Abstract
Microencapsulating stem cells in injectable microbeads can enhance delivery and localization, but their ability to act as growth factor production sources is still unknown. To address this concern, growth factor mRNA levels and production from alginate microbeads with encapsulated human adipose stem cells (ASC microbeads) cultured in both growth and chondrogenic media (GM and CM) were measured over a two week period. Human ASCs in microbeads were either commercially purchased (Lonza) or isolated from six human donors and compared to human ASCs on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS). The effects of crosslinking and alginate compositions on growth factor mRNA levels and production were also determined. Secretion profiles of IGF-I, TGF-β3 and VEGF-A from commercial human ASC microbeads were linear and at a significantly higher rate than TCPS cultures over two weeks. For human ASCs derived from different donors, microencapsulation increased pthlh and both IGF-I and TGF-β3 secretion. CM decreased fgf2 and VEGF-A secretion from ASC microbeads derived from the same donor population. Crosslinking microbeads in BaCl2 instead of CaCl2 did not eliminate microencapsulation’s beneficial effects, but did decrease IGF-I production. Increasing the guluronate content of the alginate microbead increased IGF-I retention. Decreasing alginate molecular weight eliminated the effects microencapsulation had on increasing IGF-I secretion. This study demonstrated that microencapsulation can enhance chondrogenic growth factor production and that chondrogenic medium treatment can decrease angiogenic growth factor production from ASCs, making these cells a potential source for paracrine factors that can stimulate cartilage regeneration.
Keywords: Microencapsulation, Adipose stem cells, Alginate, Growth factor delivery, Cartilage
Introduction
Adult stem cell therapies such as adipose stem cells (ASCs) are an attractive option for various clinical applications because of their accessibility and ability to differentiate into multiple cell types[1]. However, challenges related to their delivery, such as high injection pressures[2], low retention in the desired site[3] and low viability in vivo when injected or delivered on scaffolds[4, 5], may limit their effectiveness in clinical studies[6]. To address these problems, we have recently developed a microencapsulation technology where ASC microbeads under 200 microns can be injected under low injection pressures without any changes in shape, can maintain greater than 80% cell viability for at least 3 weeks post-injection and can be localized in the desired site in vivo for at least 3 months[2].
Although ASCs can be used for a variety of clinical applications, repairing cartilage focal lesions is an attractive option because of the tissue’s limited regenerative capacity and the lack of an effective treatment[7, 8]. Current cell therapies, such as autologous chondrocyte implantation aim to directly regenerate cartilage by providing a source of cells that can then synthesize new tissue[9]. However, this strategy has had limited clinical adoption mainly due to high variability in cartilage quality and functional outcomes[10, 11]. Therefore, a new paradigm has emerged in using stem cells as growth factor production sources to stimulate diseased or damaged musculoskeletal tissues like cartilage to regenerate themselves[12, 13].
We have previously showed that ASC microbeads consisting of alginate can be preconditioned with different medium treatments to secrete factors that affect chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation in vitro and cartilage regeneration in vivo[14, 15]. Additionally, we showed that the degradation rate of these microbeads can be controlled to affect cell release rates and growth factor production[16]. To further optimize ASC microbeads as growth factor production sources for regenerating cartilage, a few unanswered issues need to be addressed. First, even though the mass transfer properties of soluble compounds and growth factors in alginate have been characterized[17-19], it is unknown how microencapsulation affects growth factor production and secretion from ASCs derived from multiple donors. Additionally, it is unknown if chondrogenic medium can also affect growth factor production and secretion from microbeads encapsulated ASCs derived from multiple human donors. Finally, although the mass transfer properties of alginate hydrogels are dependent on the divalent crosslink[20, 21] and the type of alginate polymer used[17], the effects these parameters have on growth factor expression and production from ASCs is unknown. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to determine the time course of growth factor production and secretion from microencapsulated commercially available human ASCs cultured in growth and chondrogenic media, to determine the effects of microencapsulation and chondrogenic medium treatments on human ASCs derived from different donors and to determine the effect microbead composition has on growth factor expression and production.
Materials and Methods
Cell Isolation and Passaging
To determine the extent of growth factor production and secretion from ASC microbeads over time, first passage human ASCs from a 28 year old male donor were commercially obtained (Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) and cultured up to third passage in Lonza Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth Medium (GM, Lonza, PT-3001) prior to microencapsulation. To test whether chondrogenic medium and microencapsulation had consistent effects on ASCs from different donors, adipose tissue was collected from six female patients ranging from 18 to 49 years of age (mean age ± standard error = 32.7±4.1) under an approved IRB protocol at Georgia Institute of Technology, Northside Hospital (Atlanta, GA) and Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta (Atlanta, GA). Fat was obtained by breast reduction from five donors and abdominoplasty from one donor. All patients gave written consent to both the procedure and handling of fat thereafter. ASCs were isolated using a collagenase and dispase digestion cocktail as previously described[22]. Cells were then seeded at 5,000 cells/cm2 and cultured in GM. When primary ASCs from three of the donors were at 90% confluence (P1 ASCs), they were trypsinized and microencapsulated immediately. Cells from the other 3 donors were pelleted at 500 g for 10 minutes, resuspended in GM with 5% DMSO at , cooled from room temperature to -80°C at 1°C/min, stored at -80°C overnight and transferred to liquid nitrogen for later use. After 2 to 8 months, these cryopreserved cells were then cultured up to third passage and microencapsulated (P3 ASCs). To determine the effects microbead composition had on growth factor production, cryopreserved ASCs from a 33 year old donor’s breast tissue were cultured up to third passage and microencapsulated. Prior to microencapsulation, all ASCs were positive for CD73 and CD271 and negative for CD45, indicating that these cells still maintained the surface phenotype characteristic of multipotent ASCs.
Microencapsulation
For all studies, alginate powders (FMC BioPolymer, Sandvika, Norway) were UV light sterilized overnight and dissolved in 0.22 μm sterile filtered (Thermos Fisher Scientific, Rochester, NY, USA) saline (Ricca Chemical, Arlington, TX, USA) at 20 mg/mL. ASCs were then suspended in the alginate solution at 107 cells/mL. Microbeads containing the commercial ASCs seeded homogenously throughout the hydrogel were created using a Nisco Encapsulator VAR V1 LIN-0043 (Nisco Engineering AG, Zurich, Switzerland) at a 10 mL/hr flow rate, 0.12 mm inner diameter nozzle and 6kV/cm electrostatic potential[2, 23]. Microbeads were imaged with an inverted microscope (Motic, Richmond, British Columbia , Canada) and had a mean diameter ± standard deviation of 122±15 μm (Motic Images Plus 2.0).
In studies determining growth factor production and secretion from ASC microbeads over time and in studies determining the effect of chondrogenic medium and microencapsulation on ASCs from multiple donors, microbeads with 130 kDa, 44% guluronate alginate (LVM, low viscosity high mannuronate) were crosslinked in a solution of 50 mM CaCl2 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), 150 mM glucose (Sigma) and 15 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES, Sigma) at pH 7.3 for at least 15 minutes. To determine the effect Ca++ crosslinks had on growth factor production and secretion, ASC microbeads consisting of LVM were also crosslinked in a solution of 20 mM BaCl2 (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA), 150 mM glucose and 15 mM HEPES at pH 7.3. To determine the effect alginate molecular weight and chemistry had on growth factor production and secretion, ASC microbeads were also made with the following alginates: 170 kDa, 66% guluronate (LVG, low viscosity high guluronate); <50 kDa, 44% guluronate (VLVM, very low viscosity high mannuronate); and 220kDa, 43% guluronate (MVM, medium viscosity high mannuronate). These ASC microbeads were crosslinked in the CaCl2 solution as described above. For all studies, microbeads were washed three times in GM to remove any excess crosslinking solution. ASCs were also plated in 6-well tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) plates (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) for comparison.
Chondrogenic Treatment
Once ASCs in the 6-well plates reached 90% confluence, TCPS and microbead cultures were treated with either GM or chondrogenic medium (CM) consisting of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) with 4.5g/L glucose and 1 mM sodium pyruvate (Mediatech, Manassas, VA, USA), 40 μg/ml proline (Sigma), 50 μg/ml ascorbate-2-phosphate (Sigma), 1% ITS+ (Sigma), 100 nM dexamethasone (Sigma), 10 ng/ml recombinant human transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1, R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and 100 ng/ml recombinant human bone morphogenic protein 6 (BMP-6, PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA). For studies determining cumulative growth factor production and secretion from ASC microbeads over time, media were collected with each media change at 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 14 and 15 days. For all subsequent studies, treatments lasted 7 and 14 days, RNA was collected 6 hours after the last media change as described below and media and ASC and lysates in 0.05% Triton X-100 (Sigma) were collected 24 hours after the last media change.
RNA Isolation
Alginate microbeads crosslinked in CaCl2 (Ca microbeads) were uncrosslinked in 82.5 mM sodium citrate (Sigma) whereas alginate microbeads crosslinked in BaCl2 (Ba microbeads) were uncrosslinked in 30 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, Sigma) and 135 mM NaCl (Sigma). Released cells were then pelleted and washed two more times in their respective uncrosslinking solution to remove any residual alginate. TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was added to the cell pellet, which was fed through a QIAshredder (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) and RNA was isolated using chloroform and an RNeasy Kit (QIAGEN) as previously described[24]. A high capacity reverse transcription cDNA kit (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used to reverse transcribe 1 μg RNA to cDNA.
Quantifying mRNA Levels and Growth Factor Production
mRNA levels and secretion of multiple signaling molecules were measured to assess the therapeutic potential of ASC microbeads. FGF-2, IGF-I and PTHrP were investigated because of their ability to increase chondrocyte proliferation and regulate hypertrophy[3, 6, 7, 25]. TGF-β3 secretion was investigated since TGFs are potent stimulators of proteoglycan synthesis[8, 10]. However, TGF-β1 secretion was not investigated due to its large concentration in chondrogenic medium. Noggin was investigated because of its role in cartilage differentiation[26]. VEGF-A was investigated because of its detrimental effects on cartilage regeneration[14, 27]. Sox9,aggrecan, type II collagen, type X collagen and cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) were investigated since they are well-characterized markers for the different stages of chondrogenesis[28]. mRNA levels were normalized to that of ribosomal protein subunit 18 (Rps18), a common housekeeping gene[29].
Messenger RNA levels for the genes listed in Table 1 were quantified using real-time PCR with gene-specific primers using the Step One Plus Real-time PCR System and Power Sybr® Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) as previously described[30]. All primers were designed with Beacon Designer software (Premier Biosoft, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and synthesized by Eurofins MWG Operon (Huntsville, AL, USA) unless otherwise noted (Table 1). Growth factor production was quantified using ELISA (R&D Systems) and normalized to DNA content measured by a Quant-iT PicoGreen kit (Invitrogen). For the study investigating growth factor secretion over time, all values were normalized to the final DNA concentration at day 15. Growth factor retention within the microbead were measured as previously described[15]. Quantified mRNA levels are referred to by the name of the gene whereas quantified protein levels were referred to by the name of the growth factor.
Table 1. Primer Sequences.
| Gene | Direction | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Acan | Sense | TCAGCGGTTCCTTCTCCA G |
| Antisense | GCAGTTGTCTCCTCTTCTACG | |
| Col2 | Sense | CTGCTCGTCGCCGCTGTCCTT |
| Antisense | AAGGGTCCCAGGTTCTCCATC | |
| Col10 | Sense | TTACGCTGAACGATACCAAATG |
| Antisense | GCTCTCCTCTTACTGCTATACC | |
| Comp | Sense | CCTGCGTTCTTCTGCTCAC |
| Antisense | GCGTCACACTCCATCACC | |
| Fgf2 | Sense | GCGACCCTCACATCAAGC |
| Antisense | AGCCAGTAATCTTCCATCTTCC | |
| Igf1 | Sense | GGAGGCTGGAGATGTATTG |
| Antisense | GACTTCGTGTTCTTGTTGG | |
| Nog | Sense Antisense | Global Gene Sequence (Qiagen) |
| Pthlh | Sense | CTCGCTCTGCCTGGTTAG |
| Antisense | CAATGCCTCCGTGAATCG | |
| Rps18 | Sense | CGTCTGCCCTATCAACTTTCG |
| Antisense | CTTGGATGTGGTAGCCGTTTC | |
| Sox9 | Sense | GAGCAGCGAAATCAACGAGAAAC |
| Antisense | ACAAAGTCCAAACAGGCAGAGAG | |
| Tgfbl | Sense | CAACAATTCCTGGCGATACCTC |
| Antisense | CCACGGCTCAACCACTGC | |
| Tgfb2 | Sense | CGAGAGGAGCGACGAAGAG |
| Antisense | TAGAAAGTGGGCGGGATGG | |
| Tgfb3 | Sense | CAACGAACTGGCTGTCTG |
| Antisense | CTCTGCTCATTCCGCTTAG | |
| Vegfa | Sense | CTTGCCTTGCTGCTCTACC |
| Antisense | TTCTGCCCTCCTCCTTCTG |
Statistical Analysis
All experiments had six independent cultures per treatment group and were conducted multiple times to confirm the findings. For studies involving six donors, all data are presented in the form of treatment (i.e. CM or microencapsulation [μB]) over control (i.e. GM or TCPS). For these studies, the sample sizes were 6 donors (i.e. the mean of six samples from each of the six donors) and statistical differences between the treatment and control groups and among the different groups at 1 and 2 weeks were determined via a Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test (GraphPad Prism, La Jolla, CA, USA). The significance of medium, microencapsulation, culture time, passage number and their interactions on ASC growth factor mRNA levels and production were determined via a 4-way ANOVA (MATLAB, MathWorks, Natick, MA, USA). For studies that did not investigate ASCs from six donors, only data from a single representative experiment are shown and are expressed as means ± standard errors. Statistical differences among these experimental groups were determined via ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey test (GraphPad Prism). Linear regression was used to assess cumulative growth factor secretion profiles from ASC microbeads and monolayers (GraphPad Prism). All differences and effects were considered to be statistically significant if the p-value was less than 0.05.
Results
Growth Factor Production and Secretion from ASC Microbeads over Time
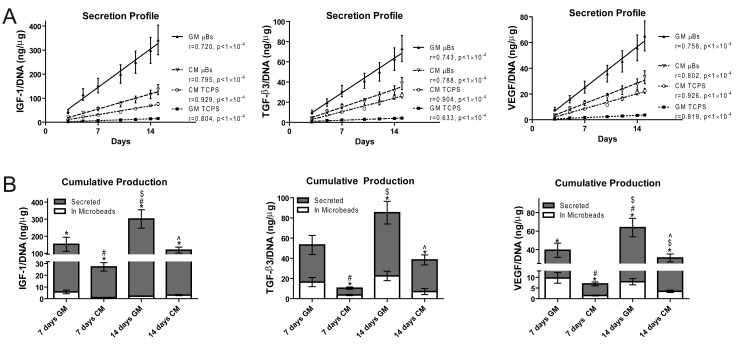
Linear regressions of the cumulative secretion profiles of IGF-I, TGF-β3 and VEGF-A from all ASC cultures were linear over a 2 week period (Figure 1A). Specifically, microencapsulation was able to increase the rate of all measured growth factor secretion in both GM and CM and the rates of IGF-I, TGF-β3 and VEGF-A secretions from all ASC cultures were significantly different compared to each other (Figure 1A, p<1×10-4). Microbeads in CM secreted less IGF-I, TGF-β3 and VEGF-A than those in GM, but TCPS cultures in CM secreted more of the same growth factors than TCPS cultures in GM.
Figure 1.
Growth Factor Production and Secretion from ASC Microbeads over Time. (A) Linear regressions of cumulative growth factor secretion profiles from ASC cultures with measurements at 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, 14 and 15 days and normalized to DNA content at day 15. ASCs were cultured in growth medium (GM) and chondrogenic medium (CM) on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) or within alginate microbeads (μB). (B) Cumulative growth factor production/DNA content secreted and maintained within ASC microbeads after 7 and 14 days in GM and CM. (n = 6 samples, mean±SE, *p<0.05 vs. in microbead, #p<0.05 vs. wk1 GM, $p<0.05 vs. wk1 CM, ^p<0.05 vs. wk2 GM).
In GM, ASC microbeads secreted 25 fold more IGF-I, 2.2 fold more TGF-β3 and 3 fold more VEGF-A than what was retained within the microbead after 7 days (Figure 1B). In CM, ASC microbeads secreted 27 fold more IGF-I, 1.9 fold more TGF-β3 and 3.7 fold more VEGF-A than what was retained within the microbead after 7 days. Although cumulative production and secretion of growth factors from microbeads increased between 7 and 14 days in both GM and CM, the amount of growth factor retained within the microbead did not change after 7 days.
Effect of Chondrogenic Medium and Microencapsulation on ASCs from Multiple Donors
For ASCs derived from 6 different donors, CM had the most apparent effect on fgf2, vegfa and nog (Figure 2A). CM decreased fgf2 in TCPS cultures by 8.8 to 9.6 fold and microbeads by 3.7 to 4.2 fold at day 7 and 14 (Figure 2A). CM treatment for 7 and 14 days also decreased vegfa in the TCPS cultures and microbeads by 4.3 to 6.5 fold. 7 and 14 days of CM treatment increased nog in TCPS cultures by 66 and 146 fold respectively, but nog in microbeads only increased by 7.2 and 12.8 fold.
Figure 2.
Effect of Chondrogenic Medium on Growth Factor mRNA Levels and Secretion from ASCs Isolated from Different Donors. (A) mRNA levels and (B) growth factor secretion/DNA content on day 7 and day 14 from ASCs cultured in chondrogenic medium (CM) on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) and within alginate microbeads (μB) normalized to matching 2-D and 3-D cultures in growth medium (GM) (n = 6 donors, mean±SE, *p<0.05 CM vs. GM, #p<0.05 vs. wk1 TCPS, $p<0.05 vs. wk1 μB, ^p<0.05 vs. wk2 TCPS). mRNA and secretion levels of other genes and growth factors can be found in Table 2.
CM did not decrease FGF-2 secretion on day 7 or 14 (Figure 2B) as FGF-2 production from TCPS cultures in CM was 2 fold higher than TCPS cultures in GM on day 7. VEGF-A secretion from microbeads in CM was 4.9 fold lower than microbeads in GM on day 14. CM also increased acan, col2, col10, comp, igf1, sox9 and tgfb3 and decreased pthlh in ASC cultures (Table 2).
Table 2. Effect of Chondrogenic Medium and Microencapsulation on ASCs from Multiple Donors.
| CM/GM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wk1 TCPS | wk1 μB | wk2 TCPS | wk2 μB | |
| mRNA Levels | ||||
| Acan/Rps18 | *94.5±41.3 | *9.9±4.0 | *184.7±95.6 | *18.3±5.6 |
| Col2/Rps18 | 3.6±1.4 | 2.4±1.5 | 2.5±0.8 | 10.0±4.5 |
| Col10/Rps18 | *48.8±33.8 | *14.9±4.2 | *11.7±7.9 | *23.4±11.2 |
| Comp/Rps18 | *8.7±2.1 | *4.1±1.0 | *8.0±1.9 | *8.2±2.4 |
| Igf1/Rps18 | *2.8±0.8 | 1.6±0.6 | 4.6±1.3 | *3.3±0.6 |
| Pthlh/Rps18 | *0.6±0.2 | *0.1±0.0 | 0.5±0.1 | *0.1±0.0 |
| Sox9/Rps18 | 1.8±0.3 | *1.9±.3 | *2.2±0.6 | *2.4±0.2 |
| Tgfb1/Rps18 | *2.0±0.2 | *1.5±.4 | *1.6±0.2 | *1.0±0.2 |
| Tgfb2/Rps18 | *1.4±0.3 | *1.0±0.5 | 1.5±0.3 | 1.1±0.3 |
| Tgfb3/Rps18 | *8.4±1.8 | 0.6±.2 | *5.0±1.2 | 0.6±0.2 |
| Growth Factor Secretion | ||||
| IGF-I/DNA | *4.7±2.4 | 1.9±0.3 | 6.0±2.9 | 2.0±0.7 |
| TGF-β3/DNA | 1.2±0.1 | 1.0±0.1 | 1.1±0.2 | 1.0±0.3 |
| μB/TCPS | ||||
| wk1 GM | wk1 CM | wk2 GM | wk2 CM | |
| mRNA Levels | ||||
| Fgf2/Rps18 | *0.3±0.1 | *.05±0.1 | 0.6±0.3 | 0.7±0.3 |
| Nog/Rps18 | 1.1±0.6 | *0.1±0.0 | 1.4±0.7 | *0.2±0.1 |
| Tgfb1/Rps18 | 1.9±0.3 | 1.5±0.4 | 1.8±0.3 | 1.0±0.2 |
| Tgfb2/Rps18 | 6.1±1.7 | 2.0±0.5 | 2.4±0.6 | 1.6±0.3 |
| Vegfa/Rps18 | 2.2±0.7 | 0.9±0.3 | 2.0±0.7 | 1.3±0.5 |
| Growth Factor Secretion | ||||
| FGF-2/DNA | 0.8±0.4 | 1.6±1.4 | *6.1±2.3 | 5.0±2.4 |
| VEGF-A/DNA | 0.5±0.2 | 1.1±0.7 | 1.3±0.5 | 2.1±1.1 |
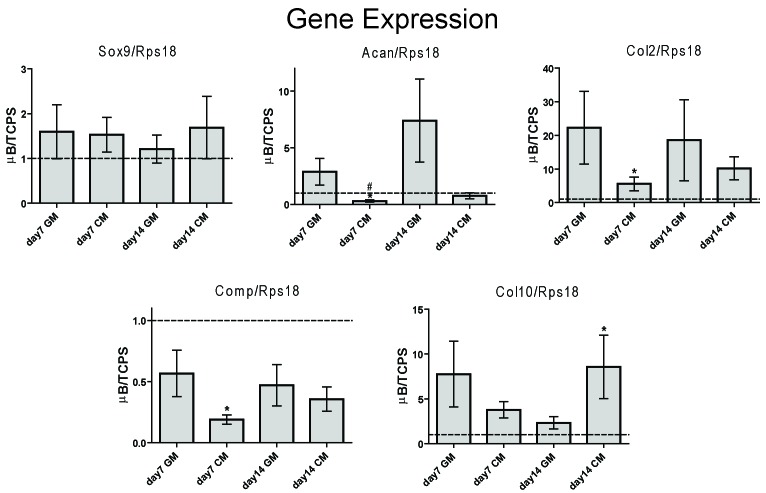
Microencapsulation had differential effects on chondrocyte phenotypic mRNA levels of ASCs. After 7 days in CM, microencapsulation decreased acan and comp by 3.3 and 5.3 fold respectively but increased col2 by 6.2 fold (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Effect of Microencapsulation on Phenotypic mRNA Levels of ASCs Isolated from Different Donors. (A) mRNA levels on day 7 and day 14 of ASC microbeads cultured in growth medium or chondrogenic medium (CM) normalized to ASCs on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) cultured in matching media. (n = 6 donors, mean±SE, *p<0.05 μB vs. TCPS, #p<0.05 vs. wk1 GM, $p<0.05 vs. wk1 CM, ^p<0.05 vs. wk2 GM). mRNA levels of ASCs cultured in chondrogenic medium (CM) on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) and within alginate microbeads (μB) normalized to matching 2-D and 3-D cultures in growth medium can be found in Table 2.
After 14 days in CM, microencapsulation increased col10 by 8.6 fold. Meanwhile, microencapsulation had no effect on sox9 in either GM or CM. For growth factor mRNA levels, microencapsulation had the most apparent effect on igf1, pthlh and tgfb3 in ASCs derived from 6 different donors (Figure 4A). Microencapsulation consistently decreased igf1 for 6 different donors with a 4.2 fold decrease in CM after 7 days (Figure 4A). The effects of microencapsulation on pthlh and tgfb3 were media dependent. Microencapsulation only increased pthlh in GM by 5.3 and 3.7 fold after 7 and 14 days respectively. Microencapsulation increased tgfb3 in GM by 8.2 and 4.8 fold after 7 and 14 days respectively but decreased tgfb3 in CM by 2.3 fold at day 7.
Figure 4.
Effect of Microencapsulation on Growth Factor mRNA Levels and Secretion from ASCs Isolated from Different Donors. (A) mRNA levels and (B) growth factor secretion/DNA content on day 7 and day 14 from ASC microbeads cultured in growth medium or chondrogenic medium (CM) normalized to ASCs on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS) cultured in matching media (n = 6 donors, mean±SE, *p<0.05 μB vs. TCPS, #p<0.05 vs. wk1 GM, $p<0.05 vs. wk1 CM, ^p<0.05 vs. wk2 GM). mRNA and secretion levels of other genes and growth factors can be found in Table 2.
Microencapsulation increased IGF-I secretion at day 7 in GM and CM by 11.9 and 7.6 fold respectively (Figure 4B). Microencapsulation also increased TGF-β3 secretion by 2.3 fold at day 7 in CM and by 4.6 fold on day 14 in GM. VEGF-A secretion from ASCs was not affected by microencapsulation, but microencapsulation did increase FGF-2 secretion at day 14 in GM and decreased nog expression after 7 and 14 days in CM (Table 2).
4-way ANOVA showed that media treatment significantly influenced acan, col10, comp, fgf2, igf1, nog pthlh and sox9 as well as IGF-I and VEGF-A secretion (Table 3).Microencapsulation significantly affected col2, col10, comp, fgf2, igf1, nog and tgfb2 as well as IGF-I and TGF-β3 secretion. Seven days versus 14 days in culture did not influence baseline gene expression but did influence FGF-2 and TGF-β3 secretion. The interaction between medium and microencapsulation had significant effects on nog, pthlh and tgfb3 but not on growth factor secretion. Although there were significant differences in baseline growth factor expression and secretion between freshly isolated P1 ASCs and cryopreserved P3 ASCs, the interaction between microencapsulation and cell passage did not affect mRNA levels but did affect FGF-2 and IGF-I secretion.
Table 3. P-values of 4-Way ANOVA of Medium, Microencapsulation (μB), Culture Time (Time) and Passage Number (Passage).
| Medium | μB | Time | Passage | μB × Medium | μB × Time | μB × Passage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA Levels | |||||||
| Acan/Rps18 | *<0.001 | 0.822 | 0.328 | 0.128 | 0.058 | 0.453 | 0.217 |
| Col2/Rps18 | 0.180 | *0.001 | 0.853 | *0.006 | 0.638 | 0.962 | 0.101 |
| Col10/Rps18 | *<0.001 | *<0.001 | 0.172 | *0.003 | 0.524 | 0.546 | 0.673 |
| Comp/Rps18 | *<0.001 | *0.001 | 0.339 | 0.198 | 0.580 | 0.720 | 0.299 |
| Fgf2/Rps18 | *<0.001 | *<0.001 | 0.931 | *0.070 | 0.074 | 0.544 | 0.831 |
| Igf1/Rps18 | *0.022 | *<0.001 | 0.546 | 0.612 | 0.537 | 0.893 | 0.978 |
| Nog/Rps18 | *<0.001 | *<0.001 | 0.795 | *0.003 | *0.019 | 0.588 | 0.232 |
| Pthlh/Rps18 | *<0.001 | 0.428 | 0.335 | *<0.001 | *<0.001 | 0.972 | 0.386 |
| Sox9/Rps18 | *0.002 | 0.352 | 0.818 | 0.654 | 0.707 | 0.787 | 0.151 |
| Tgfb1/Rps18 | 0.465 | 0.456 | 0.590 | *0.001 | 0.596 | 0.827 | 0.991 |
| Tgfb2/Rps18 | 0.968 | *0.001 | 0.328 | *<0.001 | 0.496 | 0.130 | 0.703 |
| Tgfb3/Rps18 | 0.141 | 0.393 | 0.814 | *0.045 | *<0.001 | 0.452 | 0.943 |
| Vegfa/Rps18 | *0.001 | 0.895 | 0.881 | *0.017 | 0.626 | 0.931 | 0.463 |
| Protein Secretion | |||||||
| FGF-2/DNA | 0.799 | 0.132 | *0.007 | 0.250 | 0.730 | 0.931 | *0.031 |
| IGF-I/DNA | *0.026 | *<0.001 | 0.184 | *<0.001 | 0.379 | *0.028 | *0.023 |
| TGF-β3/DNA | 0.965 | *<0.001 | *0.001 | *0.001 | 0.825 | 0.108 | 0.181 |
| VEGF-A/DNA | *<0.001 | *0.029 | 0.512 | 0.947 | 0.981 | 0.556 | 0.229 |
*p<0.05 CM vs GM for medium, μB vs.TCPS for μB, 1 week vs. 2 weeks for time, 1 passage vs. 3 passages for passage.
Effect of Microbead Composition on Growth Factor Production and Secretion
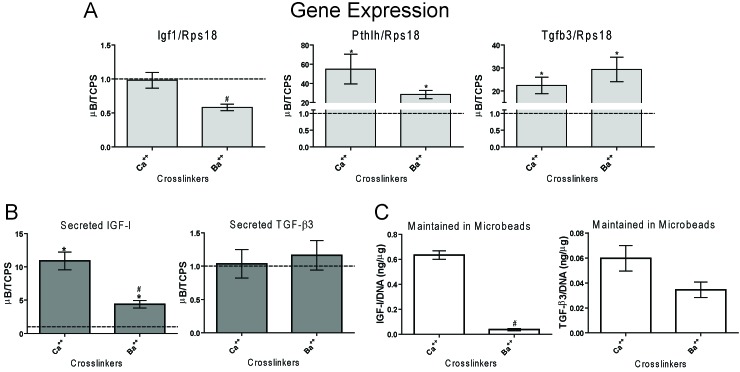
Igf1 in Ba microbeads was less than that of Ca microbeads (Figure 5A). Ba microbeads also secreted less IGF-I than Ca microbeads on day 7 (Figure 5B) and Ba microbeads maintained 10 fold less IGF-I within than Ca microbeads over 7 days (Figure 5C). However, both Ca microbeads and Ba microbeads secreted 10.9 and 4.4 fold greater IGF-I than TCPS cultures on day 7 (Figure 5B). Pthlh and tgfb3 in Ba microbeads were not statistically different from Ca microbeads and was 28 to 29 fold greater than TCPS cultures (Figure 5A). Ca and Ba microbeads secreted similar amounts of TGF-β3 on day 7 (Figure 5B) and although Ca microbeads maintained more TGF-β3 than Ba microbeads (Figure 5C), this difference was not significant.
Figure 5.
Effect of Divalent Crosslinks in ASC Microbead on Growth Factor mRNA Levels and Production. (A) mRNA levels and (B) growth factor secretion/DNA content on day 7 from ASC microbeads crosslinked in CaCl2 Ca++) or BaCl2 (Ba++), cultured in growth medium and normalized to ASCs on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS). (C) Growth factor retained within microbeads normalized to DNA content (n = 6 samples, mean±SE, *p<0.05 μB vs. TCPS, #p<0.05 vs. Ca++).
MVM microbeads had 2.3 fold lower pthlh than LVM microbeads, but all microbeads had at least 24 fold higher pthlh than TCPS cultures (Figure 6A). LVG microbeads had 2.9 fold higher tgfb3 than LVM, but all microbeads still had at least 22 fold higher tgfb3 than TCPS cultures. Although the different alginate polymers did not have a significant effect on igf1 (Figure 6A), VLVM microbeads secreted 2.8 fold less IGF-I than LVM microbeads on day 7 (Figure 6B). Additionally, LVM, LVG and MVM microbeads secreted 2.9 to 4.3 fold more IGF-I than TCPS cultures, but VLVM microbeads secreted similar levels of IGF-I to TCPS cultures on day 7. LVG microbeads retained 2.4 fold more IGF-I than LVM microbeads over 7 days (Figure 6C). The molecular weight and guluronate content of the alginate polymer had no effect on TGF-β3 secreted or retained in the microbeads (Figure 6B, C).
Figure 6.
Effect of Alginate Molecular Weight and Chemistry in ASC Microbead on Growth Factor mRNA Levels and Production. (A) Growth factor mRNA and (B) growth factor secretion/DNA content on day 7 from ASC microbeads consisting of LVM, LVG, VLVM and MVM alginates; cultured in growth medium; and normalized to ASCs on tissue culture polystyrene (TCPS). (C) Growth factor retained in microbeads normalized to DNA content (n = 6 samples, mean±SE, *p<0.05 μB vs. TCPS, #p<0.05 vs. Ca++).
Discussion
Although alginate microbeads have long been viewed as a protective vehicle for cell therapies, they have a more promising end use in controlling the production, secretion and localization of growth factors synthesized by stem cells in order to repair damaged or diseased tissues. This study demonstrated that microencapsulation alone can enhance growth factor production by ASCs and that ASC microbeads can secrete different growth factors at a constant rate over a two week period. Important for cartilage regeneration, microencapsulation increased IGF-I and TGF-β3 secretion and chondrogenic medium decreased VEGF-A secretion from ASCs derived from multiple donors (Figure 7).
Figure 7.

Summative Affect of Chondrogenic Medium and Microencapsulation on ASCs
Additionally, IGF-I production and secretion were higher for alginate microbeads with larger molecular weights and calcium crosslinks. These results suggest that a biomaterials-mediated approach using microbeads, in addition to medium induction can be used to tailor growth factor production for cartilage regeneration. This approach has been supported by other studies, which have shown barium crosslinks reducing protein secretion from alginate beads[21] and low guluronate content alginate hydrogels with a more flexible polymer backbone having greater solute diffusivity[17]. Furthermore, our findings are consistent with previous studies in which alginate microcapsules maintained growth factor gene expression and sustained growth factor release for at least 22 days while promoting bone and myocardial muscle regeneration[31, 32].
Alginate encapsulation is well known to restore the chondrocytic phenotype of dedifferentiated chondrocytes and to enhance the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells[33, 34] due to the round cell morphology and cell-cell interactions imparted by high density encapsulation[35, 36]. However, alginate microbeads may have an even more effective application in controlling the localization of chondrogenic growth factors secreted by ASCs. This study showed that alginate microbeads can retain endogenously produced IGF-I and TGF-β3. Although not directly observed in this study, alginate degradation and electrostatic interaction between the alginate and growth factor can influence growth factor diffusive properties and subsequent secretion from alginate microbeads[18, 37] and may partially explain the discrepancies between mRNA and secretion levels of certain growth factors. Moreover, although chondrogenic medium and alginate chemistry were the main drivers for manipulating growth factor secretion from ASC microbeads in this study, controlled degradation of these hydrogels can further regulate the temporal release of these growth factors[16, 38-40]. Incorporating biomimetic peptides, such as RGD, within the microbeads can also manipulate the expression of certain growth factors[32]. Therefore, these diverse attributes imparted by the hydrogel’s microenvironment make ASC microbeads ideal candidates as trophic factor production sources for cartilage regeneration.
Interestingly, microencapsulation increased mRNA levels for both PTHrP and TGF-β3 in ASCs in growth medium but decreased mRNA and the secretion profile of TGF-β3 in chondrogenic medium. Calcium has been shown to increase secretion of PTHrP from human cells[41], but this current study showed that increases in PTHrP and TGF-β3 mRNA levels were independent of the calcium crosslinks. Previous studies have shown that soluble components of serum can hinder chondrogenesis[42] whereas TGF-β1 and BMP-6 in chondrogenic medium can increase chondrocytic phenotype in ASCs[1, 34, 43]. Although the effects of individual serum components on growth factor production were not directly measured in this study, microencapsulation may have hindered the mass transport of these inhibitory soluble factors in growth medium and stimulatory soluble factors (e.g., TGF-β1, BMP-6) in chondrogenic medium. This potential explanation is supported by the detectable amounts of TGF-β3 maintained within the microbead, but disproved by the even larger amounts of TGF-β3 that were secreted over time. Regardless, no combination of microencapsulation or medium treatement optimized the ideal growth factor secretion profile of increased chondrogenic factor production (e.g., TGF-β3, IGF-I) along with decreased angiogenic factor production (e.g., VEGF-A). Therefore, subsequent studies may have to investigate different media treatments in addition to microbead formulations as we have previously explored[15].
Before the therapeutic benefit of ASC microbeads as growth factor production sources for cartilage regeneration is fully known, the effect of donor and isolation variability on ASC growth factor secretion and the subsequent effects these secreted factors have in vivo need to be explored. Several studies have investigated whether donor age or body mass index affect ASC density in tissue and their chondrogenic potential, but the results have been conflicting[44-46]. These discrepancies may be due to differences in tissue harvesting techniques, anatomical location, passage number and donor sex, all of which have been shown to affect ASC yield and differentiation potential[36, 44, 47, 48].
The variability in these parameters in this current study may have caused the inconsistencies among the different cell culture experiments, specifically in the effect of microencapsulation on growth factor secretion between different studies. Despite these discrepancies, ASCs and ASC microbeads implanted in focal cartilage defects have shown promise for cartilage regeneration in multiple studies[15, 49] and support the clinical potential of ASC microbeads as growth factor production sources for cartilage regeneration.
Conclusion
Human ASC microbeads secreted IGF - I, TGF - β3 and VEGF-A at a constant rate in both growth and chondrogenic over the course of 7 days, ASC microbeads secreted 2 to 27 fold more of these growth factors than what was maintained within the alginate. Microencapsulation consistently increased mRNAs for PTHrP and secretion of IGF-I and TGF-β3 from ASCs from multiple donors. Meanwhile, chondrogenic medium consistently decreased mRNAs for FGF-2 and secretion of VEGF-A from ASC microbeads derived from multiple donors. Crosslinking microbeads in BaCl2 instead of CaCl2 did not eliminate the beneficial effects of microencapsulation, but did decrease IGF-I mRNA and production. Increasing the guluronate content of the alginate microbead increased TGF-β3 mRNA and IGF-I retained within the microbead. Decreasing the molecular weight of the alginate used eliminated the beneficial effects microencapsulation had on IGF-I secretion while increasing the molecular weight of alginate used decrease PTHrP mRNA. This study, in conjunction with prior findings, demonstrated that ASC microbeads may be a reliable source for delivering multiple growth factors to facilitate cartilage regeneration.
Acknowledgements
Sri Vermula, Wallace H. Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA for her assistance with cell culture. Dr. Joseph K. Williams (Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta) for isolating and shipping adipose tissue.
Abbreviations
- ACAN:
Aggrecan
- ANOVA:
Analysis of Variance
- ASCs:
Adipose Stem Cells
- Ba++:
Barium Ion
- BaCl2:
Barium Chloride
- BMP:
Bone Morphogenetic Protein
- cDNA:
Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid
- Ca++:
Calcium Ion
- CaCl2:
Calcium Chloride
- CM:
Chondrogenic Medium
- COL2:
Type-II Collagen
- COL10:
Type-X Collagen
- COMP:
Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein
- DMEM:
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- DMSO:
Dimethyl Sulfoxide
- ELISA:
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
- FGF:
Fibroblast Growth Factor
- GM:
Growth Medium
- IGF:
Insulin-like Growth Factor
- LVG:
Low Viscosity High Guluronate
- LVM:
Low Viscosity High Mannuronate
- mRNA:
Messenger Ribonucleic Acid
- MVM:
Medium Viscosity High Mannuronate
- Nog:
Noggin
- μB:
Microbead
- PCR:
Polymerase Chain Reaction
- PTHrP:
Parathyroid Hormone-related Peptide
- PTHLH:
Parathyroid Hormone Linked Hormone
- RGD:
Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic Acid
- RPS18:
Ribosomal Protein S18
- SE:
Standard Error
- SOX9:
Sex Determining region Y-Box containing Gene 9
- TCPS:
Tissue Culture Polystyrene
- TGF-ß:
Transforming Growth factor-Beta
- UV:
Ultraviolet
- VEGF-A:
Vascular Endothelial Growth factor-A
- VLVM:
Very Low Viscosity High Mannuronate
Funding Statement
Sponsors/Grants: NSF Graduate Research Fellowship (Lee), 4201 Wilson Blvd, Arlington, VA, USA 22230; Department of Defense (W81XWH-11-1-0306), 1400 Defense Pentagon, Washington, DC, USA 20301-1400; Phase I SBIR grant from the Department of Defense (W81XWH-11-C-0071).
Reference
- 1.Gimble J, Guilak F.Adipose-derived adult stem cells: isolation, characterization and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy 2003; 5(5):362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Moyer HR, Kinney RC, Singh KA, Williams JK, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD.Alginate microencapsulation technology for the percutaneous delivery of adipose-derived stem cells. Ann Plast Surg 2010; 65(5):497-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takahashi T, Ogasawara T, Kishimoto J, Liu G, Asato H, Nakatsuka T, Uchinuma E, Nakamura K, Kawaguchi H, Chung UI, Takato T, Hoshi K.Synergistic effects of FGF-2 with insulin or IGF-I on the proliferation of human auricular chondrocytes. Cell Transplant 2005; 14(9):683-93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu Z, Lavine KJ, Hung IH, Ornitz DM.FGF18 is required for early chondrocyte proliferation, hypertrophy and vascular invasion of the growth plate. Dev Biol 2007; 302(1):80-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hanada K, Solchaga LA, Caplan AI, Hering TM, Goldberg VM, Yoo JU, Johnstone B.BMP-2 induction and TGF-beta 1 modulation of rat periosteal cell chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem 2001; 81 (2):284-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Beier F, Ali Z, Mok D, Taylor AC, Leask T, Albanese C, Pestell RG, LuValle P.TGFbeta and PTHrP control chondrocyte proliferation by activating cyclin D1 expression. Mol Biol Cell 2001; 12(12):3852-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Minina E, Kreschel C, Naski MC, Ornitz DM, Vortkamp A.Interaction of FGF, Ihh/Pthlh and BMP signaling integrates chondrocyte proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation. Dev Cell 2002; 3(3):439-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Im GI, Jung NH, Tae SK.Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from patients in late adulthood: the optimal conditions of growth factors. Tissue Eng 2006; 12(3):527-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brittberg M, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, Ohlsson C, Isaksson O, Peterson L.Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med 1994; 331(14):889-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Awad HA, Halvorsen YD, Gimble JM, Guilak F.Effects of transforming growth factor beta1 and dexamethasone on the growth and chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng 2003; 9(6):1301-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kolambkar YM, Peister A, Soker S, Atala A, Guldberg RE.Chondrogenic differentiation of amniotic fluid-derived stem cells. J Mol Histol 2007; 38(5):405-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Baraniak PR, McDevitt TC.Stem cell paracrine actions and tissue regeneration. Regen Med 2010; 5(1): 121-43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kim BS, Kang KS, Kang SK.Soluble factors from ASCs effectively direct control of chondrogenic fate. Cell Prolif 2010; 43(3):249-61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee CS, Burnsed OA, Raghuram V, Kalisvaart J, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z.Adipose stem cells can secrete angiogenic factors that inhibit hyaline cartilage regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 2012; 3(4):35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee CS, Watkins E, Burnsed OA, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD.Tailoring adipose stem cell trophic factor production with differentiation medium components to regenerate chondral defects. Tissue Eng Part A 2013; 19(11-12):1451-64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Leslie SK, Cohen DJ, Sedlaczek J, Pinsker EJ, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z.Controlled release of rat adipose-derived stem cells from alginate microbeads. Biomaterials 2013; 34(33):8172-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bhalla RK, Murphy J, Jones TM, Roland NJ.Foreign body reaction to calcium alginate fibre mimicking recurrent tumour of the submandibular salivary gland. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002; 40(2):172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baum C, Dullmann J, Li Z, Fehse B, Meyer J, Williams DA, von K, lle C.Side effects of retroviral gene transfer into hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2003; 101 (6):2099-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haider H, Ashraf M.Strategies to promote donor cell survival: combining preconditioning approach with stem cell transplantation. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2008; 45(4):554-66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hata R, Senoo H.L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate stimulates collagen accumulation, cell proliferation and formation of a three-dimensional tissuelike substance by skin fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 1989; 138(1):8-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tsutsumi K, Fujikawa H, Kajikawa T, Takedachi M, Yamamoto T, Murakami S.Effects of L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate magnesium salt on the properties of human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontal Res 2011;47(2):263-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Erdman CP, Dosier CR, Olivares-Navarrete R, Baile C, Guldberg RE, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD.Effects of Resveratrol on Enrichment of Adipose-derived Stem Cells and their Differentiation to Osteoblasts in Two and Three Dimensional Cultures. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6Suppl 3:s34-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee CS, Moyer HR, Gittens RA, Williams JK, Boskey AL, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z.Regulating in vivo calcification of alginate microbeads. Biomaterials 2010; 31:4926-34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fitzgerald JB, Jin M, Dean D, Wood DJ, Zheng MH, Grodzinsky AJ.Mechanical compression of cartilage explants induces multiple time-dependent gene expression patterns and involves intracellular calcium and cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem 2004; 279(18):19502-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fischer J, Dickhut A, Rickert M, Richter W.Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62(9):2696-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pathi S, Rutenberg JB, Johnson RL, Vortkamp A.Interaction of Ihh and BMP/Noggin signaling during cartilage differentiation. Dev Biol 1999; 209(2):239-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pufe T, Harde V, Petersen W, Goldring MB, Tillmann B, Mentlein R.Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces matrix metalloproteinase expression in immortalized chondrocytes. J Pathol 2004; 202(3):367-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Goldring MB, Tsuchimochi K, Ijiri K.The control of chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem 2006; 97(1):33-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peters IR, Peeters D, Helps CR, Day MJ.Development and application of multiple internal reference (housekeeper) gene assays for accurate normalisation of canine gene expression studies. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2007; 117(1-2):55-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Olivares-Navarrete R, Hyzy SL, Park JH, Dunn GR, Haithcock DA, Wasilewski CE, Boyan BD, Schwartz Z.Mediation of osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on titanium surfaces by a Wntintegrin feedback loop. Biomaterials 2011; 32(27):6399-411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grellier M, Granja PL, Fricain JC, Bidarra SJ, Renard M, Bareille R, Bourget C, Amedee J, Barbosa MA.The effect of the co-immobilization of human osteoprogenitors and endothelial cells within alginate microspheres on mineralization in a bone defect. Biomaterials 2009; 30(19):3271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kwack MH, Shin SH, Kim SR, Im SU, Han IS, Kim MK, Kim JC, Sung YK.l-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate promotes elongation of hair shafts via the secretion of insulin-like growth factor-1 from dermal papilla cells through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Br J Dermatol 2009; 160(6):1157-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gagne TA, Chappell-Afonso K, Johnson JL, McPherson JM, Oldham CA, Tubo RA, Vaccaro C, Vasios GW.Enhanced proliferation and differentiation of human articular chondrocytes when seeded at low cell densities in alginate in vitro. J Orthop Res 2000; 18(6):882-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kavalkovich KW, Boynton RE, Murphy JM, Barry F.Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells within an alginate layer culture system. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2002; 38(8):457-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Imabayashi H, Mori T, Gojo S, Kiyono T, Sugiyama T, Irie R, Isogai T, Hata J, Toyama Y, Umezawa A.Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated chondrocytes and chondrogenesis of human bone marrow stromal cells via chondrosphere formation with expression profiling by large-scale cDNA analysis. Exp Cell Res 2003; 288(1):35-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Loty S, Forest N, Boulekbache H, Sautier JM.Cytochalasin D induces changes in cell shape and promotes in vitro chondrogenesis: a morphological study. Biol Cell 1995; 83(2-3):149-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Oliveira JM, Sousa RA, Kotobuki N, Tadokoro M, Hirose M, Mano JF, Reis RL, Ohgushi H.The osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells cultured with dexamethasone-loaded carboxymethylchitosan/poly(amidoamine) dendrimer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2009; 30(5):804-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bouhadir KH, Lee KY, Alsberg E, Damm KL, anderson KW, Mooney DJ.Degradation of partially oxidized alginate and its potential application for tissue engineering. Biotechnol Prog 2001; 17(5):945-50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Boontheekul T, Kong HJ, Mooney DJ.Controlling alginate gel degradation utilizing partial oxidation and bimodal molecular weight distribution. Biomaterials 2005; 26(15):2455-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ashton RS, Banerjee A, Punyani S, Schaffer DV, Kane RS.Scaffolds based on degradable alginate hydrogels and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for stem cell culture. Biomaterials 2007; 28(36):5518-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pepper MS, Vassalli JD, Orci L, Montesano R.Biphasic effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on in vitro angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 1993; 204(2):356-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Iruela-Arispe ML, Sage EH.Endothelial cells exhibiting angiogenesis in vitro proliferate in response to TGF-beta 1. J Cell Biochem 1993; 52(4):414-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Diekman BO, Rowland CR, Lennon DP, Caplan AI, Guilak F.Chondrogenesis of adult stem cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow: induction by growth factors and cartilage-derived matrix. Tissue Eng Part A 2010; 16(2):523-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu Y, Titus L, Barghouthi M, Viggeswarapu M, Hair G, Boden SD.Glucocorticoid regulation of human BMP-6 transcription. Bone 2004; 35(3):673-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hennig T, Lorenz H, Thiel A, Goetzke K, Dickhut A, Geiger F, Richter W.Reduced chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue derived stromal cells correlates with an altered TGFbeta receptor and BMP profile and is overcome by BMP-6. J Cell Physiol 2007; 211 (3):682-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Boden SD, Liu Y, Hair GA, Helms JA, Hu D, Racine M, Nanes MS, Titus L.LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology 1998; 139(12):5125-34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Estes BT, Guilak F.Three-dimensional culture systems to induce chondrogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells. Methods Mol Biol 2011; 702:201-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Estes BT, Wu AW, Guilak F.Potent induction of chondrocytic differentiation of human adipose-derived adult stem cells by bone morphogenetic protein 6. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54(4):1222-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cui L, Wu Y, Cen L, Zhou H, Yin S, Liu G, Liu W, Cao Y.Repair of articular cartilage defect in non-weight bearing areas using adipose derived stem cells loaded polyglycolic acid mesh. Biomaterials 2009; 30(14):2683-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]