Abstract
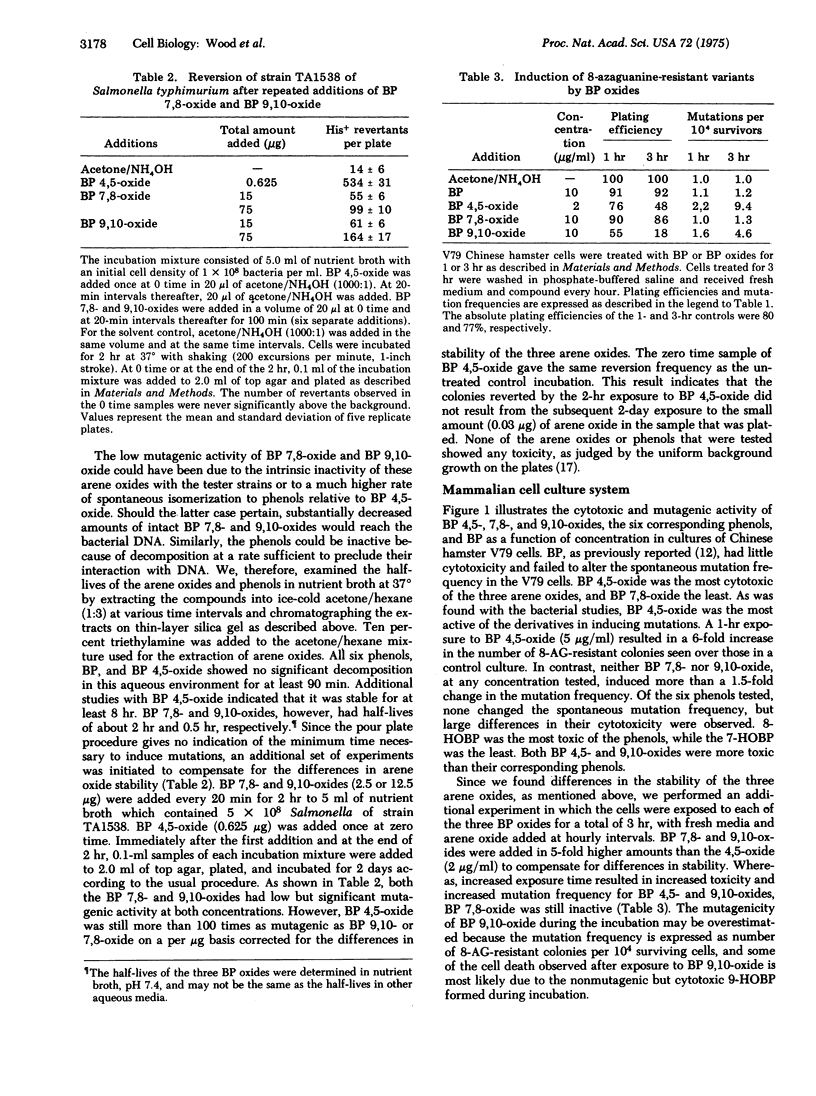
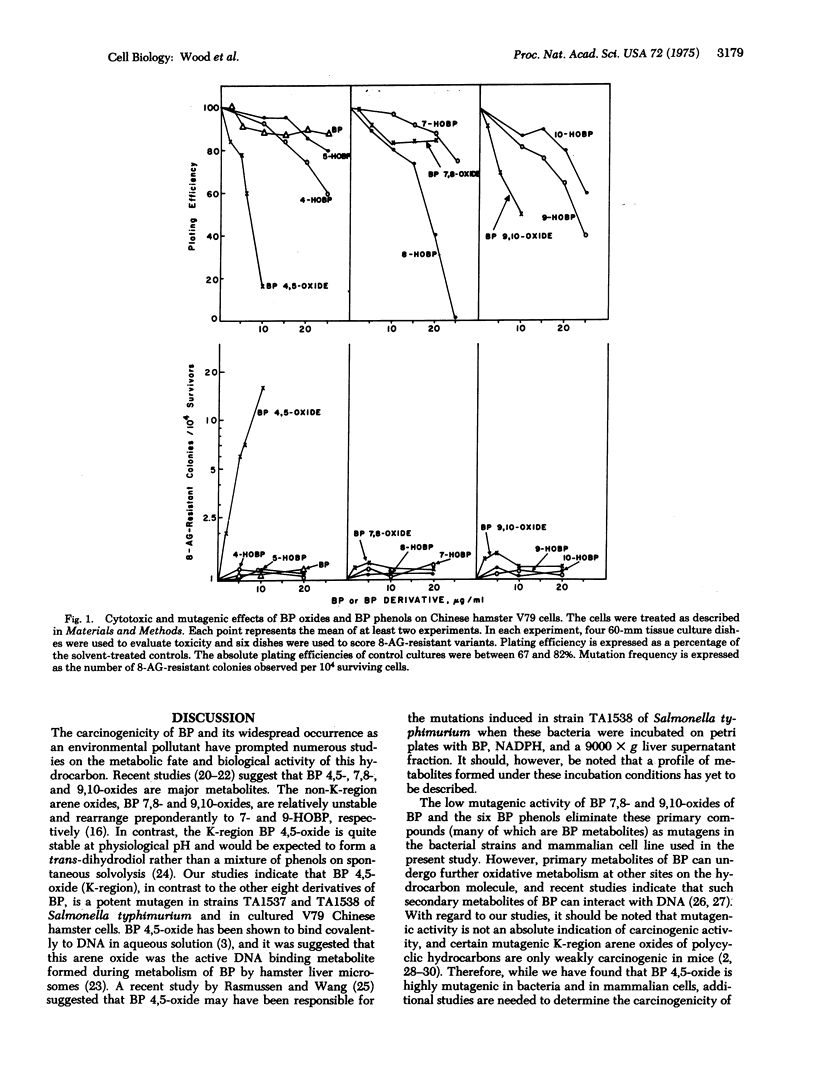
The benzo[a]pyrene 4,5-, 7,8-, and 9,10-oxides and the six corresponding phenols (4-, 5-, 7-, 8-, 9-, and 10-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene) have been tested for mutagenic and cytotoxic activity in bacteria and in a mammalian cell culture system. Benzo[a]pyrene 4,5-oxide (K-region) was highly mutagenic in two histidine-dependent strains (TA1537 and TA1538) of Salmonella typhimurium which detect frameshift mutagens. In contrast, benzo[a]pyrene 7,8- and 9,10-oxides were less than 1% as mutagenic as the 4,5-oxide. Benzo[a]pyrene 7,8- and 9,10-oxides were unstable in aqueous media, whereas the 4,5-oxide was stable for several hours. This difference in stability could not account for the different mutagenic activities of the three arene oxides. The benzo[a]pyrene oxides were inactive in a strain (TA1535) that is reverted by base pair mutagens such as N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine or in a strain (TA1536) that detects framshift mutagens similar to the acridine half-mustard ICR-191. Benzo-[a]-pyrene and the six phenols were all stable in aqueous media, but they had little or no mutagenic activity in any of the four Salmonella strains. Conversion of 8-azaguanine-sensitive Chinese hamster V79 cells to 8-azaguanine-resistant variants was increased by benzo[a]pyrene 4,5-oxide, whereas the 9,10-oxide was considerably less active. Benzo[a]pyrene and the other derivatives had little or no effect. Benzo[a]yrene 4,5-oxide was more cytotoxic to the Chinese hamster V79 cells than the 7,8- and 9,10-oxides, while 8-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene was the most cytotoxic of the six phenols.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Durston W. E., Yamasaki E., Lee F. D. Carcinogens are mutagens: a simple test system combining liver homogenates for activation and bacteria for detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Lee F. D., Durston W. E. An improved bacterial test system for the detection and classification of mutagens and carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Sims P., Grover P. L. Epoxides of carcinogenic polycyclic hydrocarbons are frameshift mutagens. Science. 1972 Apr 7;176(4030):47–49. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4030.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird W. M., Harvey R. G., Brookes P. Comparison of the cellular DNA-bound products of benzo(alpha)pyrene with the products formed by the reaction of benzo(alpha)pyrene-4,5-oxide with DNA. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):54–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgen A., Darvey H., Castagnoli N., Crocker T. T., Rasmussen R. E., Wang I. Y. Metabolic conversion of benzo(a)pyrene by Syrian hamster liver microsomes and binding of metabolites to deoxyribonucleic acid. J Med Chem. 1973 May;16(5):502–506. doi: 10.1021/jm00263a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürki K., Wheeler J. E., Akamatsu Y., Scribner J. E., Candelas G., Bresnick E. Early differential effects of 3-methylcholanthrene and its "K-region" epoxide on mouse skin. Possible implication in the two-stage mechanism of tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Oct;53(4):967–976. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu E. H., Malling H. V. Mammalian cell genetics. II. Chemical induction of specific locus mutations in Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1306–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dansette P., Jerina D. M. A facile synthesis of arene oxides at the K regions of polycylic hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Feb 20;96(4):1224–1225. doi: 10.1021/ja00811a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover P. L., Hewer A., Sims P. Formation of K-region epoxides as microsomal metabolites of pyrene and benzo(a)pyrene. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2713–2726. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover P. L., Sims P., Huberman E., Marquardt H., Kuroki T., Heidelberger C. In vitro transformation of rodent cells by K-region derivatives of polycyclic hydrocarbons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1098–1101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover P. L., Sims P. Interactions of the K-region epoxides of phenanthrene and dibenz (a,h)anthracene with nucleic acids and histone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;19(7):2251–2259. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder G., Yagi H., Dansette P., Jerina D. M., Levin W., Lu A. Y., Conney A. H. Effects of inducers and epoxide hydrase on the metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene by liver microsomes and a reconstituted system: analysis by high pressure liquid chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4356–4360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Aspiras L., Heidelberger C., Grover P. L., Sims P. Mutagenicity to mammalian cells of epoxides and other derivatives of polycyclic hydrocarbons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Kuroki T., Marquardt H., Selkirk J. K., Heidelberger C., Grover P. L., Sims P. Transformation of hamster embryo cells by epoxides and other derivatives of polycyclic hydrocarbons. Cancer Res. 1972 Jul;32(7):1391–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerina D. M., Daly J. W. Arene oxides: a new aspect of drug metabolism. Science. 1974 Aug 16;185(4151):573–582. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4151.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki T., Huberman E., Marquardt H., Selkirk J. K., Heidelberger C., Grover P. L., Sims P. Binding of K-region epoxides and other derivatives of benz(a)anthracene and dibenz(a,h)anthracene to DNA, RNA, and proteins of transformable cells. Chem Biol Interact. 1972 May;4(6):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(72)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Kuroki T., Huberman E., Selkirk J. K., Heidelberger C., Grover P. L., Sims P. Malignant transformation of cells derived from mouse prostate by epoxides and other derivatives of polycyclic hydrocarbons. Cancer Res. 1972 Apr;32(4):716–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Sodergren J. E., Sims P., Grover P. L. Malignant transformation in vitro of mouse fibroblasts by 7,12-dimethylbenz(A)anthracene and 7-hydroxymethylbenz(A)anthracene and by their K-region derivatives. Int J Cancer. 1974 Mar 15;13(3):304–310. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. C., Miller J. A. Low carcinogenicity of the K-region epoxides of 7-methylbenz(a)-anthracene and benz(a)anthracene in the mouse and rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Mar;124(3):915–919. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen R. E., Wang I. Y. Dependence of specific metabolism of benzo(a)pyrene on the inducer of hydroxylase activity. Cancer Res. 1974 Sep;34(9):2290–2295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkirk J. K., Croy R. G., Roller P. P., Gelboin H. V. High-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of benzo(alpha)pyrene metabolism and covalent binding and the mechanism of action of 7,8-benzoflavone and 1,2-epoxy-3,3,3-trichloropropane. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3474–3480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L. Epoxides in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolism and carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1974;20:165–274. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., Grover P. L., Swaisland A., Pal K., Hewer A. Metabolic activation of benzo(a)pyrene proceeds by a diol-epoxide. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):326–328. doi: 10.1038/252326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang I. Y., Rasmussen R. E., Crocker T. T. Isolation and characterization of an active DNA-binding metabolite of benzo(a)pyrene from hamster liver microsomal incubation systems. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1142–1149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



