Abstract
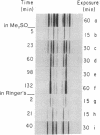
X-ray diffraction patterns from nerves bathed for about one-half hour in Ringer's solution containing dimethylsulfoxide at concentrations of 10% or more show reflections from a new, highly ordered structure with a repeat period about two-thirds that of native myelin. The proportion of myelin transformed is greater at higher concentrations, and above 40% the native pattern is no longer observed. Replacing the dimethylsulfoxide with Ringer's solution leads to the rapid reappearance of the native diffraction pattern. The effect of dimethylsulfoxide can be accounted for by the loss of water from the spaces between the membrane units without significant modification of the bilayer structure.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEN GEREN B. The formation from the Schwann cell surface of myelin in the peripheral nerves of chick embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1954 Nov;7(2):558–562. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(54)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. P., Young H. F., Nulsen F. E., Jane J. A. Physiological effects of dimethyl sulfoxide on peripheral nerves: possible role in pain relief. Exp Neurol. 1969 Jun;24(2):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaurock A. E. Structure of the nerve myelin membrane: proof of the low-resolution profile. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 28;56(1):35–52. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaurock A. E., Worthington C. R. Low-angle x-ray diffraction patterns from a variety of myelinated nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspar D. L., Kirschner D. A. Myelin membrane structure at 10 A resolution. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 12;231(19):46–52. doi: 10.1038/newbio231046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis H. L., Davis N. L., Clemons A. L. Procoagulant and nerve-blocking effects of DMSO. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Mar 15;141(1):310–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B., BURGE R. E. THE DETERMINATION OF THE FOURIER TRANSFORM OF THE MYELIN LAYER FROM A STUDY OF SWELLING PHENOMENA. J Mol Biol. 1963 Dec;7:672–682. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B. Electron microscope and x-ray diffraction studies of the effects of dehydrations on the structure of nerve myelin. I. Peripheral nerve. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Sep;8:13–29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B., MILLINGTON P. F. Effects of ionic strength of immersion medium on the structure of peripheral nerve myelin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Jan 25;3(1):89–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINEAN J. B. The role of water in the structure of peripheral nerve myelin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Jan 25;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott L. W., Katz J., Rubinstein L. J. Separate and combined effects of phenol, hyaluronidase and dimethyl sulfoxide on the sciatic nerve of the rat. I. Acute studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1968 Feb;49(2):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. F. X-RAY DIFFRACTION PATTERN OF NERVE MYELIN: A METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE PHASES. Science. 1963 Nov 29;142(3596):1173–1174. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3596.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS A. The structure of myelin sheaths in the central nervous system of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Feb;7:121–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian V. A. Long-range physical forces in the biological milieu. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1973;2:221–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.02.060173.001253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. Structural alterations in nerve fibers produced by hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):349–364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams W. M., Jr The effects of dimethyl sulfoxide on nerve conduction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Mar 15;141(1):242–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb34885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington C. R., Blaurock A. E. A low-angle x-ray diffraction study of the swelling behavior of peripheral nerve myelin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr;173(3):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]