Abstract
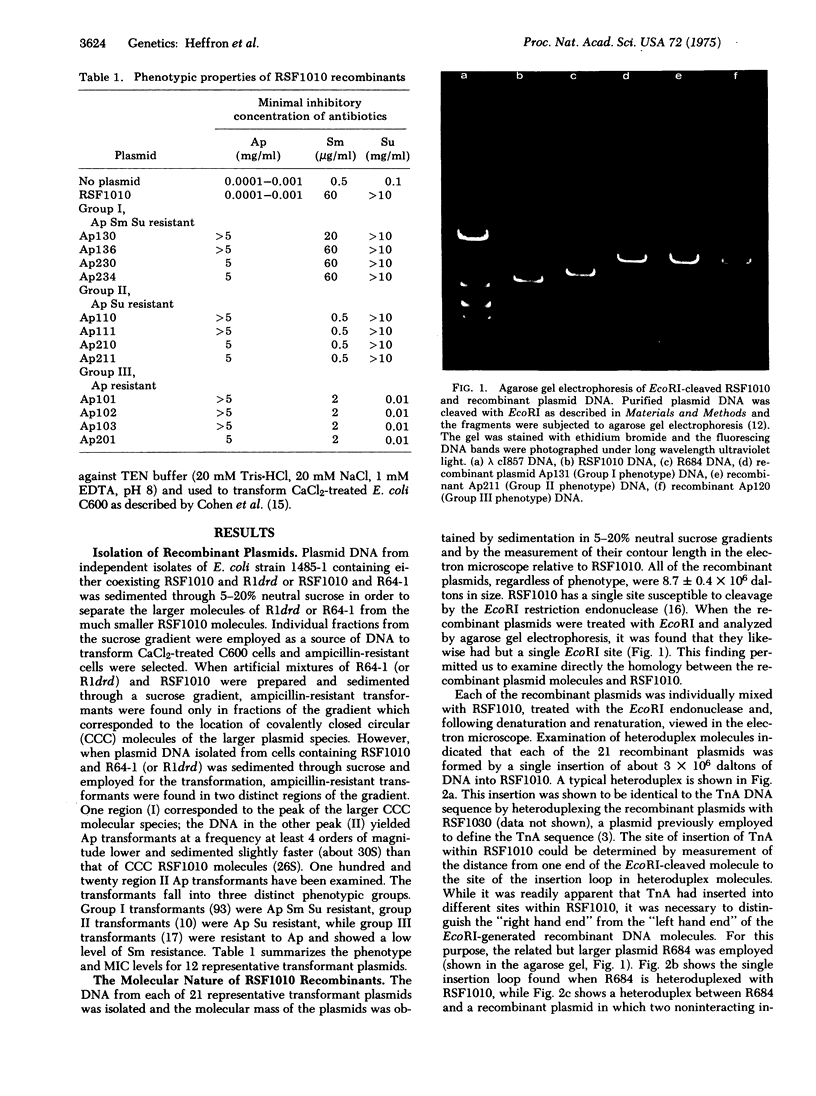
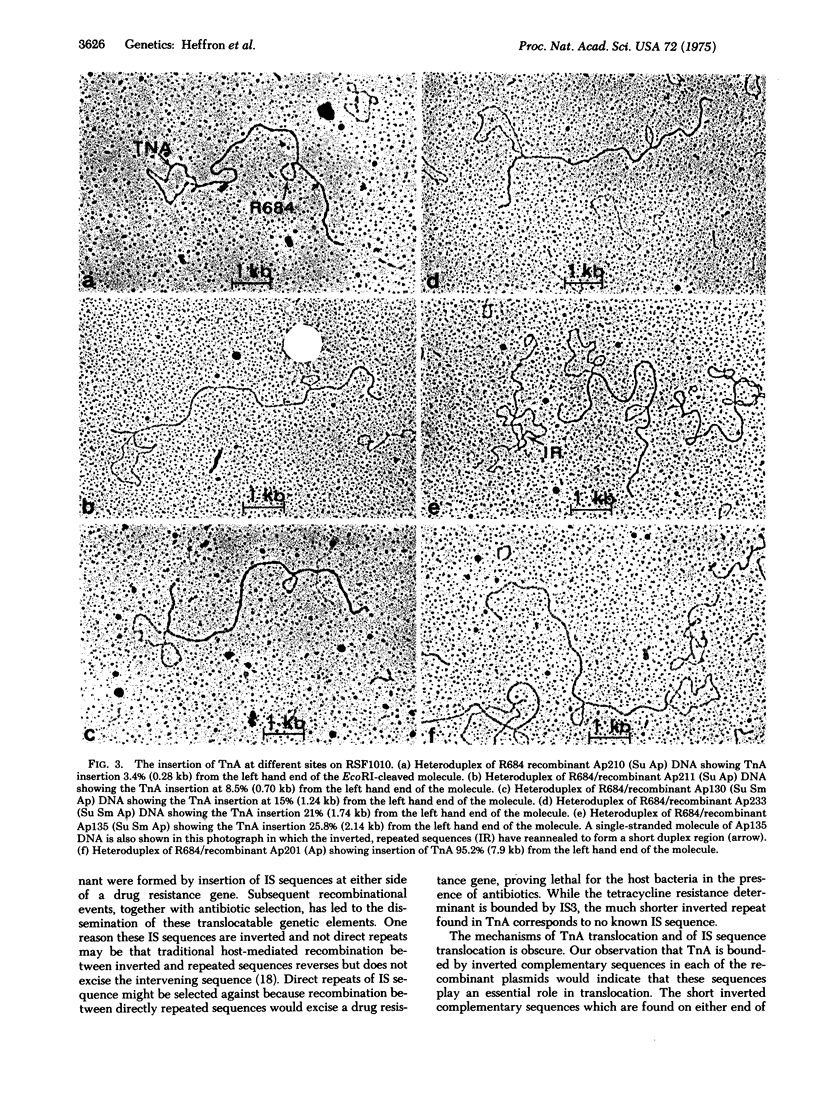
A series of recombinant plasmids was generated in Escherichia coli in which the TEM beta-lactamase translocon (TnA) was inserted into the small plasmid RSF1010. RSF1010 is a 5.5 X 10(6) dalton nonconjugative plasmid which confers resistance to streptomycin and sulfonamide. The recombinant plasmids can be classified into three clearly defined phenotypic groups. Group I is ampicillin-, streptomycin- and sulfonamide-resistant. Group II is ampicillin- and sulfonamide-resistant but has lost streptomycin resistance. Group III is ampicillin-resistant but is sensitive to sulfonamide and shows a simultaneous 30-fold reduction in the minimal inhibitory concentration of streptomycin. It was possible to map the site of insertion of TnA within RSF1010 by electron microscope studies of DNA heteroduplexes formed between RSF1010 and recombinant plasmids. Insertions of TnA occur at, at least, 12 distinct sites in a region corresponding to one-third of the RSF1010 DNA molecule. Those insertions giving rise to particular phenotypes are clustered. Insertions of TnA-like insertion sequences (IS) appear to give rise to strongly polar mutations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J. Comparison of the deoxyribonucleic acid molecular weights and homologies of plasmids conferring linked resistance to streptomycin and sulfonamides. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):618–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.618-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzee J. N., Datta N., Hedges R. W. R factors from Proteus rettgeri. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):543–552. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S., Guerry P., Hedges R. W., Datta N. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among plasmids of the I compatibility complex. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Nov;85(1):65–76. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Maxam A. The nucleotide sequence of the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among some bacterial plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):372–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.372-374.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., van Embden J., Falkow S. Molecular nature of two nonconjugative plasmids carrying drug resistance genes. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.619-630.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N., Kontomichalou P., Smith J. T. Molecular specificities of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.56-62.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E. Transposition of ampicillin resistance from RP4 to other replicons. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(1):31–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00268228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffron F., Sublett R., Hedges R. W., Jacob A., Falkow S. Origin of the TEM-beta-lactamase gene found on plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):250–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.250-256.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex study of the heterogeneity of Mu phage and prophage DNA. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Smith H. O. A restriction enzyme from Hemophilus influenzae. II. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):393–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecko D. J., Cohen S. N. Site specific recA--independent recombination between bacterial plasmids: involvement of palindromes at the recombinational loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1373–1377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupersztoch Y. M., Helinski D. R. A catenated DNA molecule as an intermediate in the replication of the resistance transfer factor R6K in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 15;54(4):1451–1459. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. Deletion mutants of simian virus 40 generated by enzymatic excision of DNA segments from the viral genome. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne K., Cohen S. N. Occurrence of insertion sequence (IS) regions on plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid as direct and inverted nucleotide sequence duplications. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):776–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.776-781.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P., Saedler H. Insertion mutations in microorganisms. Biochimie. 1972;54(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Weisblum B. Construction of a colicin E1-R factor composite plasmid in vitro: means for amplification of deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):354–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.354-362.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]