Abstract
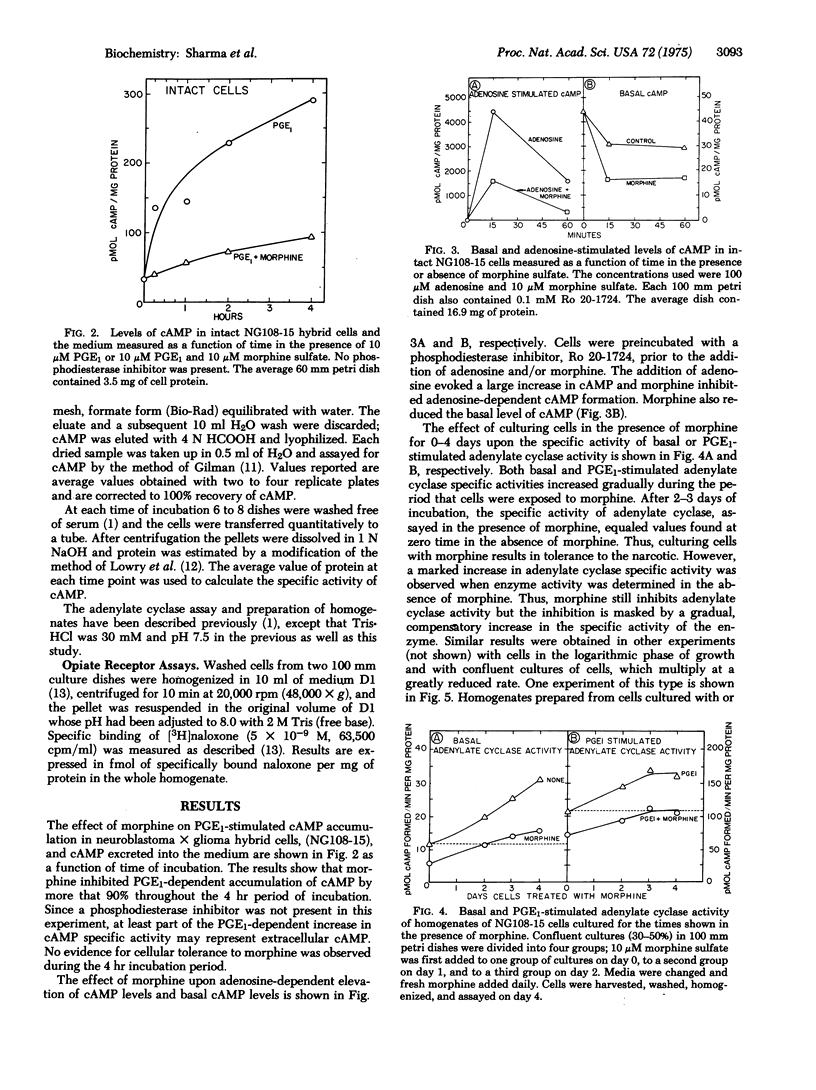
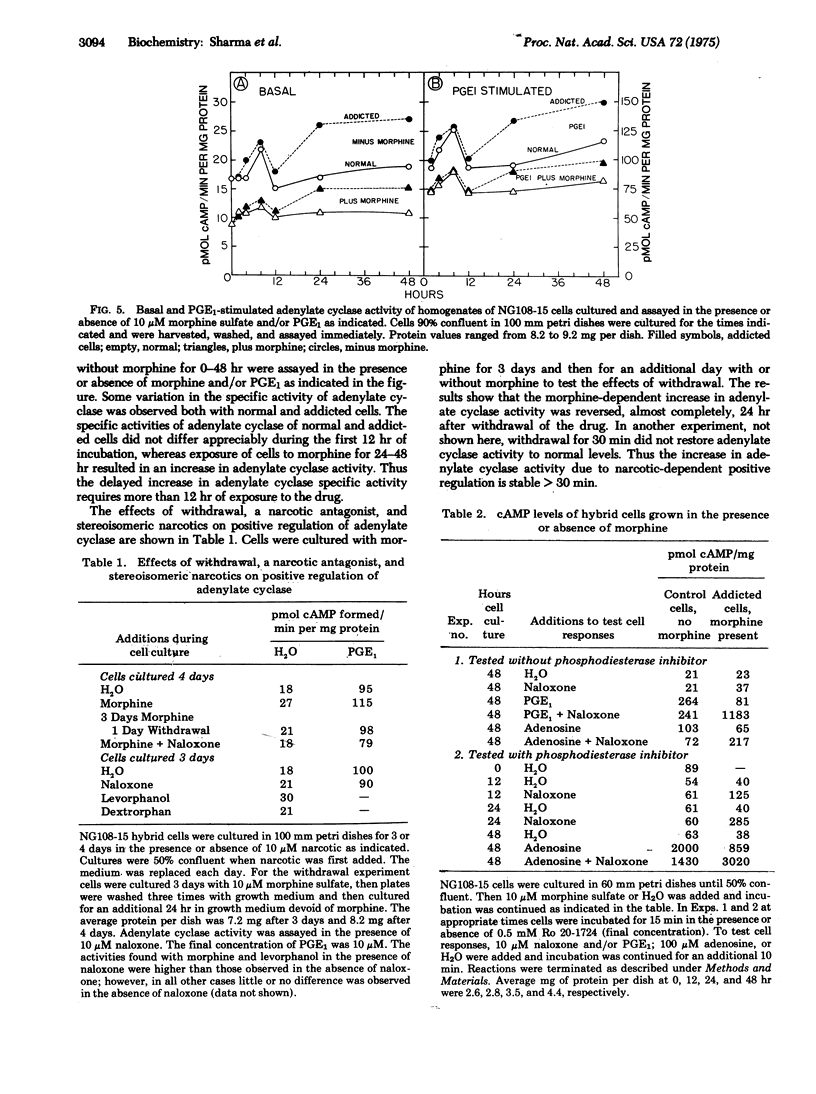
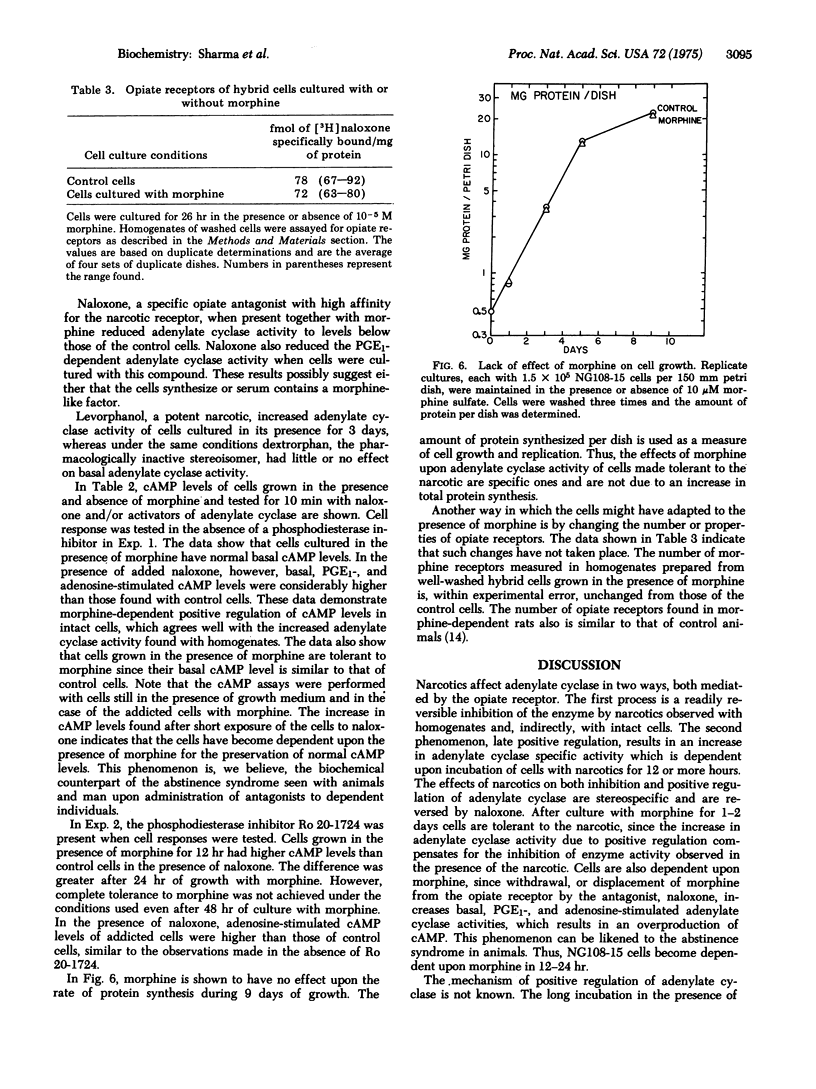
Narcotics affect adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1] in two opposing ways, both mediated by the opiate receptor. The first process is the readily reversible inhibition of the enzyme by narcotics; the second is a compensatory increase in enzyme activity which is delayed in onset and relatively stable. Late positive regulation of the enzyme counteracts the inhibitory influence of morphine and is responsible for narcotic dependence and tolerance. The coupled inhibitory and positive regulatory mechanisms for adenylate cyclase provide a means of activating and deactivating neural circuits hours after the initial event and thus may play a role in a memory process.
Full text
PDF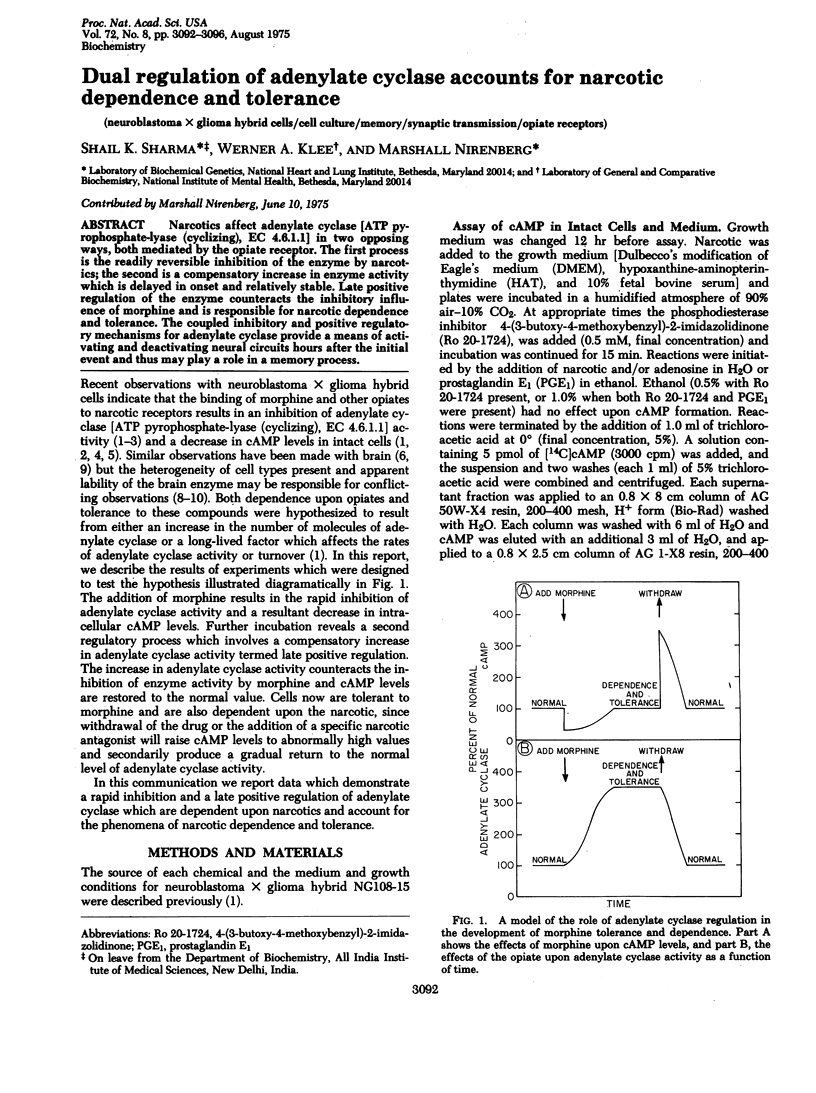

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Hypothesis: Inhibition of E prostaglandin-sensitive adenyl cyclase as the mechanism of morphine analgesia. Prostaglandins. 1974 Sep 10;7(5):361–376. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(74)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Roy A. C. Morphine-like drugs inhibit the stimulation of E prostaglandins of cyclic AMP formation by rat brain homogenate. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):24–27. doi: 10.1038/248024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Nirenberg M. A neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cell line with morphine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3474–3477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Streaty R. A. Narcotic receptor sites in morphine-dependent rats. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):61–63. doi: 10.1038/248061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri S. K., Cochin J., Volicer L. Effect of morphine sulfate on adenylate cyclase and phosphodiesterase activities in rat corpus striatum. Life Sci. 1975 Mar 1;16(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90352-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Nirenberg M., Klee W. A. Morphine receptors as regulators of adenylate cyclase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tell G. P., Pasternak G. W., Cuatrecasas P. Brain and caudate nucleus adenylate cyclase: effects of dopamine, GTP, E prostaglandins and morphine. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):242–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80896-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber J., Fischer K., Latzin S., Hamprecht B. Morphine antagonises action of prostaglandin in neuroblastoma and neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cells. Nature. 1975 Jan 10;253(5487):120–122. doi: 10.1038/253120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traber J., Reiser G., Fischer K., Hamprecht B. Measurements of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and membrane potential in neuroblastoma times glioma hybrid cells: opiates and adrenergic agonists cause effects opposite to those of prostaglandin E1. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80836-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


