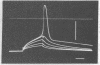
Abstract
The action of 1-pyrene-butyrylcholine, a new cholinergic fluorescent probe, has been studied at the cellular level using electrophysiological and fluorescence techniques. The spectroscopic properties of the probe were found to be similar to those pf pyrene-butyric acid, the excited-state lifetime in air-saturated aqueous solutions being 92 nsec. At micromolar concentrations the probe was found to exert a nondepolarizing, reversible blocking action at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. The same cholinolytic effect was observed in hypersensitive denervated muscles. The synaptic localization of the probe could be observed with fluorescence microscopy using sub- and micromolar concentrations. Treatment of the nerve-muscle preparations with proteolytic enzymes, resulting in the separation of the nerve ending from the muscle end-plate, enabled a distinction to be made between the fluorescence arising from these two parts of the synapse. Intense presynaptic fluorescence was observed, and was not altered by micromolar concentrations of alpha-bungarotoxin, d-tubocurarine, hemicholinium, or cholinesterase inhibitors. Faint reversible staining of the end-plate region was observed in enzymically treated muscles and was inhibited by prior treatment with alpha-bungarotoxin. Fluorescent alpha-toxin revealed similar patterns of fluorescence in the end-plate of enzyme-treated muscles. The postsynaptic localization of the fluorescent probe is therefore tentatively identified as the one producing the cholinolytic effect upon binding to acetylcholine receptor sites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Sokoll M. D., Sonesson B., Thesleff S. Studies on the nature of the cholinergic receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1968 Aug;4(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(68)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. J., Cohen M. W. Fluorescent staining of acetylcholine receptors in vertebrate skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):385–400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W., Sakmann B. Effects of proteolytic enzymes on function and structure of frog neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol. 1973 May;230(3):673–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Gaddum J. H. Choline esters in tissue extracts. J Physiol. 1933 Oct 6;79(3):255–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Macmurchie D. D., Elliott E., Wolcott R. G., Landel A. M., Raftery M. A. Elapid neurotoxins. Purification, characterization, and immunochemical studies of -bungarotoxin. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 25;11(9):1663–1668. doi: 10.1021/bi00759a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Salzberg B. M., Davila H. V., Ross W. N., Landowne D., Waggoner A. S., Wang C. H. Changes in axon fluorescence during activity: molecular probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(1):1–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01869968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Changes in end-plate activity produced by presynaptic polarization. J Physiol. 1954 Jun 28;124(3):586–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. On the localization of acetylcholine receptors. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):157–181. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eibl H., Arnold D., Weltzien H. U., Westphal O. Zur Synthese von alpha- und beta-Lecithinen und ihren Atheranaloga. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem. 1967;709:226–230. doi: 10.1002/jlac.19677090124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Kelly R. B. Enzymatic detachment of endplate acetylcholinesterase from muscle. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 14;232(28):62–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio232062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J. THE LOCALIZATION OF CHOLINESTERASE ACTIVITY IN RAT CARDIAC MUSCLE BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1964 Nov;23:217–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp J. A., Weber G. Fluorescence polarization of pyrenebutyric-bovine serum albumin and pyrenebutyric-human macroglobulin conjugates. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6309–6315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUELER F. W. The mechanism of action of the hemicholiniums. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1960;2:77–97. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Borris D. P., De Robertis E., Barrantes F. J., La Torre J. L., Llorente de Carlin M. C. The use of a cholinergic fluorescent probe for the study of the receptor proteolipid. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;7(5):530–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]