Abstract
In the title compound, [PdCl2(C5H7N3OS)], the PdII atom adopts a distorted square-planar coordination sphere defined by two N atoms of the bidentate ligand and two Cl atoms. The mean deviation from the coordination plane is 0.029 Å. The methyl group is not coplanar with the plane of the metallacycle [torsion angle C—O—N—C = 20.2 (4)°]. Steric repulsion between the methyl group and atoms of the metallacycle is manifested by shortened intramolecular H⋯C contacts of 2.27, 2.38 and 2.64 Å, as compared with the sum of the van der Waals radii of 2.87 Å. The amino group participates via one H atom in the formation of an intramolecular N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bond. In the crystal, the other H atom of the amino group links molecules via bifurcated N—H⋯(Cl,O) hydrogen bonds into chains parallel to [001].
Keywords: crystal structure; palladium; multi-functional ligand; 4-[(methoxyimino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-amine (MIMTA)
Related literature
4-[(Methoxyimino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-amine (MIMTA) belongs to the class of polyfunctional oximes that are potential biologically active complexing agents (Dodoff et al., 2009 ▸; Elo, 2004 ▸; Scaffidi-Domianello et al., 2011 ▸; Donde & Patil, 2011 ▸; Kuwar et al., 2006 ▸). Palladium complexes based on MIMTA are thus interesting in biomedicine (Orysyk et al., 2013 ▸). For the structures of related complexes, see: Orysyk et al. (2015 ▸); Mokhir et al. (2002 ▸). For van der Waals radii, see: Zefirov (1997 ▸).
Experimental
Crystal data
[PdCl2(C5H7N3OS)]
M r = 334.50
Orthorhombic,
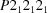
a = 4.347 (3) Å
b = 13.583 (2) Å
c = 16.411 (3) Å
V = 969.0 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.64 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.4 × 0.3 × 0.2 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012 ▸) T min = 0.742, T max = 1.000
4284 measured reflections
2106 independent reflections
2028 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.019
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.022
wR(F 2) = 0.047
S = 1.04
2106 reflections
120 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 969 Friedel pairs
Absolute structure parameter: 0.39 (4)
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Agilent, 2012 ▸); cell refinement: CrysAlis CCD; data reduction: CrysAlis RED (Agilent, 2012 ▸); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 1037339
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3H3ACl2 | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.124(3) | 151 |
| N3H3BCl1i | 0.86 | 2.48 | 3.280(3) | 156 |
| N3H3BO1i | 0.86 | 2.45 | 3.015(3) | 124 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Experimental
PdCl2 (0.036 g, 0.2 mmol) was dissolved in 6N HCl (3 ml) at 313–323 K, and ethanol (7 ml) was added. To the resulting light-brown solution was added a hot solution of 4-[(methoxyimino)methyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-amine (0.031 g, 0.2 mmol), dissolved in ethanol (10 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred for one hour under reflux and cooled down to room temperature whereupon orange needle-like single crystals were filtered off, washed with ethanol and diethyl ether and dried in a vacuum desiccator over CaCl2. Yield: 0.045 g (65%).
S2. Refinement
All hydrogen atoms were located from difference Fourier maps and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso = 1.2Ueq (except Uiso = 1.5Ueq for the methyl group). The structure was refined from a crystal twinned by inversion (Flack parameter value 0.39 (4)).
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

Crystal packing of the title compound with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| [PdCl2(C5H7N3OS)] | Dx = 2.293 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 334.50 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Cell parameters from 2494 reflections |
| a = 4.347 (3) Å | θ = 3.8–31.7° |
| b = 13.583 (2) Å | µ = 2.64 mm−1 |
| c = 16.411 (3) Å | T = 294 K |
| V = 969.0 (7) Å3 | , orange |
| Z = 4 | 0.4 × 0.3 × 0.2 mm |
| F(000) = 648 |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer | 2106 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2028 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.019 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1827 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.0° |
| ω scans | h = −5→5 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Agilent, 2012) | k = −17→16 |
| Tmin = 0.742, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −21→21 |
| 4284 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.022 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.047 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0225P)2 + 0.1807P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 2106 reflections | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 120 parameters | Δρmin = −0.36 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 969 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure parameter: 0.39 (4) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Pd1 | 0.15497 (6) | 0.986930 (16) | 0.742144 (12) | 0.02751 (7) | |
| Cl1 | −0.1238 (2) | 1.04846 (7) | 0.84901 (5) | 0.0396 (2) | |
| Cl2 | −0.0192 (2) | 1.11559 (6) | 0.66418 (5) | 0.0411 (2) | |
| S1 | 0.6968 (2) | 0.84020 (7) | 0.53414 (5) | 0.0394 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.2794 (6) | 0.86291 (19) | 0.88793 (12) | 0.0379 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.3271 (7) | 0.87185 (19) | 0.80514 (14) | 0.0306 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.3996 (6) | 0.91712 (19) | 0.65287 (15) | 0.0291 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.3636 (8) | 1.0058 (2) | 0.53113 (15) | 0.0489 (8) | |
| H3A | 0.2466 | 1.0498 | 0.5526 | 0.059* | |
| H3B | 0.4153 | 1.0104 | 0.4807 | 0.059* | |
| C1 | 0.5024 (9) | 0.8046 (3) | 0.92925 (18) | 0.0389 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.4798 | 0.8132 | 0.9870 | 0.058* | |
| H1B | 0.7050 | 0.8249 | 0.9130 | 0.058* | |
| H1C | 0.4729 | 0.7366 | 0.9156 | 0.058* | |
| C2 | 0.4954 (8) | 0.8100 (2) | 0.76650 (18) | 0.0328 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.5819 | 0.7552 | 0.7916 | 0.039* | |
| C3 | 0.5408 (8) | 0.8314 (2) | 0.68133 (18) | 0.0315 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.7074 (9) | 0.7815 (3) | 0.62715 (19) | 0.0375 (8) | |
| H4 | 0.8138 | 0.7236 | 0.6379 | 0.045* | |
| C5 | 0.4632 (8) | 0.9318 (2) | 0.57529 (18) | 0.0317 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Pd1 | 0.03240 (12) | 0.02459 (11) | 0.02555 (10) | −0.00010 (10) | −0.00195 (9) | 0.00015 (8) |
| Cl1 | 0.0450 (5) | 0.0412 (5) | 0.0327 (4) | 0.0059 (4) | 0.0021 (4) | −0.0055 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.0511 (5) | 0.0326 (4) | 0.0394 (4) | 0.0092 (4) | −0.0021 (4) | 0.0062 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0506 (6) | 0.0390 (5) | 0.0286 (4) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0042 (4) | −0.0028 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0456 (14) | 0.0444 (14) | 0.0237 (9) | 0.0096 (12) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0059 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0373 (15) | 0.0304 (14) | 0.0240 (11) | −0.0015 (15) | −0.0013 (12) | 0.0048 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0361 (16) | 0.0239 (13) | 0.0273 (12) | −0.0007 (12) | −0.0025 (11) | 0.0012 (10) |
| N3 | 0.077 (2) | 0.0424 (17) | 0.0276 (12) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0087 (14) | 0.0054 (12) |
| C1 | 0.045 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0260 (14) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0007 (16) | 0.0053 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0409 (18) | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0303 (15) | 0.0048 (15) | −0.0018 (15) | 0.0024 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0388 (18) | 0.0277 (17) | 0.0282 (14) | −0.0013 (15) | −0.0032 (14) | −0.0001 (13) |
| C4 | 0.045 (2) | 0.0342 (18) | 0.0333 (15) | 0.0069 (17) | −0.0021 (16) | −0.0014 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0385 (18) | 0.0316 (18) | 0.0251 (14) | −0.0029 (16) | 0.0012 (14) | 0.0012 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Pd1—Cl1 | 2.2897 (10) | N3—H3A | 0.8600 |
| Pd1—Cl2 | 2.2943 (9) | N3—H3B | 0.8600 |
| Pd1—N1 | 2.018 (3) | N3—C5 | 1.313 (4) |
| Pd1—N2 | 2.044 (3) | C1—H1A | 0.9600 |
| S1—C4 | 1.723 (3) | C1—H1B | 0.9600 |
| S1—C5 | 1.742 (3) | C1—H1C | 0.9600 |
| O1—N1 | 1.380 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C1 | 1.423 (4) | C2—C3 | 1.441 (4) |
| N1—C2 | 1.282 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.332 (5) |
| N2—C3 | 1.397 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C5 | 1.318 (4) | ||
| Cl1—Pd1—Cl2 | 88.54 (4) | O1—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| N1—Pd1—Cl1 | 94.96 (8) | O1—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| N1—Pd1—Cl2 | 176.43 (8) | H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 |
| N1—Pd1—N2 | 79.34 (10) | H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| N2—Pd1—Cl1 | 173.65 (8) | H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 |
| N2—Pd1—Cl2 | 97.20 (8) | N1—C2—H2 | 122.4 |
| C4—S1—C5 | 90.16 (16) | N1—C2—C3 | 115.2 (3) |
| N1—O1—C1 | 114.6 (2) | C3—C2—H2 | 122.4 |
| O1—N1—Pd1 | 121.1 (2) | N2—C3—C2 | 115.6 (3) |
| C2—N1—Pd1 | 117.8 (2) | C4—C3—N2 | 116.1 (3) |
| C2—N1—O1 | 121.0 (3) | C4—C3—C2 | 128.3 (3) |
| C3—N2—Pd1 | 112.1 (2) | S1—C4—H4 | 125.0 |
| C5—N2—Pd1 | 137.0 (2) | C3—C4—S1 | 110.0 (3) |
| C5—N2—C3 | 110.9 (3) | C3—C4—H4 | 125.0 |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 120.0 | N2—C5—S1 | 112.9 (2) |
| C5—N3—H3A | 120.0 | N3—C5—S1 | 121.7 (2) |
| C5—N3—H3B | 120.0 | N3—C5—N2 | 125.4 (3) |
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.5 | ||
| Pd1—N1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (4) | N1—C2—C3—N2 | 0.9 (5) |
| Pd1—N2—C3—C2 | −1.4 (4) | N1—C2—C3—C4 | 178.7 (4) |
| Pd1—N2—C3—C4 | −179.5 (3) | N2—Pd1—N1—O1 | 175.8 (3) |
| Pd1—N2—C5—S1 | 179.58 (19) | N2—Pd1—N1—C2 | −0.7 (3) |
| Pd1—N2—C5—N3 | −1.1 (6) | N2—C3—C4—S1 | −0.2 (4) |
| Cl1—Pd1—N1—O1 | −7.0 (2) | C1—O1—N1—Pd1 | −156.2 (2) |
| Cl1—Pd1—N1—C2 | 176.4 (3) | C1—O1—N1—C2 | 20.2 (4) |
| Cl1—Pd1—N2—C3 | −25.3 (9) | C2—C3—C4—S1 | −178.0 (3) |
| Cl1—Pd1—N2—C5 | 155.6 (5) | C3—N2—C5—S1 | 0.5 (4) |
| Cl2—Pd1—N1—O1 | 161.6 (12) | C3—N2—C5—N3 | 179.8 (3) |
| Cl2—Pd1—N1—C2 | −14.9 (15) | C4—S1—C5—N2 | −0.5 (3) |
| Cl2—Pd1—N2—C3 | −179.7 (2) | C4—S1—C5—N3 | −179.8 (3) |
| Cl2—Pd1—N2—C5 | 1.2 (3) | C5—S1—C4—C3 | 0.4 (3) |
| O1—N1—C2—C3 | −176.4 (3) | C5—N2—C3—C2 | 177.9 (3) |
| N1—Pd1—N2—C3 | 1.1 (2) | C5—N2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) |
| N1—Pd1—N2—C5 | −178.0 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3A···Cl2 | 0.86 | 2.34 | 3.124 (3) | 151 |
| N3—H3B···Cl1i | 0.86 | 2.48 | 3.280 (3) | 156 |
| N3—H3B···O1i | 0.86 | 2.45 | 3.015 (3) | 124 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1/2, −y+2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WM5096).
References
- Agilent (2012). CrysAlis RED and CrysAlis CCD. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Dodoff, N. I., Kubiak, M., Kuduk-Jaworska, J., Mastalarz, A., Kochel, A., Vassilieva, V., Vassilev, N., Trendafilova, N., Georgieva, I., Lalia-Kantouri, M. & Apostolova, M. (2009). Chemija, 4, 208–217.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Donde, K. J. & Patil, V. R. (2011). J. Pharm. Res 1, 206–209.
- Elo, H. (2004). Chemotherapy, 50, 229–233. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kuwar, A. S., Shimpi, S. R., Mahulikar, P. P. & Bendre, R. S. (2006). J. Sci. Ind. Res. 8, 665–669.
- Mokhir, A. A., Gumienna-Kontecka, E., Świątek-Kozlowska, J., Petkova, E. G., Fritsky, I. O., Jerzykiewicz, L., Kapshuk, A. A., Sliva, T. Yu. & Yu, (2002). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 329, 113–121.
- Orysyk, S. I., Bon, V. V., Zholob, O. O., Pekhnyo, V. I., Orysyk, V. V., Zborovskii, Yu. L. & Vovk, M. V. (2013). Polyhedron, 51, 211–221.
- Orysyk, S. I., Zholob, O. O., Bon, V. V., Nikulina, V. V., Orysyk, V. V., Nikolaienko, T. V., Garmanchuk, L. V., Zborovskii, Yu. L., Tolstanova, G. M., Khranovska, N. M., Pekhnyo, V. I. & Vovk, M. V. (2015). Polyhedron, 85, 208–220.
- Scaffidi-Domianello, Yu. Yu., Legin, A. A., Jakupec, M. A., Arion, V. B., Kukushkin, V. Yu., Galanski, M. & Keppler, B. K. (2011). Inorg. Chem 21, 10673–10681. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zefirov, Yu. V. (1997). Kristallografiya, 42, 936–958.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026619/wm5096fig2.tif
Crystal packing of the title compound with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
CCDC reference: 1037339
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


