Abstract
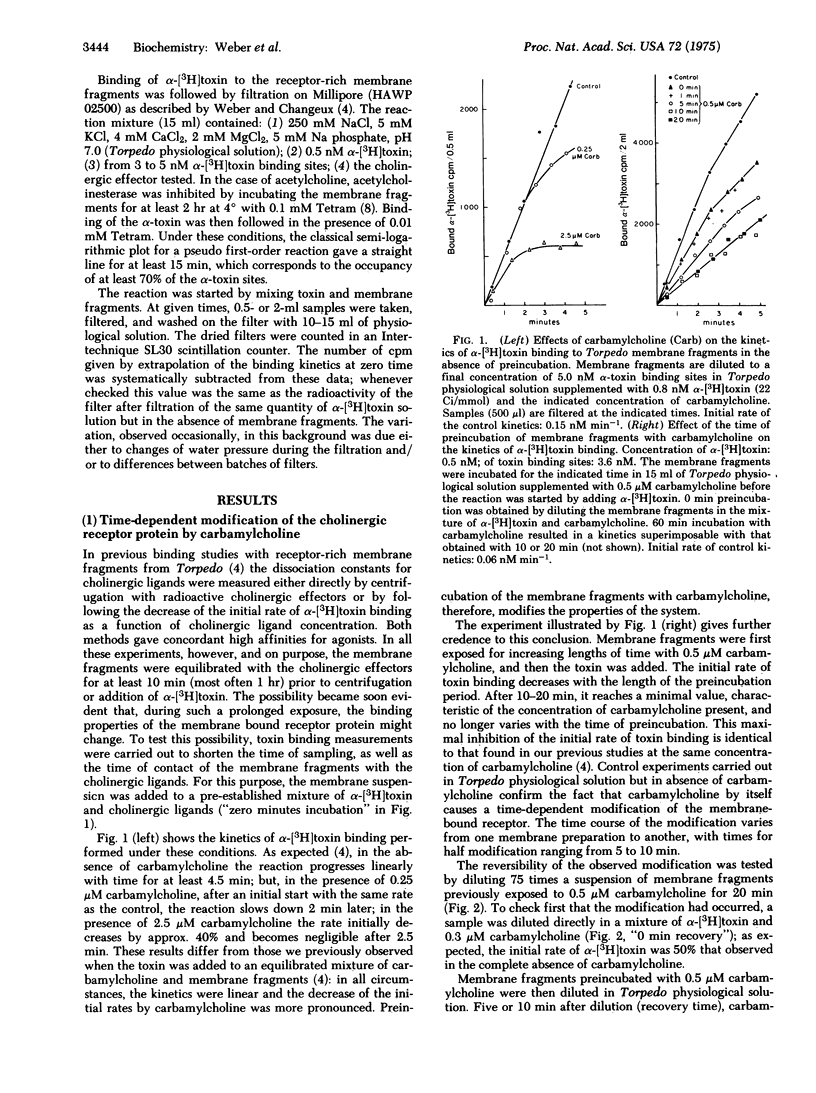
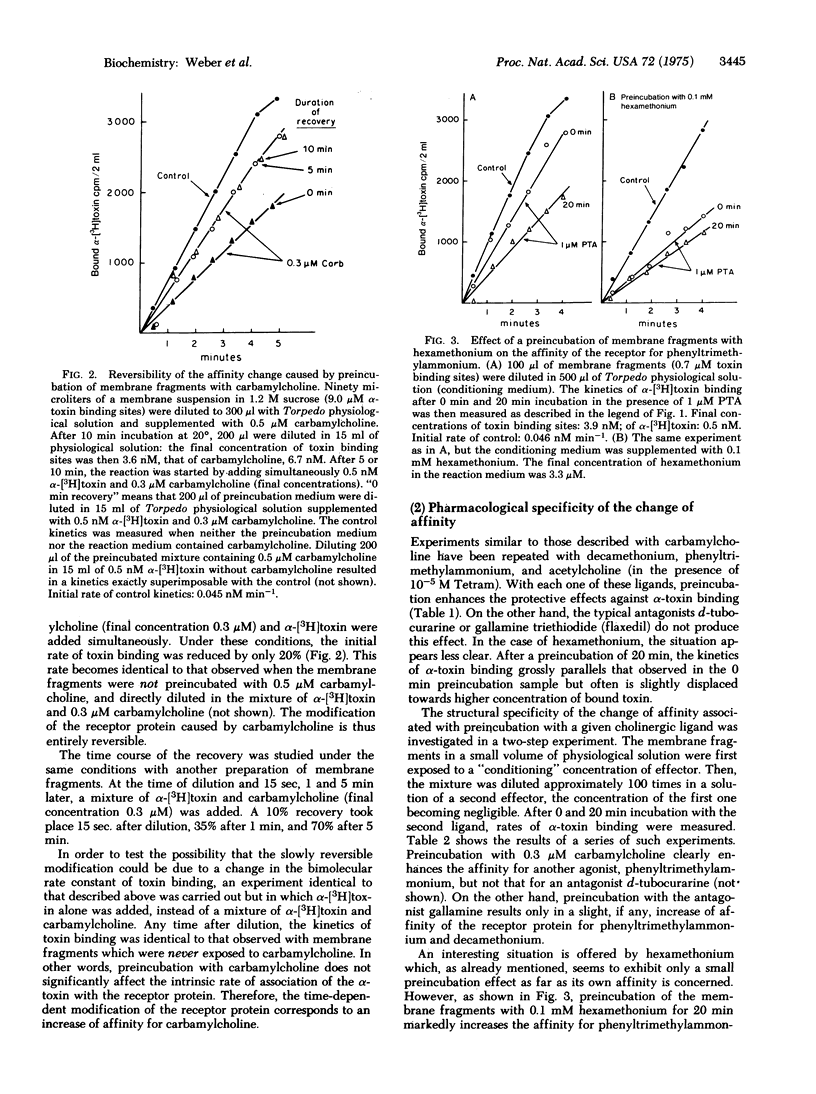
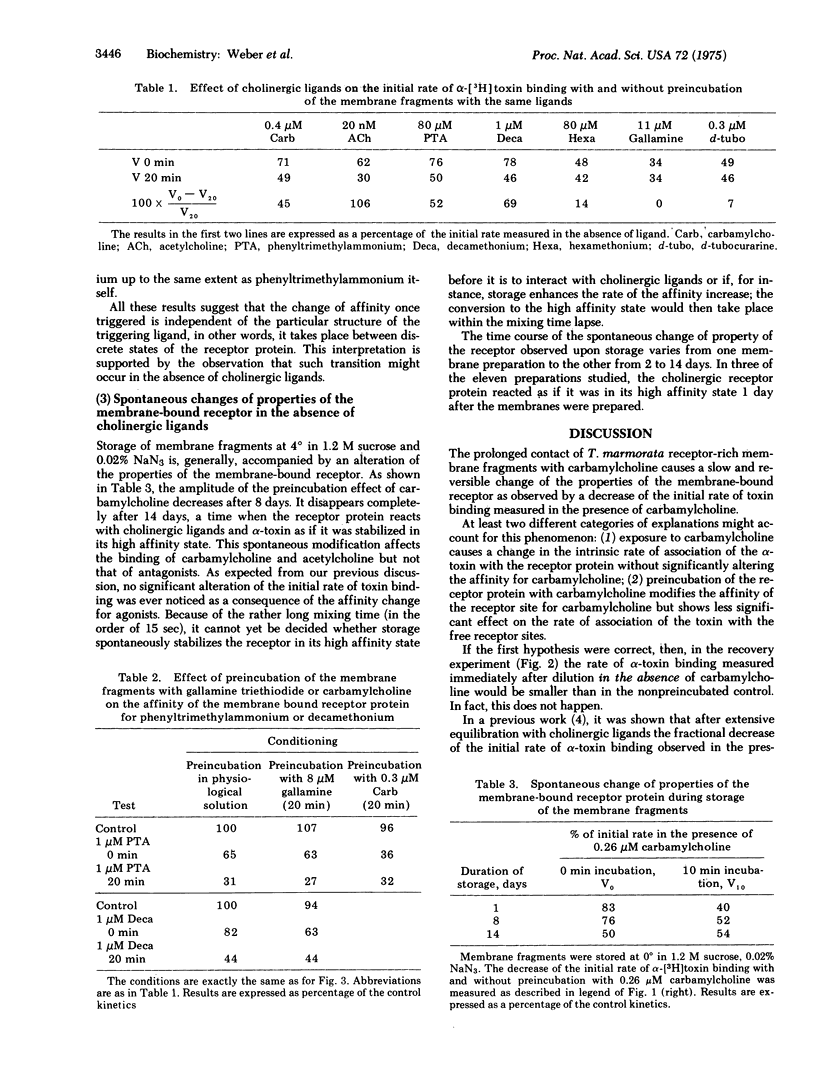
Exposure of receptor-rich membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata to carbamylcholine causes a slow (half-time of 5--10 min) and reversible change of properties of the cholinergic receptor protein manifested by a decrease of the initial rate of Naja nigricollis alpha-[3H]toxin binding in the presence of carbamylcholine. This change corresponds to a 5- to 20-fold increase of affinity for carbamylcholine. Other agonists, acetylcholine, phenyltrimethylammonium, show the same effect but not the antagonists d-tubocurarine and flaxedil. Decamethonium and hexamethonium show little, if any, agonistic effect in vitro on the same membrane fragments but cause the affinity change. This regulatory property can be lost after aging of the preparation of membrane fragments. Since the affinity increase progresses with a similar time course as the decrease of amplitude of the permeability response consecutive to agonist preincubation, it is proposed that, in the membrane at rest, the receptor protein is present under a state of low affinity for agonists and that the reversible stabilization by the agonists of a high affinity state corresponds to the "pharmacological desensitization" of the system as predicted by one of the models of Katz and Thesleff.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brisson A., Devaux P. F., Changeux J. P. Effet anesthésique local de plusieurs composés liposolubles sur la réponse de l'électroplaque de Gymnote à la carbamylcholine et sur la liaison de l'acétylcholine au récepteur cholinergique de Torpille. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1975 May 12;280(18):2153–2156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Huchet M., Meunier J. C. Extraction à partir du tissu électrique de gymnote d'une protéine présentant plusieurs propriétés caractéristiques du récepteur physiologique de l'acétylcholine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jun 8;270(23):2864–2867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Meunier J. C., Huchet M. Studies on the cholinergic receptor protein of Electrophorus electricus. I. An assay in vitro for the cholinergic receptor site and solubilization of the receptor protein from electric tissue. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;7(5):538–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Weber M., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Purification from Torpedo marmorata electric tissue of membrane fragments particularly rich in cholinergic receptor protein. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80538-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Britten A. G., Eldefrawi A. T. Acetylcholine binding to Torpedo electroplax: relationship to acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1971 Jul 23;173(3994):338–340. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3994.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Purification and molecular properties of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Changeux J. P. Reconstitution of a chemically excitable membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1479–1483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menez A., Morgat J. -L., Fromageot P., Ronseray A. -M., Boquet P., Changeux J. -P. Tritium labelling of the alpha-neurotoxin of Naja nigricollis. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 1;17(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Comparison between the affinities for reversible cholinergic ligands of a purified and membrane bound state of the acetylcholine-receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 15;32(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody T., Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. Binding of acetylcholine and related compounds to purified acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo Californica electroplax. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):761–772. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Sugiyama H., Changeux J. P. Démonstration de la désensibilisation pharmacologique du récepteur de l'acétylcholine in vitro avec des fragments de membrane excitable de Torpille. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Nov 25;279(22):1721–1724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. A new kind of drug antagonism: evidence that agonists cause a molecular change in acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):394–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama H., Changeux J. P. Interconversion between different states of affinity for acetylcholine of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. 3. Effects of local anaesthetics on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



