Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate the risk of recurrence in patients with intermediate-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) after intravesical instillation with chemotherapeutic agents or Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy. A cohort of 746 patients with intermediate-risk NMIBC comprised the study group. The primary outcome was time to first recurrence. The recurrence rates of the transurethral resection (TUR) alone, chemotherapy, and BCG groups were determined using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Risk factors for recurrence were identified using Cox regression analysis. In total, 507 patients (68.1%), 78 patients (10.5%), and 160 (21.4%) underwent TUR, TUR+BCG, or TUR+chemotherapy, respectively. After a median follow-up period of 51.7 months (interquartile range=33.1-77.8 months), 286 patients (38.5%) developed tumor recurrence. The 5-yr recurrence rates for the TUR, chemotherapy, and BCG groups were 53.6%±2.7%, 30.8%±5.7%, and 33.6%±4.7%, respectively (P<0.001). Chemotherapy and BCG treatment were found to be predictors of reduced recurrence. Cox-regression analysis showed that TUR+BCG did not differ from TUR+chemotherapy in terms of recurrence risk. Adjuvant intravesical instillation is an effective prophylactic that prevents tumor recurrence in intermediate-risk NMIBC patients following TUR. In addition, both chemotherapeutic agents and BCG demonstrate comparable efficacies for preventing recurrence.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Urinary Bladder Neoplasm, BCG Vaccine, Transurethral Resection, Chemotherapy
INTRODUCTION
Low-grade urothelial neoplasms demonstrate better clinical outcomes than high-grade tumors. Although these neoplasms rarely progress to fatal cancer, recurrence remains a major problem (1, 2). After transurethral resection (TUR), intravesical instillation of Bacillus Calmette Guérin (BCG) therapy is currently regarded as the most-effective available treatment for managing non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). The European Association of Urology (EAU) guidelines also propose using BCG to treat NMIBC (3, 4). Full-dose BCG with 1-yr maintenance dosing is recommended for intermediate-risk NMIBC patients because it is considered more effective than chemotherapy for preventing recurrence. However, BCG treatment demonstrates more adverse effects than chemotherapy, and its benefits relative to chemotherapy in terms of long-term outcomes remain unclear. For this reason, BCG with maintenance and intravesical chemotherapy both continue to be administered (4, 5). EAU produced new guidelines in 2013, and solitary TaG2 lesions were reclassified as intermediate-risk and T1G2 lesions were reclassified as high-risk (6). This reclassification reduced the risk level of intermediate-risk NMIBC in comparison to the risk level of intermediate-risk NMIBC, as defined by previous guidelines.
The present study was performed to determine if the type of adjuvant therapy following TUR (i.e., BCG vs. chemotherapy) affects long-term recurrence risk in patients with intermediate-risk NMIBC, as determined using 2013 EAU guidelines. Recurrence risk was also assessed in a subgroup of patients with multiple TaG2 tumors, which is a slightly higher-risk intermediate-risk NMIBC class that was evaluated in a recent randomized control trial (RCT) on the relative efficacies of different BCG schedules (7).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Patients with the following types of tumors were enrolled in this study: solitary, biopsy-proven, completely resected pTaG2 tumors; multiple/solitary, recurrent, and large (>3 cm) pTa tumors; or grade 1-2 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (according to the 1973 World Health Organization [WHO] classification). Exclusion criteria included the following: T1 tumors; G3 tumors; carcinoma in situ (CIS); multiple, recurrent, and large (>3 cm) TaG1-G2 tumors; primary, solitary, small (<3 cm) TaG1 tumors; ≥stage T2 tumors; age >85 yr; and concurrent or previous tumors in the upper urinary tract or prostatic urethra.
Study population and interventions
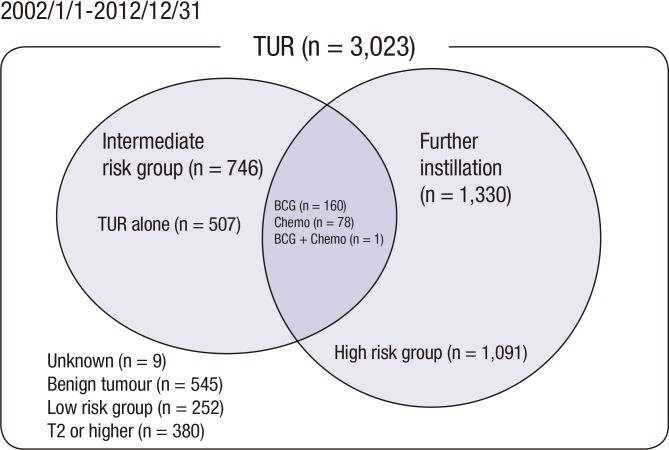
We obtained data on our NMIBC patients from our institutional database, which prospectively registers all baseline patient characteristics, tumor evaluations, detailed surgical information, and adjuvant therapy schedules after TUR. In total, 3,023 consecutive patients underwent TUR between 2002-2012. Of these, 746 had been diagnosed with intermediate-risk NMIBC, as defined by the 2013 EAU Guidelines. This group comprised the study cohort. Of these patients, 507 (68.1%) underwent TUR alone (designated as the TUR-alone group). The remaining 239 patients underwent adjuvant intravesical instillation with either BCG (n=160 [21.4% of the study cohort]; designated as the BCG group) or chemotherapeutic agents after TUR (n=78 [10.5% of the study cohort]; designated as the Chemo group). In the latter group, 61 and 17 patients received epirubicin and mitomycin C, respectively. A single patient who underwent both BCG and chemotherapy was excluded (Fig. 1). The BCG treatment regimen consisted of 5×108 colony forming units (CFU) BCG (Oncotice, Organon Teknika, Boxtel, The Netherlands), which was administered once-weekly for 6 consecutive weeks starting at 7-15 days after TUR. The Chemotherapy group received epirubicin (50 mg/50 mL) or mitomycin C (MMC) (40 mg/50 mL), which was administered once-weekly for 8 consecutive weeks starting at 7-15 days after TUR. BCG maintenance was not performed on any patient. Cystoscopy was repeated every 3 months for the first year, thereafter every 6 months. Recurrence was defined as histological evidence of recurrence, and all visible lesions were resected.
Fig. 1.
Diagram of the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT). Risk stratification was determined according to the 2013 EAU guidelines. Benign tumors included inverted papilloma, polypoid cytitis, urothelial atypia, follicular cytitis, cystitis cystica, nephrogenic adenoma, cystitis glandularis, eosinophilic cystitis, and focal intestinal metaplasia.
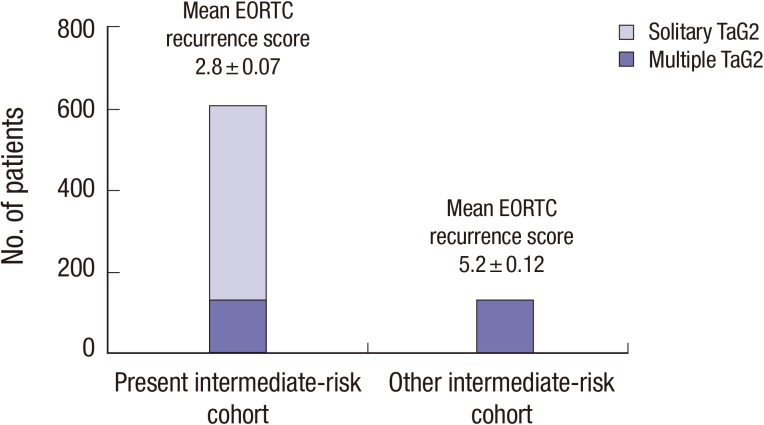
To evaluate any changes in the risk of recurrence in the intermediate-risk NMIBC cohort caused by the introduction of the 2013 EAU guidelines, the entire study group (which consisted of patients with solitary and multiple TaG2 tumors) was compared with a subgroup of patients with multiple tumors who are classified as a slightly higher-risk intermediate-risk NMIBC class (this group was evaluated in a recent RCT on the relative efficacies of BCG maintenance) (Fig. 2) (7).
Fig. 2.
The study group consisted of patients with solitary or multiple TaG2 tumors. To assess the effects of different stratification strategies on the efficacy of BCG vs. chemotherapy, only the subgroup of patients with multiple TaG2 tumors was examined. These groups significantly differed in terms of mean recurrence scores according to the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) (P < 0.001), which indicates that the multiple TaG2 subgroup was at higher risk of tumor recurrence than the overall study cohort.
Study endpoints
The primary study endpoint was time to first recurrence. This included progression to muscle-invasive disease, distant metastasis, and death due to bladder cancer.
Statistical analyses
Categorical variables are presented as frequencies and percentages, and groups were compared using the chi-square test. Continuous variables are presented as the mean±standard deviation (SD) or median with range, and groups were compared using ANOVA or the Kruskal-Wallis test, as appropriate. Time to first recurrence was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Independent predictors of tumor recurrence were determined using Cox regression modeling. All reported P values are two-sided, and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. SAS (version 9.1; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and SPSS (version 21; IBM Corporation, Somers, NY, USA) were used to perform all statistical analyses.
Ethics statement
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee/review board of Asan Medical Center (2014-0235). Informed consent was waived by the board.
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics of the study group
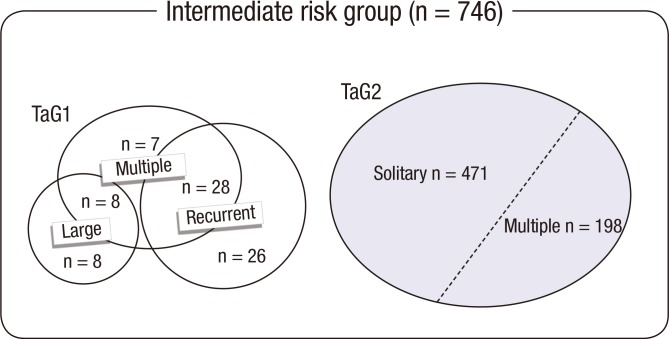
The mean age of the NMIBC study cohort at surgery was 62.1±11.8 yr, and 608 patients (81.1%) were men. All tumors were classified as Ta stage: 10.2% were G1 tumors; 17.2% were recurrent tumors; and 67.8% were single tumors. The cohort consisted of patients with multiple TaG1 tumors (43 patients; 5.8%), large TaG1 tumors (16 patients; 2.1%), recurrent TaG1 tumors (54 patients; 7.2%), solitary TaG2 tumors (471 patients; 63.1%), and multiple TaG2 tumors (198 patients; 26.5%) (Fig. 3). Second resections were performed on 16 patients (2.1%). Immediate instillation was performed on 20 patients (2.7%). Prior instillation had been performed on 76 patients (10.2%). Table 1 summarizes the baseline demographics of the patient cohort. The TUR-alone, BCG, and Chemotherapy subgroups did not significantly differ in terms of sex, smoking status, recurrent lesions, morphology, second resection, immediate chemotherapy, or tumor size. However, the patients in the TUR-alone and BCG groups were older than the patients in the Chemo group. The BCG group was more likely to have multifocal lesions than the Chemo and TUR-alone groups, while the TUR-alone group was more likely to have G1 tumors than the BCG and Chemo groups. Patients who underwent BCG demonstrated higher European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) recurrence scores than patients who underwent chemotherapy or TUR-alone. However, these 3 groups did not significantly differ in terms of EORTC progression scores.
Fig. 3.
Composition of the study group. Patients had multiple TaG1 tumors (43 patients; 5.8%), large TaG1 tumors (16 patients; 2.1%), recurrent TaG1 tumors (54 patients; 7.2%), solitary TaG2 tumors (471 patients; 63.1%), or multiple TaG2 tumors (198 patients; 26.5%). Patients with large TaG2 tumors (106 patients; 14.2%) and recurrent TaG2 tumors (129 patients; 17.3%) are not shown because the solitary and multiple TaG2 tumor categories include all TaG2 tumors.
Table 1.
Demographic and tumor characteristics
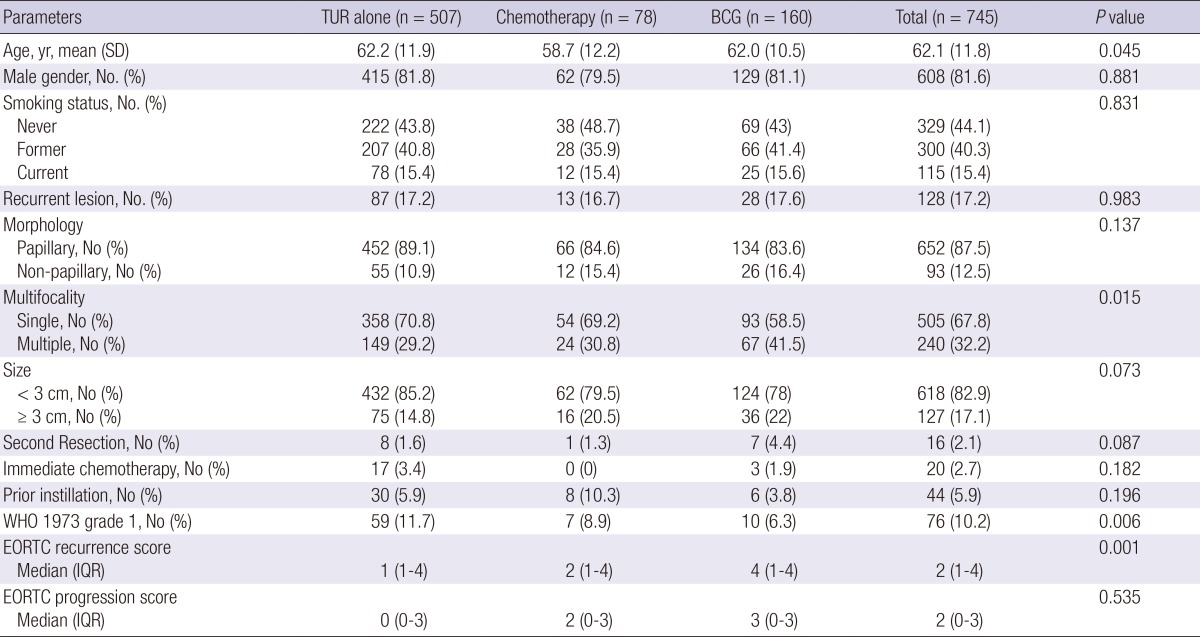
SD, standard deviation; WHO, world health organization; EORTC, European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer; IQR, interquartile range.
Follow-up, tumor recurrence, and progression in the study group
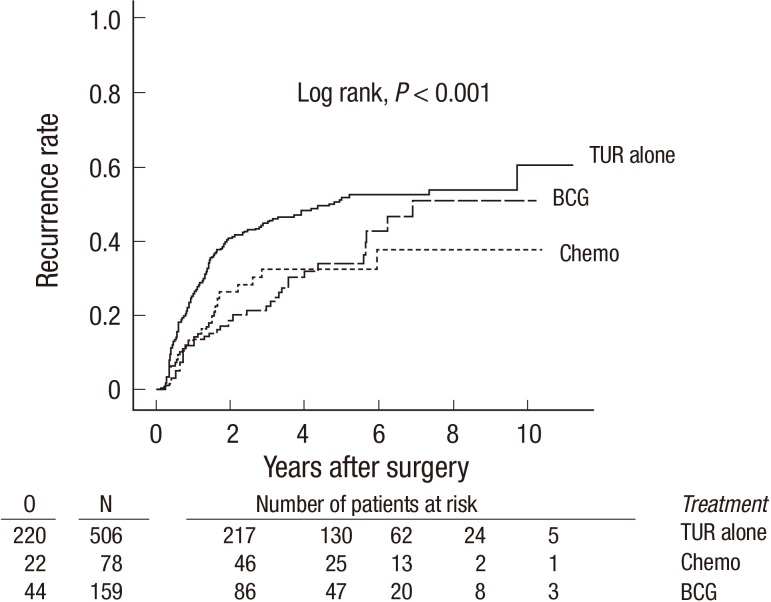
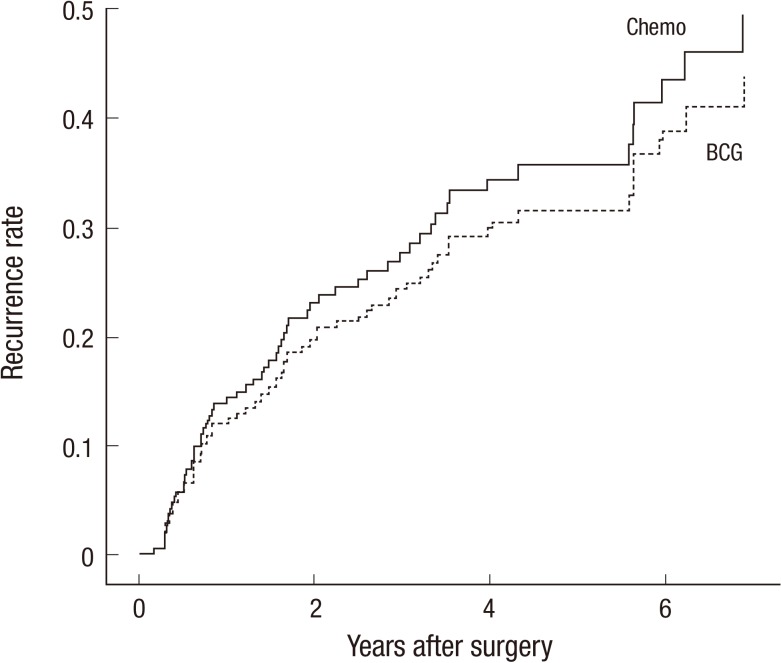
The median follow-up period was 51.7 months (interquartile range=33.1-77.8 months). The 5-yr recurrence rates of the BCG, Chemotherapy, and TUR-alone groups were 33.6%±4.7%, 30.8% ±5.7%, and 53.6%±2.7%, respectively (P<0.001; Fig. 4). The 5-yr recurrence rates for MMC and epirubicin were 30.2%±13.1% and 31.6%±6.9%, respectively (P=0.78). Tumor progression was noted in 4 patients who underwent TUR alone and 2 patients in the BCG group. Treatment interruption for toxicity was only required in 4 patients in the BCG group: 3 patients developed fever, and 1 patient developed hematuria.
Fig. 4.
Unadjusted Kaplan-Meier estimates of the recurrence rates of various study groups. Chemo, chemotherapy; BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; O, observed number of events; N, number of patients.
Predictors of tumor recurrence in the study group
Multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that significant and independent predictors of tumor recurrence include adjuvant treatment (chemotherapy vs. none; HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.36-0.89; P=0.013) (BCG vs. none; HR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.31-0.62; P<0.001), age (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, 1.01-1.98; P<0.001), morphology (HR, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.00-1.98; P=0.013), multiplicity (HR, 1.50; 95% CI, 1.15-2.00; P=0.003), size (HR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.78-3.29; P<0.001), and recurrent lesions at baseline (HR, 2.55; 95% CI, 1.80-3.61; P<0.001) (Table 2). However, none of the following variables were predictive of recurrence: second resection (yes vs. no; HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 0.72-2.95; P=0.29), immediate instillation (yes vs. no; HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.12-2.02; P=0.33), or prior instillation (yes vs. no; HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 0.14-2.52; P=0.93).
Table 2.
Predictors of tumor recurrence determined using multivariate Cox proportional-hazards modeling
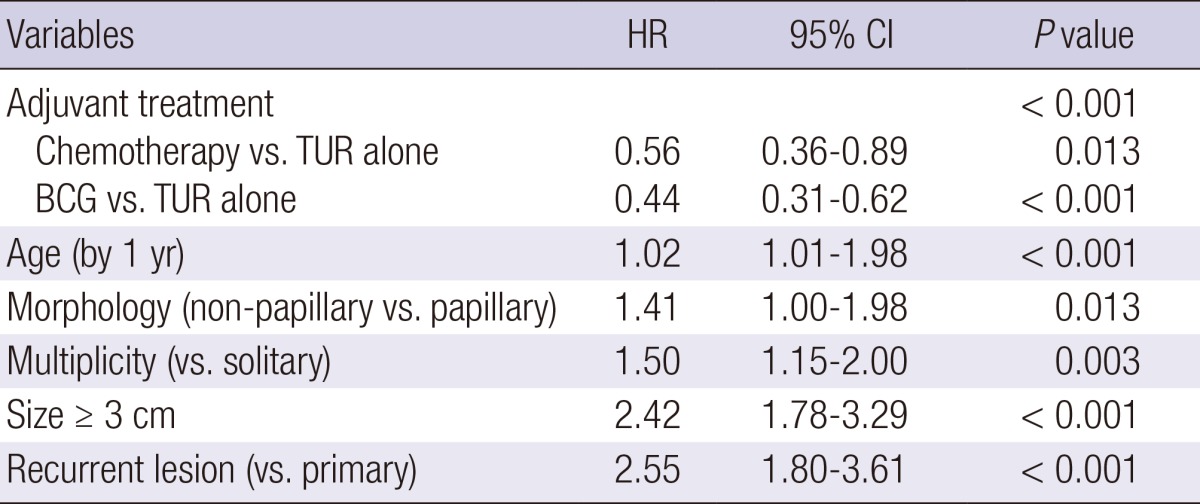
Variables with P<0.20 in univariate models were candidates for multivariate model. Multivariate analyses involved stepwise backward-elimination procedure, and only those with P<0.10 were used in the final model. HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; TUR, transurethral resection; BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin.
Comparison of BCG and chemotherapy in terms of recurrence risk in the study group
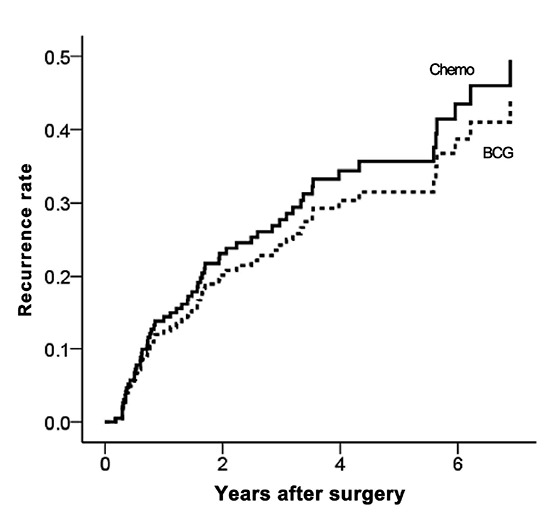
Our Cox regression analysis showed that the BCG group demonstrated a similar risk of recurrence as the Chemotherapy group (HR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.45-1.32; P=0.35) (Table 3; Fig. 5). Similar results were obtained using propensity score-adjusted Cox-regression analysis (HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.50-1.49; P=0.58).
Table 3.
Hazard ratios (HRs) for tumor recurrence in patients who received adjuvant therapy and chemotherapy or BCG
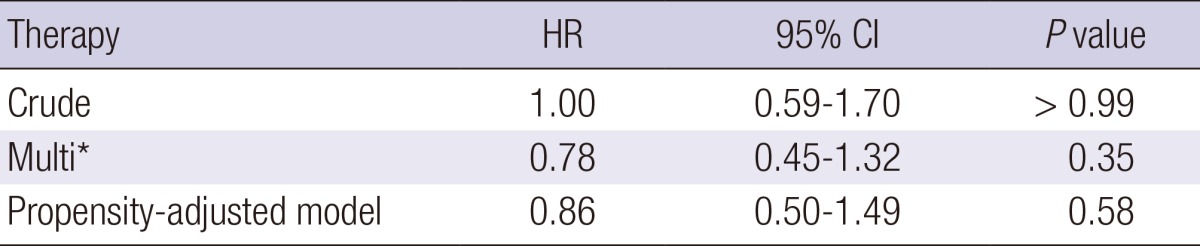
*Multivariate analyses incorporated significant covariates influencing tumor recurrence including age, tumor morphology (non-papillary vs. papillary), multiplicity (vs. solitary), tumor size (≥3 cm vs. <3 cm), and recurrent lesion (vs. primary tumor). BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; CI, confidence interval.
Fig. 5.
Comparison of BCG vs. chemotherapy in terms of reducing recurrence in the study group. Cox regression analysis: hazard ratio (HR), 0.78; 95% confidence intervals (CI), 0.45-1.32; P = 0.35. Propensity score-adjusted Cox-regression analysis: HR, 0.86; 95% CI, 0.50-1.49; P = 0.58.
Comparison of BCG and chemotherapy in terms of recurrence risk in patients with solitary and multiple TaG2 tumors
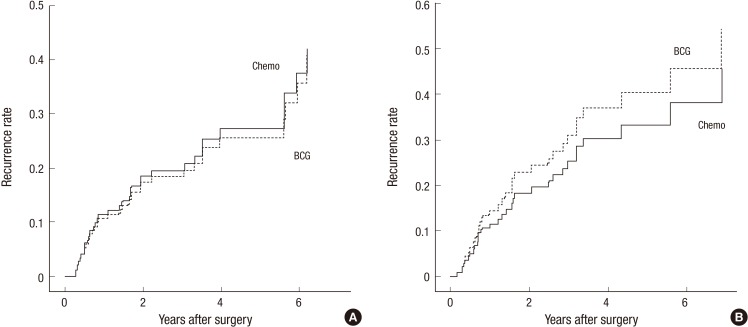
The multiple TaG2 tumor subgroup (which represents the NMIBC group included in a recent RCT that compared BCG and chemotherapy) demonstrated a significantly higher mean EORTC recurrence score than present study group (P<0.001) (Fig. 2). When the subgroup was assessed using Cox regression analysis, chemotherapy tended to be superior to BCG (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 0.60-3.66). However, this difference was not statistically significant (P=0.28) (Fig. 6). This tendency was also determined using propensity score-adjusted Cox-regression analysis (HR, 1.32; 95% CI, 0.54-3.49; P=0.45). The solitary TaG2 tumor subgroup was also assessed using Cox regression analysis, and chemotherapy and BCG demonstrated equally reduced recurrence in intermediate-risk NMIBC patients (HR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.45-1.95; P=0.85).
Fig. 6.
Comparison of BCG vs. chemotherapy in terms of reducing recurrence in the (A) solitary and (B) multiple TaG2 tumor subgroups. Cox-regression analysis: hazard ratio (HR), 0.93; 95% confidence intervals (CI), 0.45-1.95; P = 0.85 (solitary TaG2). Cox regression analysis: HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 0.60-3.66; P = 0.28 (multiple TaG2). Chemo, chemotherapy; BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin.
DISCUSSION
The NMIBC classification - specifically, Ta/T1/CIS stage tumors - represents a heterogeneous group of tumors with varying oncological outcomes. Therefore, to determine the appropriate management strategy for these cancers, it is important to stratify patients according to their risks of recurrence and progression (8). However, intermediate-risk patients are especially complex, and the most appropriate management strategy remains unclear. Several guidelines were published before 2010 (5) that report adjuvant therapy as a viable choice for managing patients with intermediate-risk NMIBC. However, it still remains unclear if BCG followed by maintenance is superior to chemotherapy in intermediate-risk patients. Initially, several meta analyses suggested that BCG after TUR is superior to both TUR alone and chemotherapy after TUR in terms of preventing tumor recurrence (9, 10, 11). Other studies also indicate that maintenance BCG prevents, or at least delays, the risk of tumor progression (12, 13, 14). However, in these studies, the distinction between intermediate- and high-risk groups was unclear, and patients with T1 tumors were included in the intermediate-risk group. Subsequently, a recent individual patient data meta-analysis that compared the efficacy of BCG versus mitomycin C could not confirm the superiority of BCG over chemotherapy (15).
New EAU guidelines on bladder cancer were presented in 2013. These guidelines are based on research on the diagnosis and treatment of NMIBC that were published between 2010-2012 (6), and they differ somewhat from former guidelines in terms of risk stratification and treatment recommendations. In particular, solitary TaG2 lesions are now considered intermediate-risk (not low-risk), while T1G2 lesions are now considered high risk (not intermediate risk). However, when the 2013 guidelines were produced, it remained unclear if BCG is considered superior to chemotherapy for intermediate-risk NMIBC, and thus both treatments continue to be recommended as viable adjuvant therapies for intermediate-risk NMIBC patients.
A RCT performed by EORTC on the relative efficacies of BCG maintenance was also recently published. This study included 1,355 patients, and its results suggest that intermediate-risk patients should receive full-dose BCG for 1 yr. Although this study did include patients in the intermediate-risk group who had with multiple TaG2 tumors (as required by the 2013 EAU guidelines), most patients with solitary TaG2 tumors were not included in this group (7). This suggests that the intermediate-risk cohort of this RCT was at a higher inherent risk of tumor recurrence than if it had been strictly selected according to the 2013 EAU guidelines. In turn, this suggests that this RCT cannot be used to inform treatment decisions for patients who meet the 2013 criteria for intermediate-risk NMIBC.
The present study was performed to determine if BCG and chemotherapy demonstrate similar efficacies in intermediate-risk NMIBC patients, as strictly defined by the current EAU guidelines. A total of 746 consecutive patients were identified. Of these, 507 patients did not receive intravesical instillation, probably because they were previously categorized as low-risk (these patients served as the controls). We found that chemotherapeutic agents and BCG demonstrated comparable efficacies in terms of preventing recurrence in the study cohort. We then analyzed the relative efficacies of the adjuvant treatments in the subgroup of patients with multiple TaG2 tumors, which resembled the group analyzed as part of the recently published RCT. The EORTC recurrence scores clearly indicate that this subgroup was at higher risk than the rest of the study cohort (Fig. 2). Chemotherapy tended to be superior to BCG in the multiple TaG2 subgroup, although this difference was not statistically significant (Fig. 6). These observations support the notion that the stratification strategy can markedly influence the results of studies on the relative efficacy of BCG and chemotherapy. However, it should be emphasized that our study had a relatively small sample size and there may have been selection bias, which could have interfered with the results. Moreover, we did not perform BCG maintenance on any patient, which may have reduced the overall efficacy of BCG.
Although our cohort did not receive BCG maintenance, the recurrence rate was not higher than expected: the 5-yr recurrence rates in the BCG and Chemotherapy groups were 33.6%±4.7% and 30.8%±5.7%, respectively. Moreover, progression was only noted in 6 patients (0.8%). This improvement in the recurrence rates may be due to advances in TUR techniques. One study examined recurrence rates over a 10-yr period and reported that the use of better endoscopes and more meticulous TUR techniques reduced the recurrence rate, although the TUR procedure was not described (16). Notably, several studies also report that restaging TUR at the time of NMIBC presentation can significantly reduce recurrence (17, 18). However, because restaging TUR is not essential for treating intermediate-risk patients, only a few patients in our institute have undergone this procedure.
Our current study was subjected to the limitations inherent to any retrospective analysis of observational data. The decision to select adjuvant treatment after TUR was driven by the patient's perioperative condition and physician preference. Although we used propensity score analysis to adjust for selection biases, it remains possible that unmeasured confounders, procedural bias, and detection bias may have affected our results.
Large meta-analyses of RTCs have already reported that intravesical instillation after TUR reduces recurrence in NMIBC patients (12, 13, 14, 15). However, heterogeneous cohorts of NMIBC patients should be strictly subdivided according to risk intensity because the treatment results can be influenced by risk stratification. Accordingly, our present study shows that chemotherapy and BCG equally reduced recurrence in intermediate-risk NMIBC patients, whereas several recent RCT studies on a slightly higher-risk cohort reported that BCG is superior to chemotherapy. This discrepancy indicates that further prospective randomized trials are warranted in order to determine which therapeutic regimens are optimal.
Footnotes
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Conception and coordination of the study: Han KS, You D, Kim CS. Design of ethical issues: Jeong IG, Kwon T, Hong B, Hong JH. Acquisition of data: Han KS, Kim CS. Data review: Han KS, You D, Ahn H, Ahn TY. Statistical analysis: Han KS. Manuscript preparation: Han KS, You D, Kim CS. Manuscript approval: all authors
References
- 1.Oosterlinck W, Solsona E, Akaza H, Busch C, Goebell PJ, Malmstrom PU, Ozen H, Sved P. Low-grade Ta (noninvasive) urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 2005;66:75–89. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.07.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Holmang S, Johansson SL. Stage Ta-T1 bladder cancer: the relationship between findings at first followup cystoscopy and subsequent recurrence and progression. J Urol. 2002;167:1634–1637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP, Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW, Kurth K. Predicting recurrence and progression in individual patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: a combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur Urol. 2006;49:466–465. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.12.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R, Kaasinen E, Böhle A, Palou-Redorta J, Rouprêt M European Association of Urology (EAU) EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, the 2011 update. Eur Urol. 2011;59:997–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brausi M, Witjes JA, Lamm D, Persad R, Palou J, Colombel M, Buckley R, Soloway M, Akaza H, Böhle A. A review of current guidelines and best practice recommendations for the management of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer by the International Bladder Cancer Group. J Urol. 2011;186:2158–2167. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Babjuk M, Burger M, Zigeuner R, Shariat SF, van Rhijn BW, Compérat E, Sylvester RJ, Kaasinen E, Bohle A, Palou Redorta J, et al. European Association of Urology. EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: update 2013. Eur Urol. 2013;64:639–653. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Oddens J, Brausi M, Sylvester R, Bono A, van de Beek C, van Andel G, Gontero P, Hoeltl W, Turkeri L, Marreaud S, et al. Final results of an EORTC-GU cancers group randomized study of maintenance bacillus Calmette-Guerin in intermediate- and high-risk Ta, T1 papillary carcinoma of the urinary bladder: one-third dose versus full dose and 1 year versus 3 years of maintenance. Eur Urol. 2013;63:462–472. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.10.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Witjes JA, Palou J, Soloway M, Lamm D, Kamat AM, Brausi M, Persad R, Buckley R, Colombel M, Böhle A. Current clinical practice gaps in the treatment of intermediate- and high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) with emphasis on the use of bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG): results of an international individual patient data survey (IPDS) BJU Int. 2013;112:742–750. doi: 10.1111/bju.12012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Shelley MD, Kynaston H, Court J, Wilt TJ, Coles B, Burgon K, Mason MD. A systematic review of intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin plus transurethral resection vs transurethral resection alone in Ta and T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2001;88:209–216. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Han RF, Pan JG. Can intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduce recurrence in patients with superficial bladder cancer? A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Urology. 2006;67:1216–1223. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Böhle A, Jocham D, Bock PR. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C for superficial bladder cancer: a formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on recurrence and toxicity. J Urol. 2003;169:90–95. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sylvester RJ, van der MEIJDEN AP, Lamm DL. Intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin reduces the risk of progression in patients with superficial bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of the published results of randomized clinical trials. J Urol. 2002;168:1964–1970. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Böhle A, Bock PR. Intravesical bacille Calmette-Guerin versus mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer: formal meta-analysis of comparative studies on tumor progression. Urology. 2004;63:682–686. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2003.11.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sylvester RJ, Brausi MA, Kirkels WJ, Hoeltl W, Calais Da Silva F, Powell PH, Prescott S, Kirkali Z, van de Beek C, Gorlia T, et al. EORTC Genito-Urinary Tract Cancer Group. Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guerin, and bacillus Calmette-Guerin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol. 2010;57:766–773. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.12.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Malmstrom PU, Sylvester RJ, Crawford DE, Friedrich M, Krege S, Rintala E, Solsona E, Di Stasi SM, Witjes JA. An individual patient data meta-analysis of the long-term outcome of randomised studies comparing intravesical mitomycin C versus bacillus Calmette-Guerin for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2009;56:247–256. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.04.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zabora J, BrintzenhofeSzoc K, Curbow B, Hooker C, Piantadosi S. The prevalence of psychological distress by cancer site. Psychooncology. 2001;10:19–28. doi: 10.1002/1099-1611(200101/02)10:1<19::aid-pon501>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grimm MO, Steinhoff C, Simon X, Spiegelhalder P, Ackermann R, Vogeli TA. Effect of routine repeat transurethral resection for superficial bladder cancer: a long-term observational study. J Urol. 2003;170:433–437. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000070437.14275.e0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Schwaibold HE, Sivalingam S, May F, Hartung R. The value of a second transurethral resection for T1 bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2006;97:1199–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]