Abstract
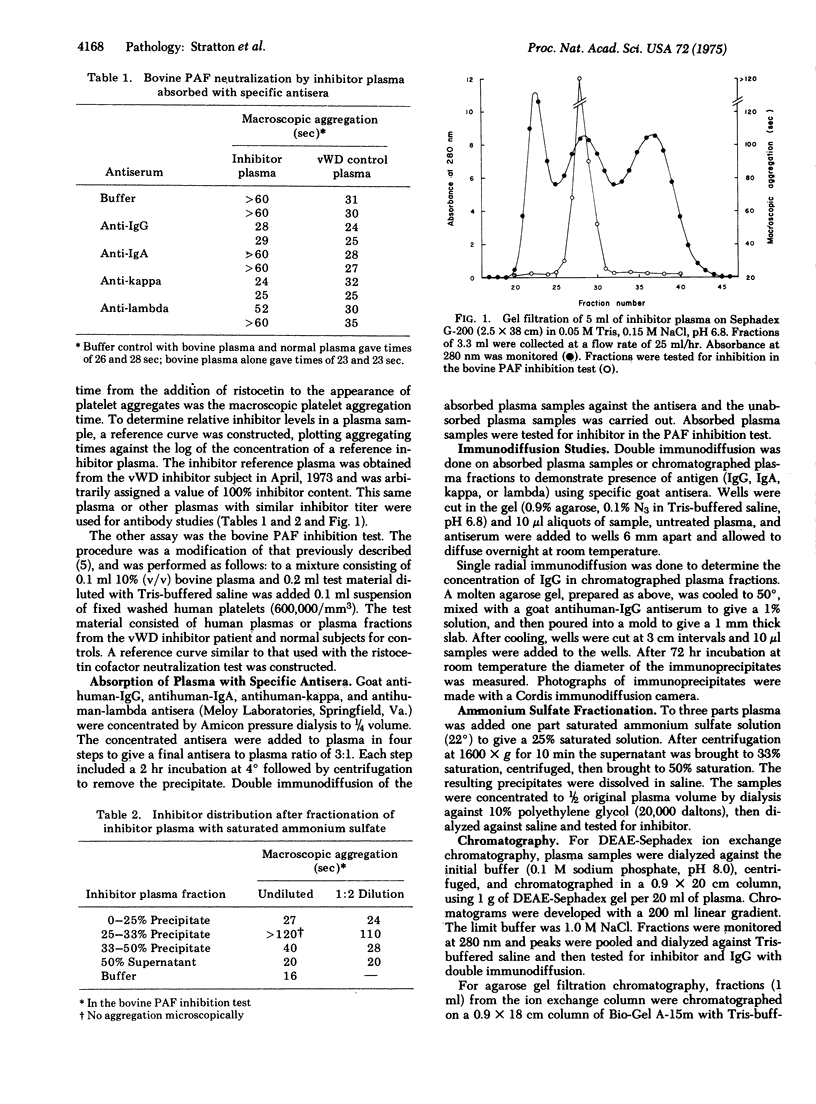
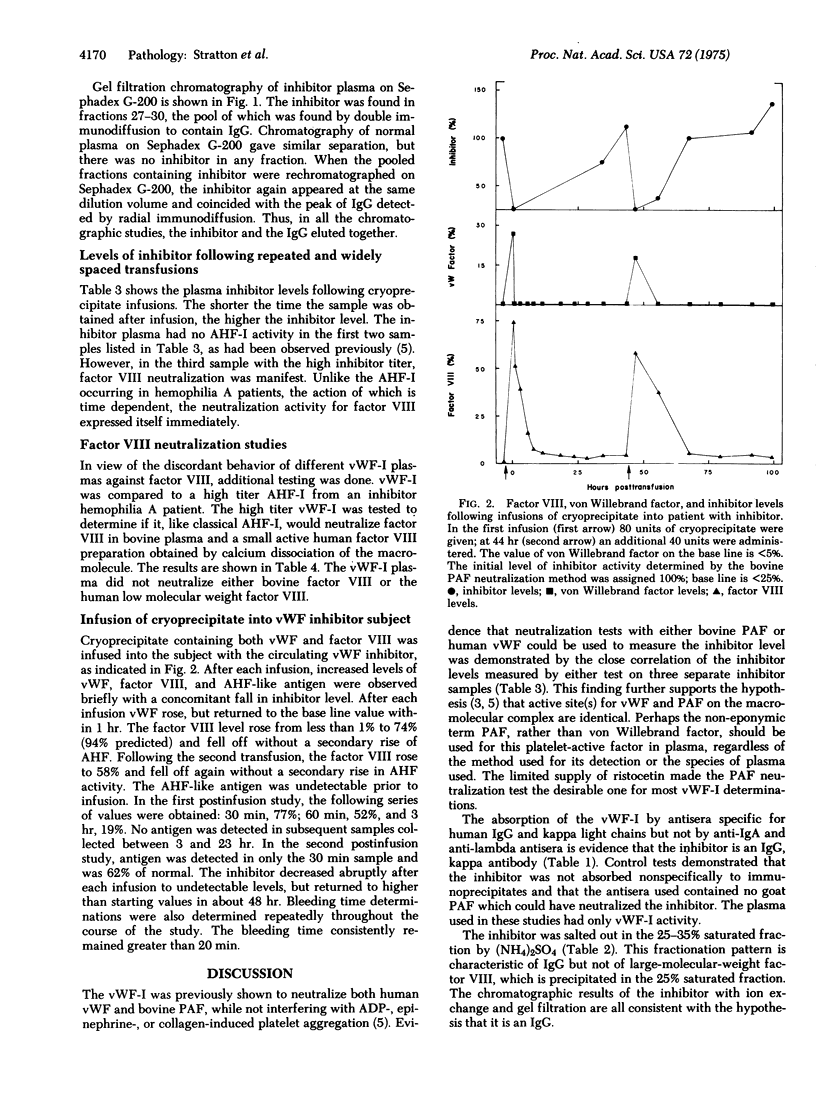
A circulating plasma inhibitor of the "von Willebrand factor" was observed in a multiply tranfused subject with severe von Willebrand's disease. The platelet-active von Willebrand factor is associated with a plasma protein macromolecular complex that is deficient in the disease. The inhibitor appears to be an IgG antibody, kappa type, based on neutralization tests with goat antisera to specific human immunoglobulins. The IgG and inhibitor separated out together in plasma fractions obtained by "salting-out" and chromatographic procedures. Two separate inhibitor neutralization tests for the platelet-active factor, one with human plasma and ristocetin, the other with bovine plasma, gave similar results, based on the macroscopic aggregation time test of fixed human platelets. With cryoprecipitate transfusions the inhibitor was transiently neutralized with the temporary appearance of von Willebrand factor, factor VIII, and factor VIII-like antigen in the plasma. The plasma inhibitor level increased after transfusion, suggesting an anamnestic response. Lower titer inhibitor plasmas neutralized only the platelet activity. Highest titer plasma also neutralized human factor VIII, but only in part; it did not neutralize either bovine factor VIII or the human small active factor VIII fragment. The anti-factor VIII activity of the von Willebrand factor inhibitor may be due to steric hindrance, dependent on the spatial relationship of factor VIII sites on the macromolecular complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Platelets fixed with paraformaldehyde: a new reagent for assay of von Willebrand factor and platelet aggregating factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW E. M., HEINDEL C. C., ROBERTS H. R., GRAHAM J. B. HETEROZYGOSITY AND HOMOZYGOSITY IN VON WILLEBRAND'S DISEASE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Mar;118:684–687. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Graham J. E., Cooper H. A., Allain J. P., Wagner R. H. Assay of von Willebrand factor in von Willebrand's disease and hemophilia: use of a macroscopic platelet aggregation test. Thromb Res. 1975 Mar;6(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaetano G., Donati M. B., Vermylen J. Evidnece that human platelet aggregating activity in porcine plasma is a property of von Willbrand factor. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1974 Dec 31;32(2-3):549–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Cooper H. A., Webster W. P., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Plasma aggregating factor (bovine) for human platelets: a marker for study of antihemophilic and von Willebrand Factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2814–2818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs T. R., Webster W. P., Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Von Willebrand factor: gene dosage relationships and transfusion response in bleeder swine--a new bioassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2087–2090. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUHRER M. E., LECHLER E., CORNELL C. N., KIRKLAND J. L. ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR LEVELS IN BLEEDER SWINE FOLLOWING INFUSIONS OF PLASMA AND SERUM. Am J Physiol. 1965 Mar;208:508–510. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarji K. E., Stratton R. D., Wagner R. H., Brinkhous K. M. Nature of von Willebrand factor: a new assay and a specific inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



