Abstract
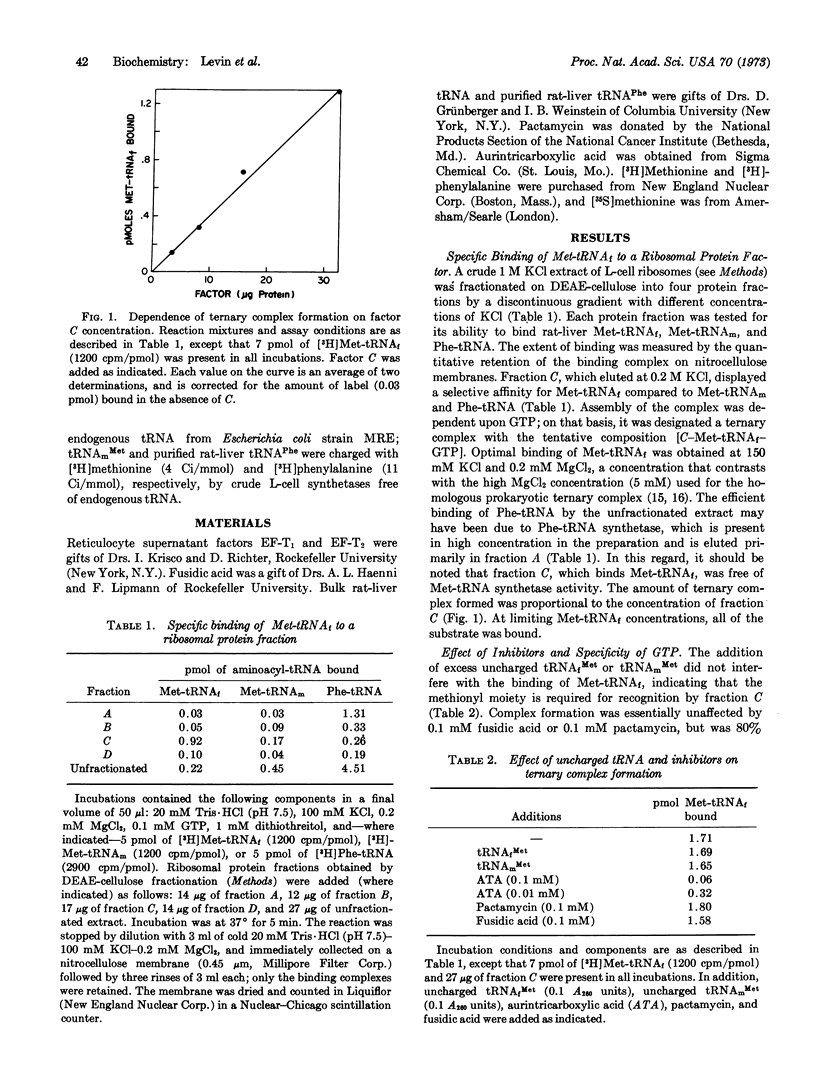
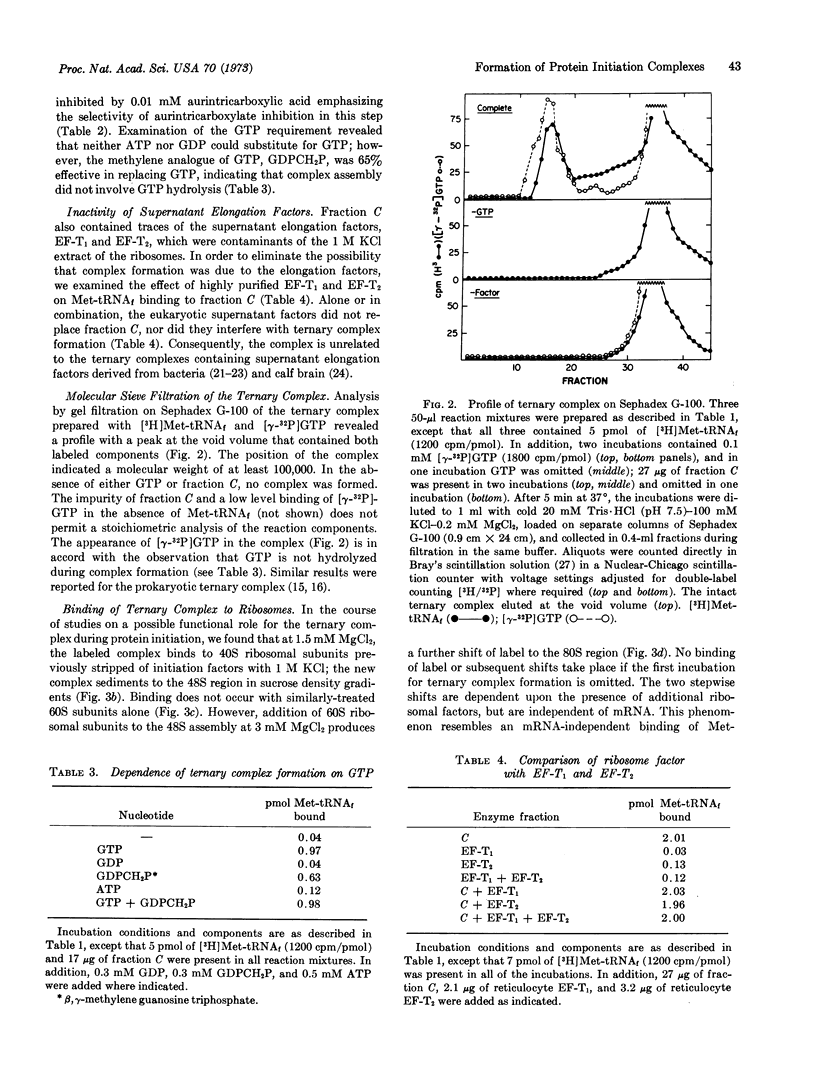
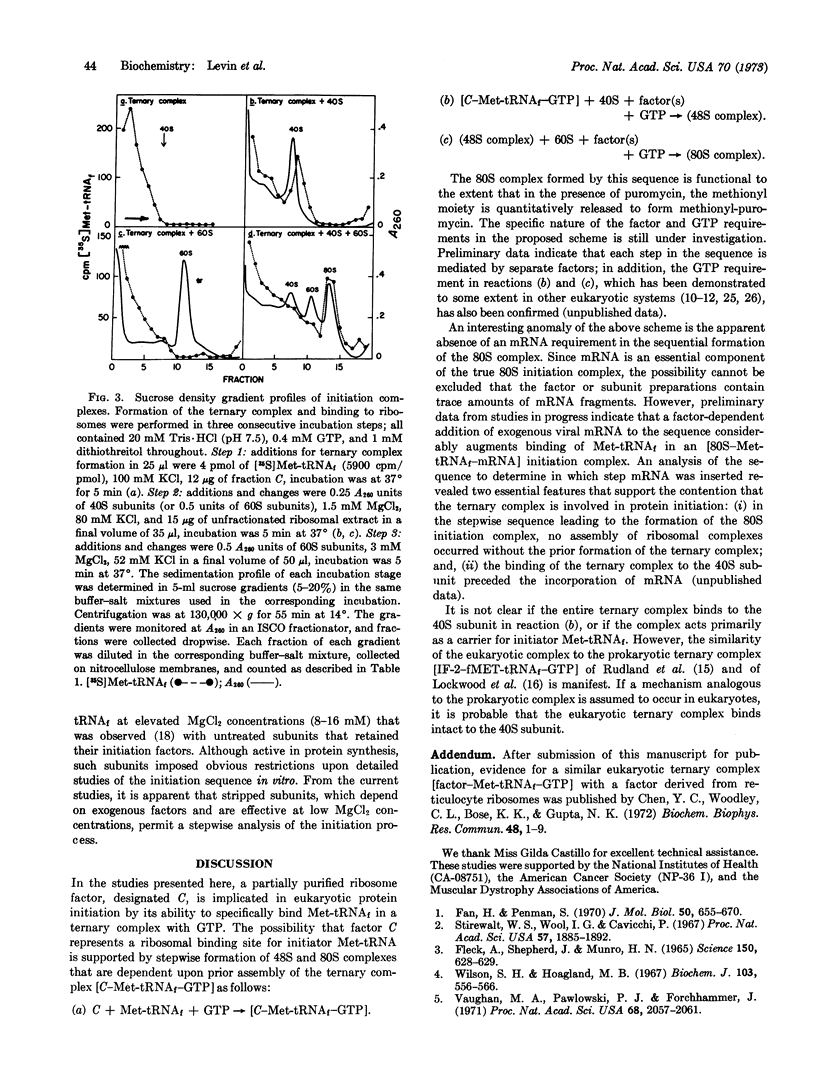
A protein factor contained in a 1 M KCl extract of L-cell ribosomes and partially purified by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose forms a specific ternary complex with rat-liver Met-tRNAf and GTP. The complex is measured by its quantitative retention on nitrocellulose membranes. Complex assembly is optimal at 100 mM KCl and 0.2 mM MgCl2, and is independent of mRNA and of ribosomes. The GTP requirement can be replaced over 65% by its methylene analogue GDPCH2P, indicating that GTP hydrolysis is not involved. Complex formation is inhibited by 10 μM aurintricarboxylic acid, but is unaffected by 100 μM pactamycin, 100 μM fusidic acid, or by excess uncharged methionine tRNAf. The ternary complex is relatively stable and appears at the void volume during filtration on Sephadex G-100. At 1-3 mM MgCl2 and in the presence of other factors, the ternary complex is implicated in protein initiation by (i) its capacity to bind to the 40S ribosomal subunit to form a 48S complex; and (ii) the subsequent association of the 48S complex with a 60S subunit to form a functional “80S complex.”
Keywords: binding assay, L-cells, ribosome subunits, protein inhibitors
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Anderson W. F. Initiation of hemoglobin synthesis: comparison of model reactions that use artificial templates with those using natural messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):706–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. II. Inhibition of protein synthesis at the level of initiation during mitosis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):655–670. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck A., Shepherd J., Munro H. N. Protein synthesis in rat liver: influence of amino acids in diet on microsomes and polysomes. Science. 1965 Oct 29;150(3696):628–629. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3696.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. Interaction of guanosine 5'-triphosphate with a supernatant fraction from E. coli and aminoacyl-sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1574–1578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Thompson W. C. Studies on the formation of the initiation complex in eukaryotes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):470–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J. P., Keller E. B. Protein chain initiation by methionyl-tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):416–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Formation of a mammalian initiation complex with reovirus messenger RNA, methionyl-tRNA F , and ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood A. H., Chakraborty P. R., Maitra U. A complex between initiation factor IF2, guanosine triphosphate, and fMet-tRNA: an intermediate in initiation complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3122–3126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick W., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in HeLa cells: translation at elevated temperatures. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan;39(2):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90320-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. M., Weissbach H. Interaction of brain transferase I with guanosine nucleotides and aminoacyl-tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):254–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90657-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Skoultchi A., Klein A., Lengyel P. Peptide chain elongation: discrimination against the initiator transfer RNA by microbial amino-acid polymerization factors. Nature. 1968 Dec 28;220(5174):1304–1307. doi: 10.1038/2201304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudland P. S., Whybrow W. A., Clark B. F. Recognition of bacterial initiator tRNA by an initiation factor. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 19;231(20):76–78. doi: 10.1038/newbio231076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Laycock D. G., Crystal R. G., Anderson W. F. Requirement for GTP in the initiation process on reticulocyte ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2246–2251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Prichard P. M., Gilbert J. M., Merrick W. C., Anderson W. F. Separation of reticulocyte initiation factor M 2 activity into two components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorey R. L., Ravel J. M., Garner C. W., Shive W. Formation and properties of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid-guanosine triphosphate-protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4555–4564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirewalt W. S., Wool I. G., Cavicchi P. The relation of RNA and protein synthesis to the sedimentation of muscle ribosomes: effect of diabetes and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1885–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach S. S., Thach R. E. 1 molecule of guanosine triphosphate is present in each 30S initiation complex. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 17;229(7):219–221. doi: 10.1038/newbio229219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M. H., Jr, Pawlowski P. J., Forchhammer J. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in HeLa cells deprived of single essential amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2057–2061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Iwasaki K., Miller M. J., Sabol S., Sillero M. A., Vasquez C. Initiation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. II. Role of the initiation factors in polypeptide synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:291–299. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. P., Verma D. P., Seal S. N., Marcus A. Role of ribosomal subunits in eukaryotic protein chain initiation. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):167–168. doi: 10.1038/236167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Leader D. P., Wool I. G. Initiation factor promoted reassociation of eukaryotic ribosomal subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):994–1000. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90560-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. H., Hoagland M. B. Physiology of rat-liver polysomes. The stability of messenger ribonucleic acid and ribosomes. Biochem J. 1967 May;103(2):556–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1030556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., Henshaw E. C., Hirsch C. A. Effects of deprival of glucose or individual amino acids on polyribosome distribution and rate of protein synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 18;259(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



