Abstract
In the title compound, C17H22N2O4S, a thiopiperidine derivative, the piperidine ring has an envelope conformation with the methylene C atom opposite to the C=S bond as the flap. The nitromethyl substituent is equatorial while the ethoxycarbonyl group is axial. The mean planes of the nitromethyl group, the carboxy group and phenyl ring are inclined to the mean plane through the five planar atoms of the piperidine ring [maximum deviation = 0.070 (4) Å] by 56.8 (2), 83.8 (5) and 87.1 (2)°, respectively. There is an intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond involving an H atom of the ethoxycarbonyl group and a nitro O atom. In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [100]. The chains are linked by further C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming corrugated layers lying parallel to (001).
Keywords: crystal structure, thiopiperidine, piperidine-2-thiones, hydrogen bonding
Related literature
For general background on piperidines and their derivatives, see: Poupart et al. (1999 ▸); Pinnick et al. (1990 ▸); Mukaiyama & Hoshino (1960 ▸); Ballini et al. (2007 ▸); Sośnicki (2009 ▸). For their biological activity, see: Leung et al. (2000 ▸). For their use in organometallic reactions, see: Tamaru et al. (1978 ▸, 1979 ▸). For details of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Groom & Allen (2014 ▸).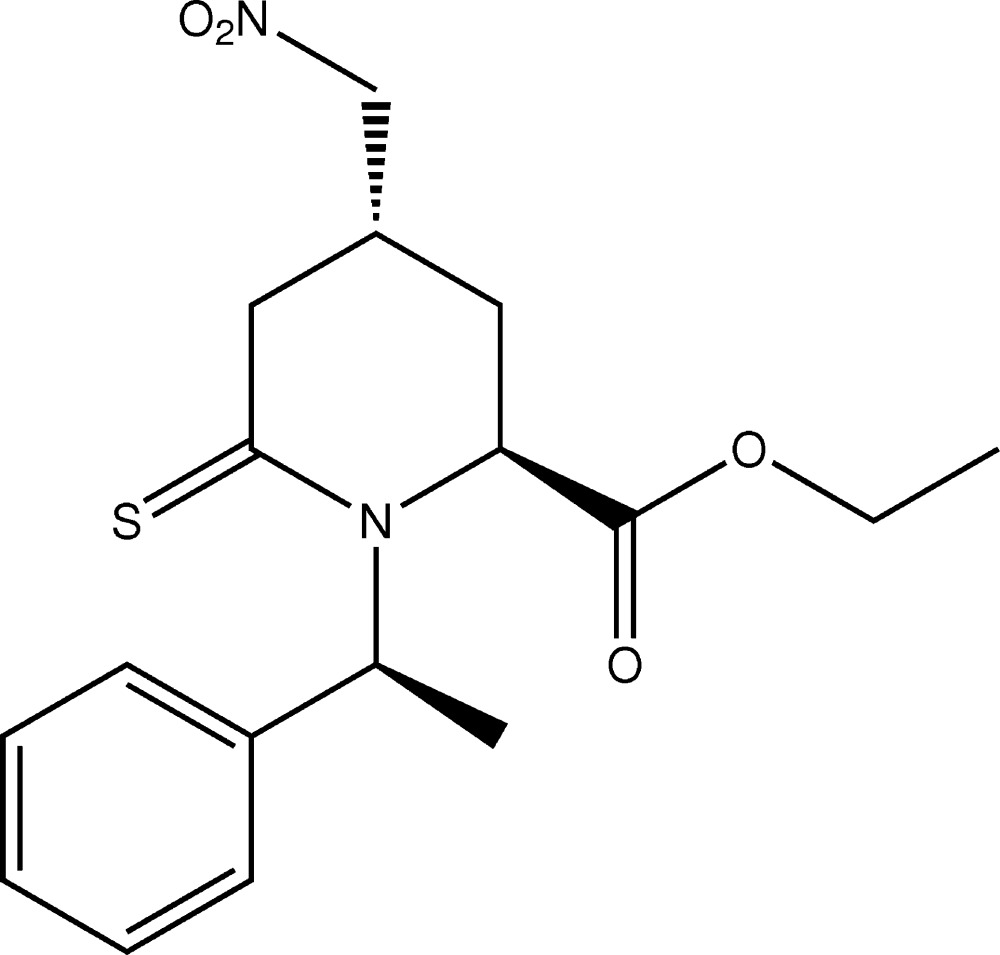
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H22N2O4S
M r = 350.42
Orthorhombic,
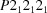
a = 5.7999 (2) Å
b = 10.0103 (6) Å
c = 30.4050 (18) Å
V = 1765.28 (16) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.21 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.20 × 0.09 × 0.05 mm
Data collection
Agilent Xcalibur Atlas Gemini diffractometer
Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) T min = 0.979, T max = 0.991
8486 measured reflections
3373 independent reflections
2306 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.054
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.056
wR(F 2) = 0.104
S = 1.04
3373 reflections
219 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 705 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸)
Absolute structure parameter: 0.16 (8)
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Agilent, 2014 ▸); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▸) and Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 2012 ▸), PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036fig2.tif
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details; H atoms not involved in the intermolecular hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity).
CCDC reference: 1037775
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C16H16AO3 | 0.96 | 2.49 | 3.419(8) | 163 |
| C2H2AO1i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.404(5) | 147 |
| C17H17BO3ii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.380(6) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 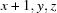 ; (ii)
; (ii) 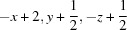 .
.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to CONACyT (project 154104) for financial support and AZ thanks CONACyT for a postdoctoral scholarship (165517).
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
The Michael addition is one of the most important synthetic strategies performed in organic synthesis. Among the many applications, conjugate addition to α,β-unsaturated δ-lactams has been used in the synthesis of functionalized piperidines, due to a wide range of biological activities (Leung et al., 2000). Similar to α,β-unsaturated δ-lactams, α,β-unsaturated δ-thiolactams are promising Michael acceptors affording 4-substituted piperidine-2-thiones (Sośnicki, 2009). They also form C—C bonds in the reaction with organometallics such as alkyllithium, alkylmagnesium (Tamaru et al., 1978) and lithium enolates (Tamaru et al., 1979). Among a broad range of nucleophiles applied to the C—C bond formation, the addition of aliphatic nitrocompounds play a significant role (Ballini et al., 2007). In the presence of a base catalyst, the introduction of a nitroalkyl group into a α,β-unsaturated compound represent a key step in the preparation of chiral molecules due to versatile reactivity of the nitro functionality. The corresponding nitro compounds can be transformed into a wide range of synthetically valuable products such as amines (Poupart et al., 1999), ketones (Pinnick et al., 1990), carboxylic acids, nitrile oxides and other functionalities (Mukaiyama et al., 1960).
In the title compound, Fig. 1, the piperidine ring has an envelope conformation with puckering parameters Q = 0.528 (4) Å, θ = 129.0 (4)°, φ = 314.6 (6)°, q2 = 0.411 (4)° and q3 = -0.332 (4)°. The phenyl-ethyl group linked atom N1 of the piperidine ring, shows a dihedral angle of 101.6 (4)° from the mean plane of the piperidine ring. The carboxyethyl group is placed in a axial position (torsion angle = 15.8 (3)°) and the nitromethyl group in an equatorial position (torsion angle = 73.7 (3)°) on the piperidine ring. The C5═S1 distance is 1.682 (4) Å, similar to that found for other piperidine-2-thiones (CSD; Groom & Allen, 2014). There is an intramolecular C-H···O hydrogen bond present (Table 1).
In the crystal, molecules are linked by C-H···O hydrogen bonds forming chains along [100], which are linked by further C-H···O hydrogen bonds forming corrugated layers lying parallel to (001); see Table 1 and Fig. 2.
S2. Experimental
α,β-Unsaturated piperidine-2-thione derived from (S)-(-)-phenylethylamine (1.0 mmol) was dissolved in a solution of nitroalkane, and a catalytic amount of DBU was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. When the reaction was complete, 5 ml of concentrated NH4Cl was added and the solution was extracted twice with ethyl acetate. The organic phase was dried, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica (petroleum ether/ethyl acetate 80:20) giving the title compound as a white solid (yield 80%; m.p. 383- 385 K). It was crystallized using petroleum ether/dichloromethane, giving colourless prismatic crystals. [α]D20= -92.3 (c 1.0, CH2Cl2). IR (KBr pellet, cm-1): ν= 3746, 2977, 2929, 1739, 1551, 1461, 1196, 1075, 701, 548. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.31 (t, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 1.33 (m, 1H), 1.52 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 3H), 2.25 (ddd, J = 1.9, 5.7, 13.7 Hz, 1H), 2.79 (m, 1H), 2.99 (dd, J = 7.2, 18.3 Hz, 1H), 3.37 (ddd, J = 0.6, 7.7, 18.3 Hz, 1H), 4.05 (dd, J = 2.4, 5.4 Hz, 1H), 4.21 (dd, J = 8.4, 12.8 Hz, 1H), 4.27 (m, 2H), 4.35 (dd, J = 6.1, 12.8 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (m, 5H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 14.1, 14.5, 28.5, 29.9, 43.4, 55.6, 58.4, 62.5, 78.8, 127.0–129.0, 138.2, 170.0, 199.1.
S3. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2. The C-bound H atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined as riding on their parent atoms, with C–H = 0.93–0.98 Å and with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and = 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms. In the final cycles of refinement 18 reflections were omitted owing to poor agreement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
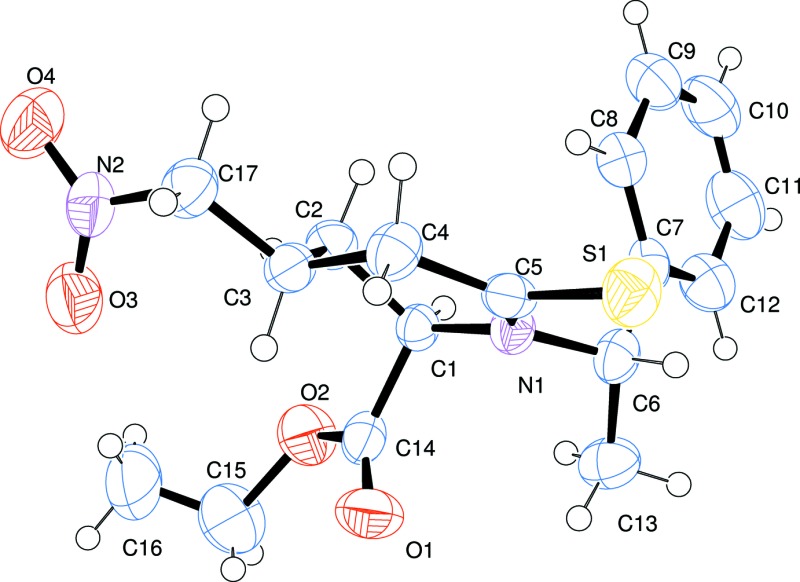
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
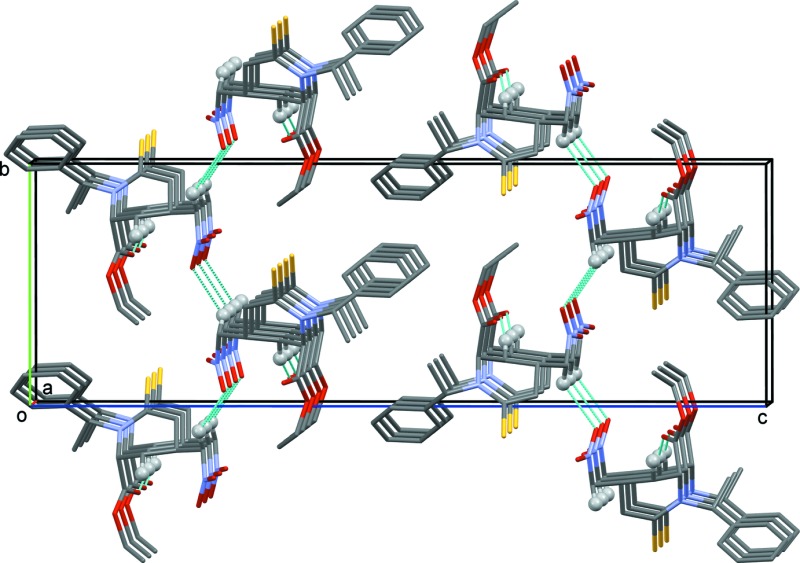
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details; H atoms not involved in the intermolecular hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity).
Crystal data
| C17H22N2O4S | F(000) = 744 |
| Mr = 350.42 | Dx = 1.319 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 2144 reflections |
| a = 5.7999 (2) Å | θ = 3.6–22.4° |
| b = 10.0103 (6) Å | µ = 0.21 mm−1 |
| c = 30.4050 (18) Å | T = 293 K |
| V = 1765.28 (16) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.09 × 0.05 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Atlas Gemini diffractometer | 3373 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 2306 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.054 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5564 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.1°, θmin = 2.9° |
| w scans | h = −7→6 |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | k = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.979, Tmax = 0.991 | l = −37→28 |
| 8486 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0336P)2 + 0.2223P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 3373 reflections | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 219 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 705 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.16 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.19570 (19) | 0.59698 (11) | 0.34603 (4) | 0.0521 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.2788 (5) | 0.1293 (3) | 0.35882 (11) | 0.0613 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.5823 (6) | 0.2794 (4) | 0.38339 (13) | 0.0335 (9) | |
| H1 | 0.6554 | 0.2775 | 0.4124 | 0.04* | |
| N1 | 0.4157 (5) | 0.3912 (3) | 0.38245 (10) | 0.0348 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.8838 (6) | 0.0880 (4) | 0.27210 (11) | 0.0706 (10) | |
| C2 | 0.7699 (6) | 0.2959 (4) | 0.34888 (12) | 0.0401 (10) | |
| H2A | 0.8704 | 0.2185 | 0.3489 | 0.048* | |
| H2B | 0.8622 | 0.3743 | 0.3554 | 0.048* | |
| C6 | 0.3122 (7) | 0.4254 (4) | 0.42575 (13) | 0.0424 (10) | |
| H6 | 0.1929 | 0.4925 | 0.42 | 0.051* | |
| C3 | 0.6547 (7) | 0.3112 (4) | 0.30381 (13) | 0.0387 (10) | |
| H3 | 0.5528 | 0.2346 | 0.2988 | 0.046* | |
| O2 | 0.6039 (5) | 0.0483 (3) | 0.38838 (11) | 0.0661 (10) | |
| N2 | 0.9716 (7) | 0.1947 (4) | 0.26262 (12) | 0.0515 (10) | |
| C7 | 0.4909 (7) | 0.4921 (4) | 0.45523 (15) | 0.0411 (10) | |
| C5 | 0.3778 (6) | 0.4662 (4) | 0.34676 (14) | 0.0379 (10) | |
| C13 | 0.1904 (8) | 0.3059 (5) | 0.44649 (14) | 0.0544 (12) | |
| H13A | 0.0961 | 0.2627 | 0.4248 | 0.082* | |
| H13B | 0.0952 | 0.3359 | 0.4704 | 0.082* | |
| H13C | 0.3031 | 0.244 | 0.4574 | 0.082* | |
| C14 | 0.4629 (7) | 0.1445 (4) | 0.37579 (14) | 0.0410 (10) | |
| C17 | 0.8290 (7) | 0.3186 (4) | 0.26649 (14) | 0.0508 (11) | |
| H17A | 0.7477 | 0.3333 | 0.239 | 0.061* | |
| H17B | 0.93 | 0.3944 | 0.2713 | 0.061* | |
| O4 | 1.1672 (6) | 0.2065 (4) | 0.24925 (12) | 0.0746 (10) | |
| C4 | 0.5101 (7) | 0.4380 (4) | 0.30508 (14) | 0.0441 (11) | |
| H4A | 0.6114 | 0.5132 | 0.2995 | 0.053* | |
| H4B | 0.4006 | 0.4341 | 0.281 | 0.053* | |
| C12 | 0.4732 (8) | 0.4867 (5) | 0.50057 (16) | 0.0576 (13) | |
| H12 | 0.3535 | 0.4388 | 0.5134 | 0.069* | |
| C8 | 0.6741 (8) | 0.5636 (4) | 0.43755 (15) | 0.0524 (12) | |
| H8 | 0.6916 | 0.5674 | 0.4072 | 0.063* | |
| C11 | 0.6311 (10) | 0.5515 (5) | 0.52687 (17) | 0.0707 (15) | |
| H11 | 0.616 | 0.5467 | 0.5573 | 0.085* | |
| C9 | 0.8308 (8) | 0.6293 (5) | 0.46405 (19) | 0.0646 (14) | |
| H9 | 0.9505 | 0.6778 | 0.4514 | 0.078* | |
| C10 | 0.8102 (10) | 0.6231 (5) | 0.50910 (19) | 0.0708 (15) | |
| H10 | 0.9156 | 0.6666 | 0.5272 | 0.085* | |
| C15 | 0.5480 (11) | −0.0877 (5) | 0.3739 (3) | 0.107 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.5214 | −0.1435 | 0.3995 | 0.128* | |
| H15B | 0.4069 | −0.0858 | 0.3568 | 0.128* | |
| C16 | 0.7207 (13) | −0.1424 (7) | 0.3491 (2) | 0.138 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.7451 | −0.0886 | 0.3233 | 0.207* | |
| H16B | 0.678 | −0.2313 | 0.3404 | 0.207* | |
| H16C | 0.8602 | −0.1458 | 0.366 | 0.207* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0540 (6) | 0.0423 (6) | 0.0600 (8) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0103 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0488 (17) | 0.053 (2) | 0.082 (2) | −0.0121 (15) | −0.0068 (17) | −0.0028 (16) |
| C1 | 0.031 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0039 (18) | −0.0003 (19) | −0.0017 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0360 (16) | 0.0332 (19) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0034 (15) | 0.0024 (15) | 0.0013 (16) |
| O3 | 0.096 (3) | 0.049 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.0215 (19) | −0.0059 (18) |
| C2 | 0.034 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0007 (18) | −0.005 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C6 | 0.039 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.047 (3) | 0.010 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0018 (19) |
| C3 | 0.036 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.039 (2) | −0.0018 (19) | 0.002 (2) | 0.0004 (19) |
| O2 | 0.0655 (19) | 0.0378 (18) | 0.095 (3) | 0.0108 (17) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0027 (17) |
| N2 | 0.059 (2) | 0.056 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.008 (2) | −0.0078 (19) |
| C7 | 0.048 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.043 (3) | 0.008 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C5 | 0.0345 (19) | 0.033 (2) | 0.047 (3) | −0.0050 (17) | −0.003 (2) | 0.001 (2) |
| C13 | 0.052 (2) | 0.063 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.011 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| C14 | 0.044 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.041 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C17 | 0.056 (2) | 0.047 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| O4 | 0.0502 (18) | 0.092 (3) | 0.082 (2) | 0.0043 (19) | 0.014 (2) | −0.014 (2) |
| C4 | 0.045 (2) | 0.045 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C12 | 0.068 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.053 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.003 (2) |
| C8 | 0.054 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.056 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.006 (3) | −0.011 (2) |
| C11 | 0.098 (4) | 0.063 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.014 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C9 | 0.063 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.079 (4) | −0.006 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.018 (3) |
| C10 | 0.077 (3) | 0.057 (3) | 0.078 (4) | −0.003 (3) | −0.019 (3) | −0.021 (3) |
| C15 | 0.105 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.184 (7) | 0.008 (3) | 0.034 (5) | −0.014 (4) |
| C16 | 0.166 (7) | 0.073 (4) | 0.176 (7) | −0.028 (5) | 0.101 (6) | −0.048 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C5 | 1.682 (4) | C5—C4 | 1.508 (5) |
| O1—C14 | 1.195 (5) | C13—H13A | 0.96 |
| C1—H1 | 0.98 | C13—H13B | 0.96 |
| C1—N1 | 1.479 (5) | C13—H13C | 0.96 |
| C1—C2 | 1.521 (5) | C17—H17A | 0.97 |
| C1—C14 | 1.535 (5) | C17—H17B | 0.97 |
| N1—C6 | 1.487 (5) | C4—H4A | 0.97 |
| N1—C5 | 1.338 (5) | C4—H4B | 0.97 |
| O3—N2 | 1.218 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.93 |
| C2—H2A | 0.97 | C12—C11 | 1.378 (7) |
| C2—H2B | 0.97 | C8—H8 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.532 (5) | C8—C9 | 1.381 (6) |
| C6—H6 | 0.98 | C11—H11 | 0.93 |
| C6—C7 | 1.524 (6) | C11—C10 | 1.372 (7) |
| C6—C13 | 1.526 (6) | C9—H9 | 0.93 |
| C3—H3 | 0.98 | C9—C10 | 1.376 (7) |
| C3—C17 | 1.521 (5) | C10—H10 | 0.93 |
| C3—C4 | 1.522 (5) | C15—H15A | 0.97 |
| O2—C14 | 1.321 (5) | C15—H15B | 0.97 |
| O2—C15 | 1.467 (6) | C15—C16 | 1.369 (8) |
| N2—C17 | 1.495 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.96 |
| N2—O4 | 1.211 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.96 |
| C7—C12 | 1.383 (6) | C16—H16C | 0.96 |
| C7—C8 | 1.390 (6) | ||
| N1—C1—H1 | 108.3 | O1—C14—C1 | 125.5 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 111.8 (3) | O1—C14—O2 | 125.8 (4) |
| N1—C1—C14 | 111.6 (3) | O2—C14—C1 | 108.6 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 108.3 | C3—C17—H17A | 109.1 |
| C2—C1—C14 | 108.4 (3) | C3—C17—H17B | 109.1 |
| C14—C1—H1 | 108.3 | N2—C17—C3 | 112.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—C6 | 114.9 (3) | N2—C17—H17A | 109.1 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 123.2 (3) | N2—C17—H17B | 109.1 |
| C5—N1—C6 | 121.5 (3) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.8 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 110 | C3—C4—H4A | 108 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 110 | C3—C4—H4B | 108 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 108.4 (3) | C5—C4—C3 | 117.3 (3) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.4 | C5—C4—H4A | 108 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 110 | C5—C4—H4B | 108 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 110 | H4A—C4—H4B | 107.2 |
| N1—C6—H6 | 106.5 | C7—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| N1—C6—C7 | 110.3 (3) | C11—C12—C7 | 120.7 (5) |
| N1—C6—C13 | 111.8 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 106.5 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| C7—C6—C13 | 114.5 (3) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.5 (4) |
| C13—C6—H6 | 106.5 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 108.9 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C17—C3—C2 | 112.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.3 (5) |
| C17—C3—H3 | 108.9 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.3 |
| C17—C3—C4 | 110.2 (3) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 107.5 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.1 (5) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 108.9 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C14—O2—C15 | 117.0 (4) | C11—C10—C9 | 118.8 (5) |
| O3—N2—C17 | 118.5 (4) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.6 |
| O4—N2—O3 | 123.8 (4) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.6 |
| O4—N2—C17 | 117.6 (4) | O2—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| C12—C7—C6 | 121.2 (4) | O2—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 117.5 (4) | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.9 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.2 (4) | C16—C15—O2 | 112.0 (5) |
| N1—C5—S1 | 123.4 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.2 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 119.5 (3) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.2 |
| C4—C5—S1 | 117.0 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C13—H13A | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C6—C13—H13B | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C13—H13C | 109.5 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 | ||
| S1—C5—C4—C3 | −173.4 (3) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −177.6 (4) |
| C1—N1—C6—C7 | 71.5 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.1 (4) |
| C1—N1—C6—C13 | −57.2 (4) | C7—C12—C11—C10 | −0.1 (7) |
| C1—N1—C5—S1 | −177.7 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.1 (7) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −0.3 (5) | C5—N1—C6—C7 | −101.6 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C17 | −175.9 (3) | C5—N1—C6—C13 | 129.7 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 62.6 (4) | C13—C6—C7—C12 | −27.2 (5) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −55.8 (4) | C13—C6—C7—C8 | 154.6 (4) |
| N1—C1—C14—O1 | 20.7 (6) | C14—C1—N1—C6 | 89.9 (4) |
| N1—C1—C14—O2 | −163.5 (3) | C14—C1—N1—C5 | −97.1 (4) |
| N1—C6—C7—C12 | −154.4 (4) | C14—C1—C2—C3 | 67.6 (4) |
| N1—C6—C7—C8 | 27.4 (5) | C14—O2—C15—C16 | 120.1 (6) |
| N1—C5—C4—C3 | 9.0 (5) | C17—C3—C4—C5 | −162.9 (3) |
| O3—N2—C17—C3 | 32.8 (5) | O4—N2—C17—C3 | −148.7 (4) |
| C2—C1—N1—C6 | −148.5 (3) | C4—C3—C17—N2 | −178.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—N1—C5 | 24.4 (5) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −1.2 (6) |
| C2—C1—C14—O1 | −102.9 (4) | C12—C11—C10—C9 | −0.1 (8) |
| C2—C1—C14—O2 | 72.9 (4) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.7 (7) |
| C2—C3—C17—N2 | 62.0 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.4 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −40.0 (4) | C15—O2—C14—O1 | 10.7 (7) |
| C6—N1—C5—S1 | −5.2 (5) | C15—O2—C14—C1 | −165.2 (4) |
| C6—N1—C5—C4 | 172.2 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C16—H16A···O3 | 0.96 | 2.49 | 3.419 (8) | 163 |
| C2—H2A···O1i | 0.97 | 2.55 | 3.404 (5) | 147 |
| C17—H17B···O3ii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.380 (6) | 140 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU5036).
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Ballini, R., Palmieri, A. & Righi, P. (2007). Tetrahedron, 63, 12099–12121.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Leung, D., Abbenante, G. & Fairlie, D. P. (2000). J. Med. Chem. 43, 305–341. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mukaiyama, T. & Hoshino, T. J. (1960). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 82, 5339–5342.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Pinnick, H. W. (1990). Org. React. 38, 655-792.
- Poupart, M. A., Fazal, G., Goulet, S. & Mar, L. T. (1999). J. Org. Chem. 64, 1356–1361.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sośnicki, J. G. (2009). Tetrahedron, 65, 1336-1348.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tamaru, Y., Harada, T., Iwamoto, H. & Yoshida, Z. (1978). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100, 5221–5223.
- Tamaru, Y., Harada, T. & Yoshida, Z. (1979). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101, 1316–1318.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036Isup2.hkl
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036fig1.tif
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
a . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014026711/su5036fig2.tif
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 for details; H atoms not involved in the intermolecular hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity).
CCDC reference: 1037775
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


