. 2003;28:330–5. doi: 10.1002/mus.10439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sivri A, Hascelik Z, Celiker R, Basgoze O. Early detection of neurological involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995;35:195–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rosenbaum R. Neuromuscular complications of connective tissue diseases. Muscle Nerve. 2001;24:154–69. doi: 10.1002/1097-4598(200102)24:2<154::aid-mus20>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Burns TM, Dyck PJ, Aksamit AJ. The natural history and long-term outcome of 57 limb sarcoidosis neuropathy cases. J Neurol Sci. 2006;244:77–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2006.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chin RL, Sander HW, Brannagan TH, Green PH, Hays AP, Alaedini A, Latov N. Celiac neuropathy. Neurology. 2003;60:1581–5. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000063307.84039.c7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gondim FA, Brannagan TH, 3rd, Sander HW, Chin RL, Latov N. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Brain. 2005;128:867–79. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Charron L, Peyronnard JM, Marchand L. Sensory neuropathy associated with primary biliary cirrhosis. Histologic and morphometric studies. Arch Neurol. 1980;37:84–7. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500510042006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dorfman LJ, Ransom BR, Forno LS, Kelts A. Neuropathy in the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1983;6:291–8. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ooi WW, Srinivasan J. Leprosy and the peripheral nervous system: basic and clinical aspects. Muscle Nerve. 2004;30:393–409. doi: 10.1002/mus.20113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Halperin J, Luft BJ, Volkman DJ, Dattwyler RJ. Lyme neuroborreliosis. Peripheral nervous system manifestations. Brain. 1990;113(Pt 4):1207–21. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.4.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Barohn RJ, Gronseth GS, LeForce BR, McVey AL, McGuire SA, Butzin CA, King RB. Peripheral nervous system involvement in a large cohort of human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals. Arch Neurol. 1993;50:167–71. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540020045016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kiwaki T, Umehara F, Arimura Y, Izumo S, Arimura K, Itoh K, Osame M. The clinical and pathological features of peripheral neuropathy accompanied with HTLV-I associated myelopathy. J Neurol Sci. 2003;206:17–21. doi: 10.1016/s0022-510x(02)00279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Amato AA, Collins MP. Neuropathies associated with malignancy. Semin Neurol. 1998;18:125–44. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Denny-Brown D. Primary sensory neuropathy with muscular changes associated with carcinoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1948;11:73–87. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.11.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dalmau J, Graus F, Rosenblum MK, Posner JB. Anti-Hu--associated paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy. A clinical study of 71 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1992;71:59–72. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199203000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Latov N, Sherman WH, Nemni R, Galassi G, Shyong JS, Penn AS, Chess L, Olarte MR, Rowland LP, Osserman EF. Plasma-cell dyscrasia and peripheral neuropathy with a monoclonal antibody to peripheral-nerve myelin. N Engl J Med. 1980;303:618–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Amato AA, Barohn RJ, Sahenk Z, Tutschka PJ, Mendell JR. Polyneuropathy complicating bone marrow and solid organ transplantation. Neurology. 1993;43:1513–8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]