Abstract
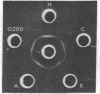
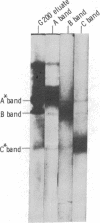
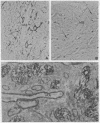
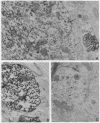
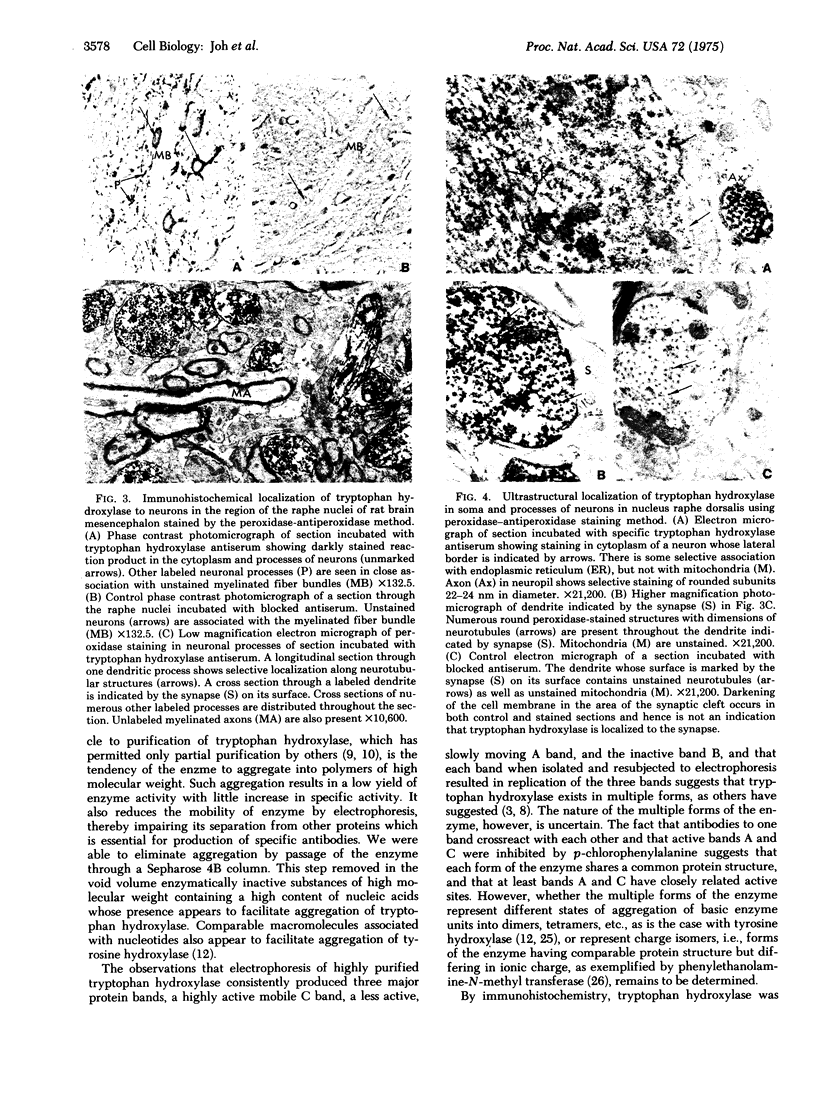
Tryptophan hydroxylase [EC 1.14.16.4; L-tryptophan, tetrahydropteridine:oxygen oxidoreductase (5-hydroxylating)], the enzyme catalyzing the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of serotonin, was purified 79-fold from the region of the raphe nucleus of rat midbrain by sequential column chromatography and disc-gel electrophoresis. In electrophoresis three bands were distinguished, A, B, and C, which, when separated and submitted individually to electrophoresis, reproduced the same three bands. Bands A and C were enzymatically active and inhibited by para-chlorohenylalanine. Antibodies produced to each of the three bands crossreacted by immuno double diffusion and electrophoresis with each other and homogenates of raphe nuclei; they completely inhibited enzyme activity only of tryptophan hydroxylase. Tryptophan hydroxylase was localized by light and electron immunohistochemistry to serotonin neutrons of the raphe. Ultrastructurally, in cell bodies, the enzyme was distributed in cytoplasm and in association with endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. In dendrites and axons, it was associated with microtubules. Tryptophan hydroxylase in brain is only neuronal and cytoplasmic, exists in multiple forms, and is associated with microtubules, suggesting it may be transported from sites of synthesis in cell body into axons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks P., Mayor D., Tomlinson D. R. Further evidence for the involvement of microtubules in the intra-axonal movement of noradrenaline storage granules. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):755–761. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christenson J. G., Dairman W., Udenfriend S. Preparation and properties of a homogeneous aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase from hog kidney. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Sinha A. K., Barchas J. D. Biosynthesis of serotonin in Raphé nuclei of rat brain: effect of p-chlorophenylalanine. J Neurochem. 1973 May;20(5):1329–1336. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kappelman A. H., Kaufman S. Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4165–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Jonsson G. A modification of the histochemical fluorescence method for the improved localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Histochemie. 1967;11(2):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00571721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geffen L. B., Livett B. G. Synaptic vesicles in sympathetic neurons. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):98–157. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gál E. M., Roggeveen A. E., Millard S. A. DL-[2-14C]p-chlorophenylalanine as an inhibitor of tryptophan 5-hydroxylase. J Neurochem. 1970 Aug;17(8):1221–1235. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichiyama A., Nakamura S., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Enzymic studies on the biosynthesis of serotonin in mammalian brain. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1699–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrott B., Geffen L. B. Rapid axoplasmic transport of tyrosine hydroxylase in relation to other cytoplasmic constituents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3440–3442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jequier E., Robinson D. S., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Further studies on tryptophan hydroxylase in rat brainstem and beef pineal. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Geghman C., Reis D. Immunochemical demonstration of increased accumulation of tyrosine hydroxylase protein in sympathetic ganglia and adrenal medulla elicited by reserpine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2767–2771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Goldstein M. Isolation and characterization of multiple forms of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;9(1):117–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Different forms of tyrosine hydroxylase in central dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons and sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 21;85(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)91021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jéquier E., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Tryptophan hydroxylase inhibition: the mechanism by which p-chlorophenylalanine depletes rat brain serotonin. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 May;3(3):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp S., Mandell A. J. Parachlorophenylalanine--its three phase sequence of interactions with the two forms of brain tryptophan hydroxylase. Life Sci I. 1972 Aug 15;11(16):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(72)90210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koe B. K., Weissman A. p-Chlorophenylalanine: a specific depletor of brain serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Dec;154(3):499–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio J. M., Wurzburger R. J., D'Angelo G. L. Different molecular forms of bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;7(2):136–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Field P. M., Becker C. G., Reis D. J. Cellular localization of tyrosine hydroxylase by immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Jan;23(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/23.1.234988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Immunohistochemical localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in brain by light and electron microscopy. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 28;85(2):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J. Ultrastructural localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in noradrenergic neurons of brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger L. A., Hardy P. H., Jr, Cuculis J. J., Meyer H. G. The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry: preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 May;18(5):315–333. doi: 10.1177/18.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Otten U., Oesch F. Axoplasmic transport of enzymes involved in the synthesis of noradrenaline: relationship between the rate of transport and subcellular distribution. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):471–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90710-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerker R. B., Kirkpatrick J. B. Neuronal microtubules, neurofilaments, and microfilaments. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;33:45–75. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]