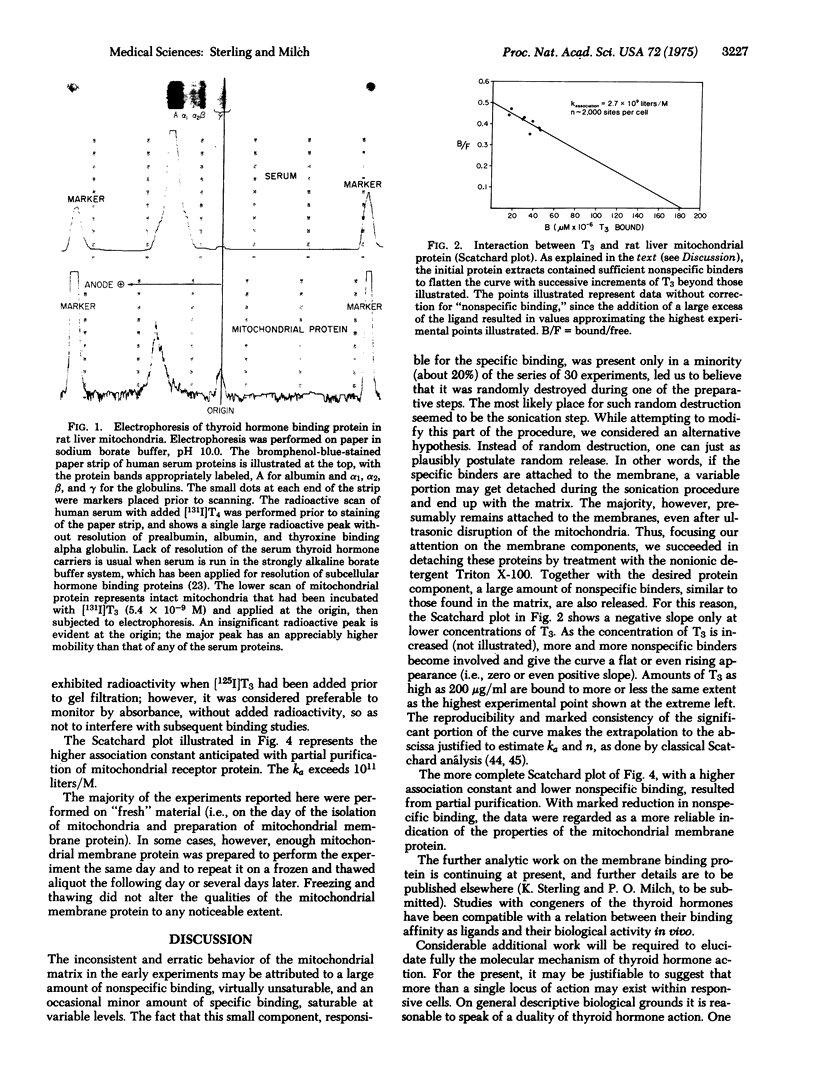
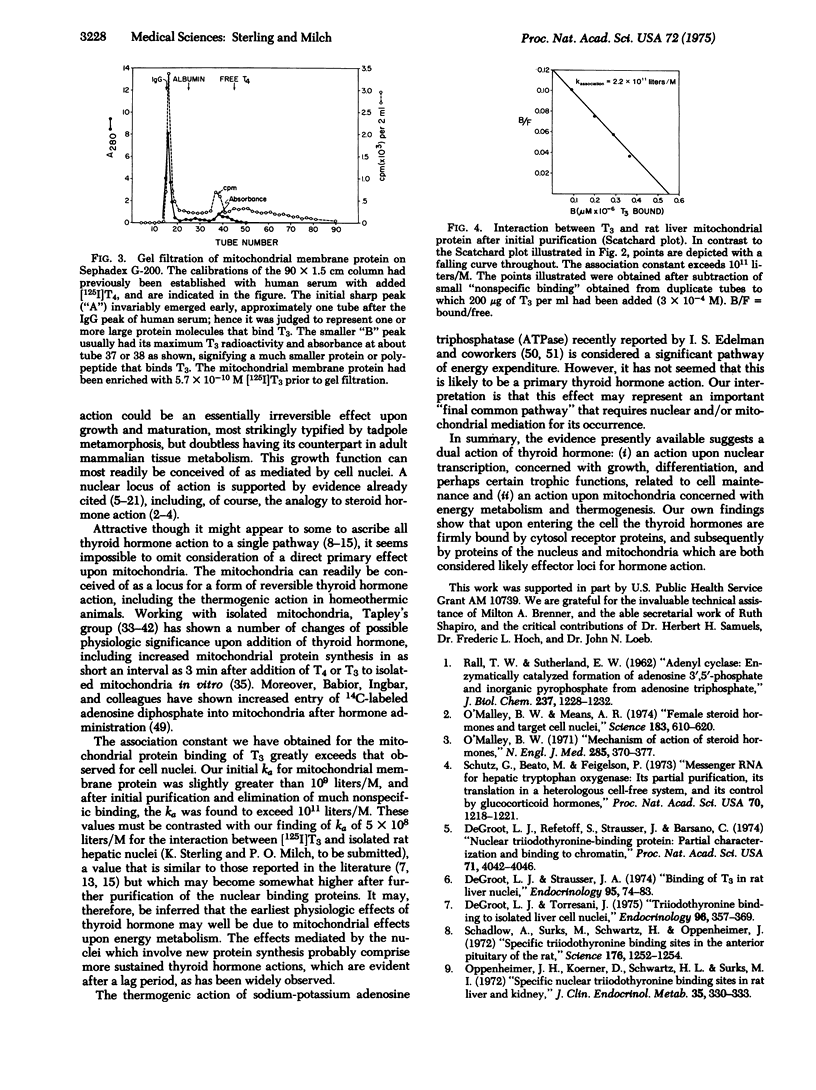
Abstract
The thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine, has been shown to be bound by the intranuclear chromatin protein associated with active DNA, where it is believed to stimulate transcription. Evidence exists that the thyroid hormones have direct action not only on nuclei, but also on mitochondria. Threfore, specific proteins that bind thyroid hormones in the mitochondria should be demonstrable. Mitochondria were isolated from homogenized rat livers by sedimentation through 0.25 M sucrose solution, followed by washing four times to free them of microsomes. Strong binding of thyroid hormones was observed in mitochondrial fractions prepared from both the membranes and the matrix. After incubation in an ice bath with increasing amonts of triiodothyronine with added tracer [125I]triiodothyronine, the matrix infrequently contained specific saturable receptor sites, but usually exhibited strong "nonspecific" interaction...
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babior B. M., Creagan S., Ingbar S. H., Kipnes R. S. Stimulation of mitochondrial adenosine diphosphate uptake by thyroid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):98–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg T., Boman D. Distribution of lysosomal enzymes between parenchymal and Kupffer cells of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 10;321(2):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J. L., Primack M. P., Tapley D. F. Effect of inhibition of mitochondrial protein synthesis in vitro upon thyroxine stimulation of oxygen consumption. Endocrinology. 1971 Aug;89(2):534–537. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-2-534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J., Popovitch J. R., Tapley D. F. Leucine transport by rat liver mitochondria in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J., Primack M. P., Tapley D. F. The relationship of mitochondrial swelling to thyroxine-stimulated mitochondrial protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1970 Nov;87(5):993–999. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-5-993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J., Tapley D. F. Stimulation by thyroxine of amino acid incorporation into mitochondria. Endocrinology. 1966 Jul;79(1):81–89. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles M. A., Ryffel G. U., Obinata M., McCarthy B. J., Baxter J. D. Nuclear receptors for thyroid hormone: evidence for nonrandom distribution within chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1787–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Handwerger B. S., Glaser F. Physical properties of a dog liver and kidney cytosol protein that binds thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6208–6217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot L. J., Strausser J. L. Binding of T3 in rat liver nuclei. Endocrinology. 1974 Jul;95(1):74–83. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-1-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot L. J., Torresani J. Triiodothyronine binding to isolated liver cell nuclei. Endocrinology. 1975 Feb;96(2):357–359. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degroot L. J., Refetoff S., Strausser J., Barsano C. Nuclear triiodothyronine-binding protein: partial characterization and binding to chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4042–4046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillman W., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Quantitative aspects of iodothyronine binding by cytosol proteins of rat liver and kidney. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):492–498. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S., Ismail-Beigi F. Thyroid thermogenesis and active sodium transport. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):235–257. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571130-2.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman I. S. Thyroid thermogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1303–1308. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Torizuka K., Miyake T., Fukase M. Specific binding proteins of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in liver soluble proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 24;201(3):479–492. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner D., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. In vitro demonstration of specific triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver nuclei. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):706–709. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Female steroid hormones and target cell nuclei. Science. 1974 Feb 15;183(4125):610–620. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4125.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W. Mechanisms of action of steroid hormones. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):370–377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102182840710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Koerner D., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Specific nuclear triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver and kidney. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1972 Aug;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1210/jcem-35-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Dillman W., Surks M. I. Effect of thyroid hormone analogues on the displacement of 125I-L-triiodothyronine from hepatic and heart nuclei in vivo: possible relationship to hormonal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):544–550. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91177-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Koerner D., Surks M. I. Limited binding capacity sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Nuclear-cytoplasmic interrelation, binding constants, and cross-reactivity with L-thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):768–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI107615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primack M. P., Buchanan J. L. Control of oxygen consumption in liver slices from normal and T4-treated rats. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):619–620. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primack M. P., Tapley D. F., Buchanan J. Stimulation of mitochondrial protein synthesis and oxygen consumption by thyroxine in vitro without deiodination to triiodothyronine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 19;244(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primack M. P., Tapley D., Buchanan J. Thyroid hormone stimulation of mitochondrial protein synthesis supported by an ATP generating system. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):840–844. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL T. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenyl cyclase. II. The enzymatically catalyzed formation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate and inorganic pyrophosphate from adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1228–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Refetoff S., Matalon R., Bigazzi M. Metabolism of L-thyroxine (T4) and L-triiodothyronine (T3) by human fibroblasts in tissue culture: evidence for cellular binding proteins and conversion of T4 to T3. Endocrinology. 1972 Oct;91(4):934–947. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-4-934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., ROSEN P., TABACHNICK M. Equilibrium dialysis studies of the binding of thyroxine by human serum albumin. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1021–1030. doi: 10.1172/JCI104552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S., Casanova J., Stanley F. Thyroid hormone action: in vitro characterization of solubilized nuclear receptors from rat liver and cultured GH1 cells. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):853–865. doi: 10.1172/JCI107825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S., Casanova J. Thyroid hormone action: in vitro demonstration of putative receptors in isolated nuclei and soluble nuclear extracts. Science. 1974 Jun 14;184(4142):1188–1191. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4142.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action in cell culture: domonstration of nuclear receptors in intact cells and isolated nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3488–3492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action. Demonstration of similar receptors in isolated nuclei of rat liver and cultured GH1 cells. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):656–659. doi: 10.1172/JCI107601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadlow A. R., Surks M. I., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Specific triiodothyronine binding sites in the anterior pituitary of the rat. Science. 1972 Jun 16;176(4040):1252–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4040.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutz G., Beato M., Feigelson P. Messenger RNA for hepatic tryptophan oxygenase: its partial purification, its translation in a heterologous cell-free system, and its control by glucocorticoid hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1218–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E., Tobias C. A. Actions of thyroid hormones on cultured human cells. Nature. 1966 Dec 17;212(5068):1318–1321. doi: 10.1038/2121318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel E., Tobias C. A. End-organ effects of thyroid hormones: subcellular interactions in cultured cells. Science. 1966 Aug 12;153(3737):763–765. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3737.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding S. W., Davis P. J. Thyroxine binding to soluble proteins in rat liver and its sex dependence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 19;229(1):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Saldanha V. F., Brenner M. A., Milch P. O. Cytosol-binding protein of thyroxine and triiodothyronine in human and rat kidney tissue. Nature. 1974 Aug 23;250(5468):661–663. doi: 10.1038/250661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Koerner D. H., Oppenheimer J. H. In vitro binding of L-triiodothyronine to receptors in rat liver nuclei. Kinectics of binding, extraction properties, and lack of requirement for cytosol proteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):50–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI107917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Koerner D., Dillman W., Oppenheimer J. H. Limited capacity binding sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Localization to the chromatin and partial characterization of the L-triiodothyronine-chromatin complex. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7066–7072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAPLEY D. F., COOPER C., LEHNINGER A. L. The action of thyroxine on mitochondria and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Dec;18(4):597–598. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TATA J. R., ERNSTER L., SURANYI E. M. Interaction between thyroid hormones and cellular constituents. I. Binding to isolated sub-cellular particles and sub-particulate fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jul 16;60:461–479. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90866-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapley D. F., Kimberg D. V., Buchanan J. L. The mitochondrion. N Engl J Med. 1967 May 25;276(21):1182–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196705252762106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai J. S., Samuels H. H. Thyroid hormone action: demonstration of putative nuclear receptors in human lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):919–922. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]