Abstract
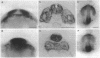
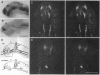
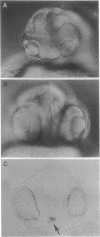
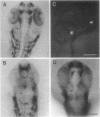
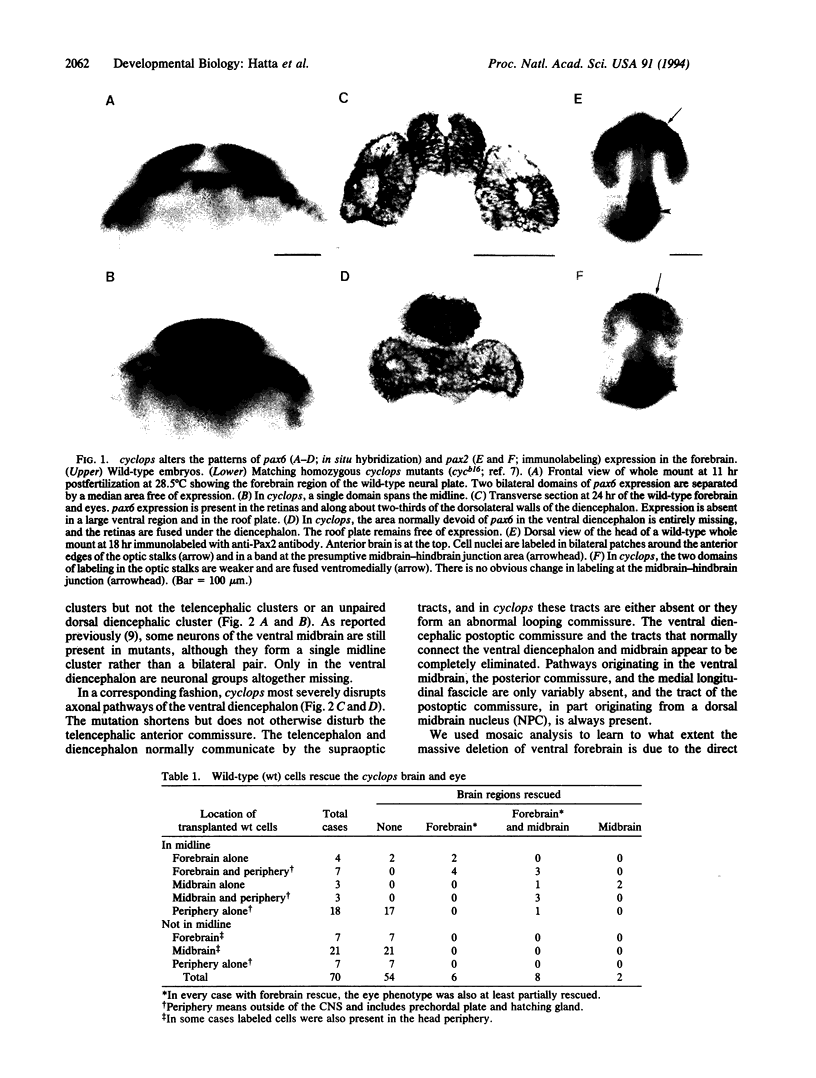
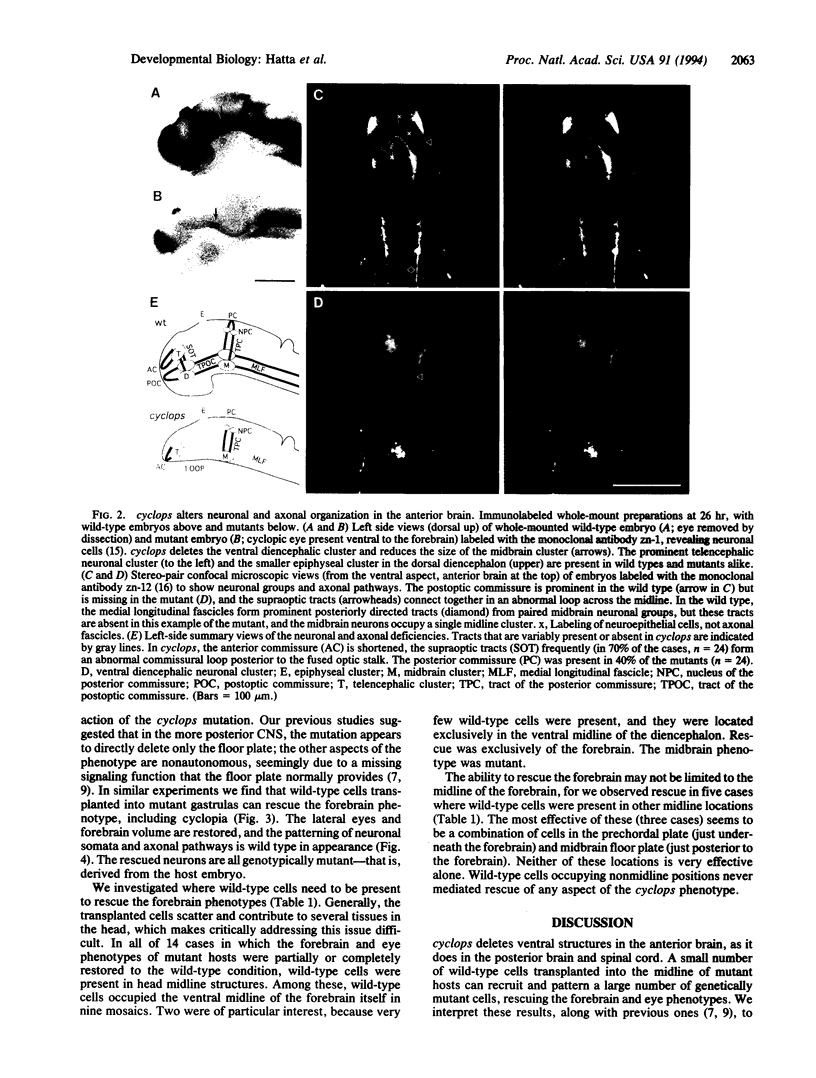
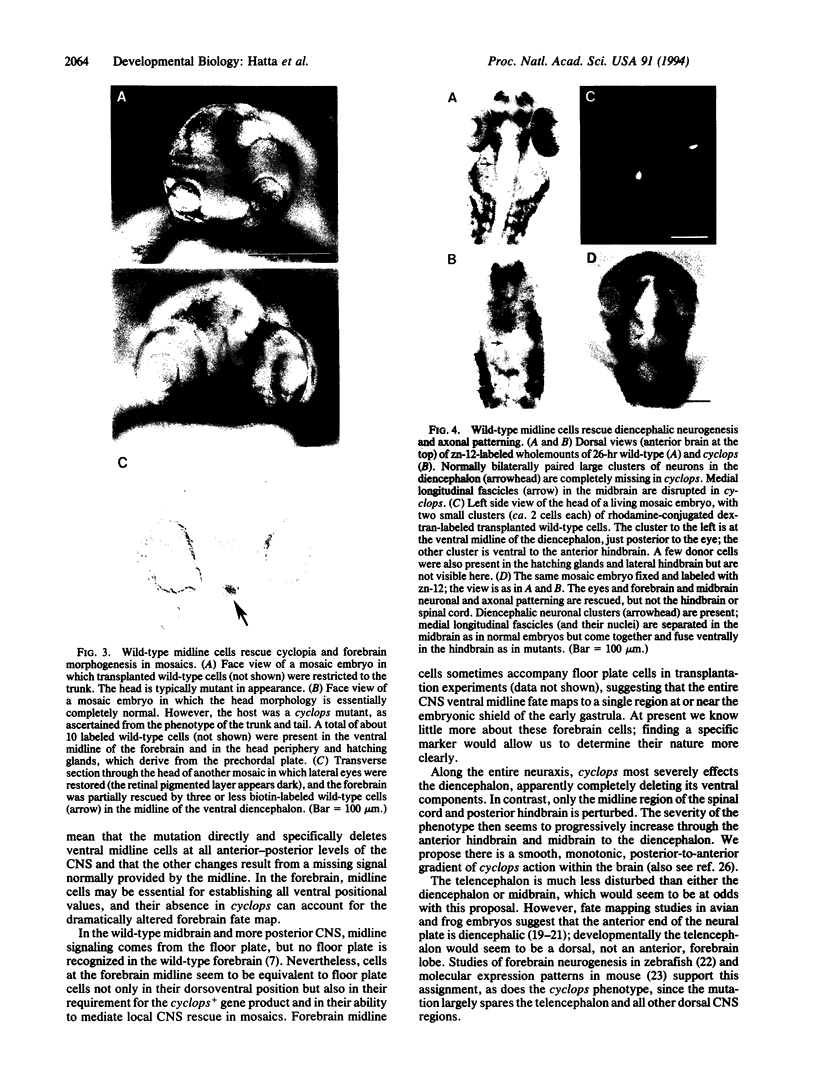
In all vertebrates the brain develops from the enlarged anterior part of the neural plate. However, in the zebrafish mutant cyclops, the girth of the central nervous system (CNS) is nearly uniform along its length. Changes in expression patterns of homeobox genes and neuronal markers reveal a massive deletion of the ventral forebrain, particularly the diencephalon, as well as its precursor region in the neural plate. The deletion is due to a nonautonomous action of the mutation: very few wild-type cells transplanted to the midline of a mutant embryo can rescue the forebrain phenotype, including cyclopia. Establishment of forebrain ventral positional coordinates may thus require inductive signaling by forebrain midline cells whose specification depends upon the cyclops gene product.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernhardt R. R., Patel C. K., Wilson S. W., Kuwada J. Y. Axonal trajectories and distribution of GABAergic spinal neurons in wildtype and mutant zebrafish lacking floor plate cells. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Dec 8;326(2):263–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.903260208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfone A., Puelles L., Porteus M. H., Frohman M. A., Martin G. R., Rubenstein J. L. Spatially restricted expression of Dlx-1, Dlx-2 (Tes-1), Gbx-2, and Wnt-3 in the embryonic day 12.5 mouse forebrain defines potential transverse and longitudinal segmental boundaries. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):3155–3172. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-03155.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitnis A. B., Kuwada J. Y. Axonogenesis in the brain of zebrafish embryos. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1892–1905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01892.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couly G., Le Douarin N. M. The fate map of the cephalic neural primordium at the presomitic to the 3-somite stage in the avian embryo. Development. 1988;103 (Suppl):101–113. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.Supplement.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagleson G. W., Harris W. A. Mapping of the presumptive brain regions in the neural plate of Xenopus laevis. J Neurobiol. 1990 Apr;21(3):427–440. doi: 10.1002/neu.480210305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson J., Thor S., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Yamada T. Early stages of motor neuron differentiation revealed by expression of homeobox gene Islet-1. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1555–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.1350865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gans C., Northcutt R. G. Neural crest and the origin of vertebrates: a new head. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):268–273. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4594.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanneman E., Trevarrow B., Metcalfe W. K., Kimmel C. B., Westerfield M. Segmental pattern of development of the hindbrain and spinal cord of the zebrafish embryo. Development. 1988 May;103(1):49–58. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K., Kimmel C. B., Ho R. K., Walker C. The cyclops mutation blocks specification of the floor plate of the zebrafish central nervous system. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):339–341. doi: 10.1038/350339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K., Kimmel C. B. Midline structures and central nervous system coordinates in zebrafish. Perspect Dev Neurobiol. 1993;1(4):257–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatta K. Role of the floor plate in axonal patterning in the zebrafish CNS. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):629–642. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Fuse S., Sohal G. S. The effect of the floor plate on pattern and polarity in the developing central nervous system. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):310–313. doi: 10.1126/science.1987648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Johansen T., Korzh V., Fjose A. Expression of the zebrafish paired box gene pax[zf-b] during early neurogenesis. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1193–1206. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Johansen T., Korzh V., Fjose A. Expression pattern of zebrafish pax genes suggests a role in early brain regionalization. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):267–270. doi: 10.1038/353267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss S., Johansen T., Korzh V., Moens U., Ericson J. U., Fjose A. Zebrafish pax[zf-a]: a paired box-containing gene expressed in the neural tube. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3609–3619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe W. K., Myers P. Z., Trevarrow B., Bass M. B., Kimmel C. B. Primary neurons that express the L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate during early development in the zebrafish. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):491–504. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Placzek M., Tessier-Lavigne M., Yamada T., Jessell T., Dodd J. Mesodermal control of neural cell identity: floor plate induction by the notochord. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):985–988. doi: 10.1126/science.2237443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puelles L., Domenech-Ratto G., Martinez-de-la-Torre M. Location of the rostral end of the longitudinal brain axis: review of an old topic in the light of marking experiments on the closing rostral neuropore. J Morphol. 1987 Nov;194(2):163–171. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051940205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püschel A. W., Gruss P., Westerfield M. Sequence and expression pattern of pax-6 are highly conserved between zebrafish and mice. Development. 1992 Mar;114(3):643–651. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püschel A. W., Westerfield M., Dressler G. R. Comparative analysis of Pax-2 protein distributions during neurulation in mice and zebrafish. Mech Dev. 1992 Sep;38(3):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90053-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. S., Parrett T., Easter S. S., Jr Axonogenesis and morphogenesis in the embryonic zebrafish brain. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):467–482. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00467.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. W., Ross L. S., Parrett T., Easter S. S., Jr The development of a simple scaffold of axon tracts in the brain of the embryonic zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. Development. 1990 Jan;108(1):121–145. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.1.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Placzek M., Tanaka H., Dodd J., Jessell T. M. Control of cell pattern in the developing nervous system: polarizing activity of the floor plate and notochord. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90247-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Straaten H. W., Hekking J. W., Wiertz-Hoessels E. J., Thors F., Drukker J. Effect of the notochord on the differentiation of a floor plate area in the neural tube of the chick embryo. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1988;177(4):317–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00315839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]