Abstract
In the title compound, C15H11ClN2O4, the central β-lactam ring is approximately planar [maximum deviation = 0.044 (2) Å for the N atom from the mean plane] and subtends dihedral angles of 61.17 (11) and 40.21 (12) °, respectively, with the nitro and chlorobenzene rings. Both substituents lie to the same side of the β-lactam core. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into C(4) chains propagating in [010]. The chains are cross-linked by C—H⋯O and weak C—H⋯π interactions, generating a three-dimensional network. The solvent molecules were found to be highly disordered and their contribution to the scattering was removed with the SQUEEZE procedure in PLATON [Spek (2009 ▸). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155], which indicated a solvent cavity of volume 318 Å3 containing approximately 114 electrons. These solvent molecules are not considered in the given chemical formula and other crystal data.
Keywords: crystal structure, β-lactam ring, C(4) chain, hydrogen bonding, N-unsubstituted 2-azetidinone, hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯π interactions
Related literature
For the application of N-unsubstituted 2-azetidinones in the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics, see: Cossio et al. (1987 ▸); Jarrahpour & Zarei (2007 ▸, 2008 ▸). For a related structure with a β-lactam ring, see: Butcher et al. (2011 ▸).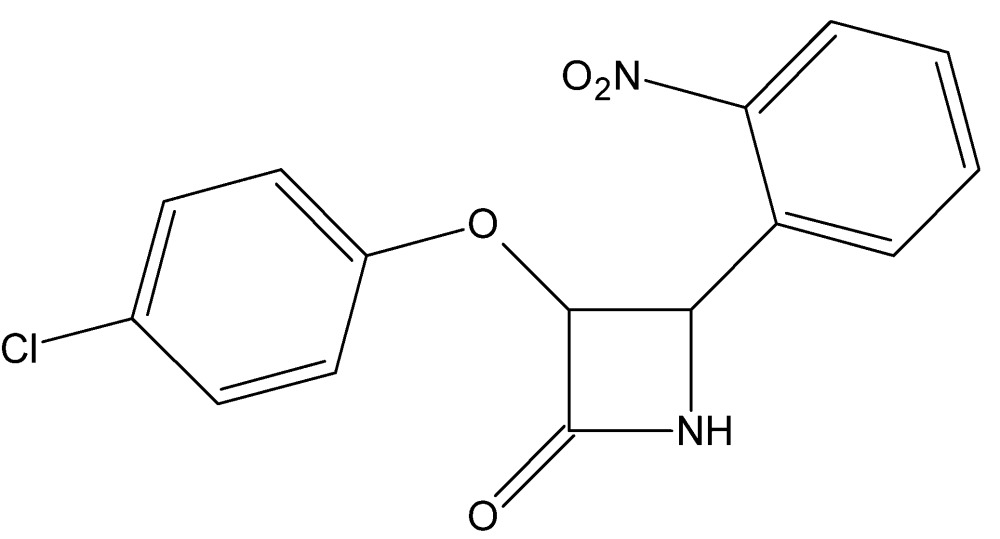
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H11ClN2O4
M r = 318.71
Monoclinic,

a = 16.9505 (4) Å
b = 4.6517 (1) Å
c = 21.7167 (6) Å
β = 99.757 (1)°
V = 1687.56 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.30 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
16293 measured reflections
4358 independent reflections
3158 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.049
wR(F 2) = 0.135
S = 1.04
4358 reflections
199 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322fig1.tif
View of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms drawn at the 30% probability level.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322fig2.tif
View of the hydrogen bonding of the title compound along b axis. Only H atoms involved in H bonding are shown.
CCDC reference: 1036035
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
Cg2 is the centroid of the nitrobenzene ring (C4C9).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1H1O1i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.936(2) | 166 |
| C8H8O3ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.307(2) | 142 |
| C15H15O2iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.338(2) | 149 |
| C3H3Cg2iv | 0.98 | 2.70 | 3.5118(19) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the X-ray laboratory of Dicle University Scientific and Technological Applied and Research Center, Diyarbakir, Turkey, for use of the X-ray diffractometer. AJ and HAS thank the Shiraz University Research Council for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Comment
N-Unsubstituted 2-azetidinones offer major synthetic opportunities in the synthesis of β-lactam antibiotics such as the carbapenems, penams, monobactams, nocardicins, and the glutamine synthetase inhibitor, tabtoxin (Cossio, et al., 1987) The application of N-unsubstituted 2-azetidinones in the semi-synthesis of the anticancer agents, Taxol and Taxotere has also been reported (Jarrahpour, et al., 2007). N-Unsubstituted 2-azetidinones have been prepared by several methods. Among these methods, oxidative cleavage by ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) of p-alkoxyphenyl moiety attached to the nitrogen of the β-lactam ring offers the most direct synthesis of N-unsubstituted β-lactams (Jarrahpour, et al., 2008).
In the title compound (Fig. 1), the β-lactam ring is nearly planar with a maximum deviation of 0.044 (2) Å for N1 from the mean plane. The carboxyl O atom O1 attached to the β-lactam ring deviates by -0.137 (1) Å from the mean plane of the ring. The β-lactam ring makes dihedral angles of 61.17 (11) and 40.21 (12) ° with the nitro and choloro-benzene rings, respectively.
All bond lengths and angles are comparable with those reported in a related structure (Butcher et al., 2011).
In the crystal, molecules are linked into [010] C(4) chains by N—H···O hydrogen bonds. C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Fig. 2) and weak C—H···π interactions link the chains into a three-dimensional network (Table 1).
S2. Experimental
A solution of (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6 (CAN) (3.00 mmol) in water (15.00 ml) was added dropwise to a solution of β-lactam (1.00 mmol) in CH3CN (30.00 ml) at room temperature and stirred for 45 min. Then water (30.00 ml) was added and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc (3 × 20 ml) and washed with 10% of NaHCO3 (40 ml). The aqueous layer of NaHCO3 was extracted again with EtOAc (15 ml), and all organic extracts were combined and washed successively with 10% NaHSO3 (2×30 ml), 10% NaHCO3 (20 ml), brine (20 ml) and then dried over sodium sulfate. After filtration and evaporation of the solvent in vacuo, the crude product was purified by column chromatography or recrystallization from hexane/EtOAc (4:6) solution to give colourless prisms (Yield 75%). Mp 350–352 K IR (KBr, cm-1): 1774 (CO β-lactam), 3217 (NH). 1H NMR (250 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ(p.p.m.): 5.74 (H-3, d, 1H, J=5.5 Hz), 6.23 (H-4, d, 1H, J=5.5 Hz), 7.27–8.15 (aromatic H, m, 8H), 9.13 (NH, brs, 1H). 13C NMR (62.9 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ(p.p.m.): 54.60 (C-4), 83.18 (C-3), 117.5, 124.7, 125.9, 128.7, 128.9, 129.1, 132.8, 134.4, 147.4, 155.8 (aromatic carbons), 165.90 (CO, β- lactam). Analysis calculated for C15H11ClN2O4: C, 51.01; H, 2.85; N, 7.93%. Found: C, 51.03; H, 2.87; N, 7.91%.
S3. Refinement
C and N-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93 - 0.98 Å and N—H =0.86 Å), and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N). The twenty two reflections were omitted owing to bad disagreement. The crystal quality and data was not good enough. A region of disordered electron density, most probably disordered solvent molecules, occupying voids of ca 318 Å3 for an electron count of 114, was removed with the SQUEEZE procedure in PLATON [Spek (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155] following unsuccessful attempts to model it as a plausible solvent molecule. Their formula mass and unit-cell characteristics were not taken into account during refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.

View of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.

View of the hydrogen bonding of the title compound along b axis. Only H atoms involved in H bonding are shown.
Crystal data
| C15H11ClN2O4 | F(000) = 656 |
| Mr = 318.71 | Dx = 1.254 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 6230 reflections |
| a = 16.9505 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–28.7° |
| b = 4.6517 (1) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 21.7167 (6) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 99.757 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1687.56 (7) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3158 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | Rint = 0.022 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 28.8°, θmin = 1.7° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −21→22 |
| 16293 measured reflections | k = −6→6 |
| 4358 independent reflections | l = −28→29 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.049 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.135 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0607P)2 + 0.3362P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 4358 reflections | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.77735 (3) | 0.02466 (16) | 0.86934 (3) | 0.0896 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.34325 (8) | 0.4694 (3) | 0.80529 (6) | 0.0684 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.49880 (7) | 0.6846 (3) | 0.60857 (6) | 0.0615 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.53550 (8) | 0.3225 (3) | 0.55969 (6) | 0.0686 (5) | |
| O4 | 0.46717 (6) | 0.2832 (2) | 0.71337 (5) | 0.0437 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.30955 (8) | 0.6612 (4) | 0.70465 (6) | 0.0523 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.48444 (8) | 0.4599 (3) | 0.58069 (6) | 0.0440 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.35588 (9) | 0.5438 (4) | 0.75408 (7) | 0.0462 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.42874 (8) | 0.5444 (3) | 0.72098 (7) | 0.0374 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.36874 (9) | 0.6469 (4) | 0.66256 (7) | 0.0399 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.34857 (9) | 0.4352 (3) | 0.60981 (7) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.27331 (10) | 0.3099 (4) | 0.59775 (8) | 0.0503 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.25251 (11) | 0.1159 (5) | 0.54958 (9) | 0.0632 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.30631 (13) | 0.0396 (4) | 0.51201 (9) | 0.0625 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.38224 (11) | 0.1547 (4) | 0.52289 (7) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.40248 (9) | 0.3484 (3) | 0.57097 (7) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.54003 (8) | 0.2358 (3) | 0.75211 (7) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.55796 (12) | 0.3387 (5) | 0.81220 (8) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.63188 (13) | 0.2760 (6) | 0.84797 (8) | 0.0733 (8) | |
| C13 | 0.68458 (10) | 0.1055 (5) | 0.82418 (8) | 0.0559 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.66690 (10) | 0.0022 (4) | 0.76469 (9) | 0.0555 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.59401 (9) | 0.0697 (4) | 0.72819 (8) | 0.0470 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.26120 | 0.72420 | 0.69920 | 0.0630* | |
| H2 | 0.46700 | 0.69550 | 0.73710 | 0.0450* | |
| H3 | 0.38230 | 0.83720 | 0.64800 | 0.0480* | |
| H5 | 0.23580 | 0.35770 | 0.62280 | 0.0600* | |
| H6 | 0.20140 | 0.03640 | 0.54260 | 0.0760* | |
| H7 | 0.29160 | −0.08920 | 0.47930 | 0.0750* | |
| H8 | 0.41950 | 0.10220 | 0.49800 | 0.0610* | |
| H11 | 0.52090 | 0.44930 | 0.82870 | 0.0790* | |
| H12 | 0.64530 | 0.35050 | 0.88810 | 0.0880* | |
| H14 | 0.70350 | −0.11280 | 0.74870 | 0.0670* | |
| H15 | 0.58190 | 0.00190 | 0.68740 | 0.0560* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0624 (3) | 0.1234 (6) | 0.0723 (3) | 0.0190 (3) | −0.0193 (3) | 0.0066 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0550 (7) | 0.1050 (12) | 0.0494 (7) | −0.0149 (7) | 0.0209 (6) | 0.0013 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0577 (7) | 0.0584 (9) | 0.0733 (8) | −0.0162 (6) | 0.0251 (6) | −0.0204 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0539 (7) | 0.0755 (10) | 0.0824 (9) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0291 (7) | −0.0164 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0356 (5) | 0.0379 (7) | 0.0547 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | −0.0002 (4) | −0.0061 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0371 (7) | 0.0678 (11) | 0.0547 (8) | 0.0115 (7) | 0.0153 (6) | −0.0048 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0467 (7) | 0.0474 (9) | 0.0407 (6) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0152 (5) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0556 (11) | 0.0471 (8) | −0.0065 (7) | 0.0130 (6) | −0.0086 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0338 (7) | 0.0349 (9) | 0.0448 (7) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0107 (6) | −0.0054 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0388 (7) | 0.0364 (9) | 0.0468 (8) | 0.0046 (6) | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0385 (7) | 0.0336 (8) | 0.0408 (7) | 0.0029 (6) | 0.0058 (6) | 0.0060 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0383 (8) | 0.0536 (11) | 0.0582 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0038 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0496 (10) | 0.0607 (13) | 0.0722 (12) | −0.0118 (9) | −0.0102 (9) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0732 (13) | 0.0551 (12) | 0.0522 (9) | −0.0058 (10) | −0.0093 (9) | −0.0082 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0623 (10) | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0051 (7) | −0.0030 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0431 (8) | 0.0354 (9) | 0.0375 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0390 (9) | 0.0424 (7) | −0.0039 (6) | 0.0069 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0613 (11) | 0.0918 (17) | 0.0446 (9) | 0.0206 (11) | 0.0075 (8) | −0.0113 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0692 (12) | 0.1051 (19) | 0.0405 (9) | 0.0120 (12) | −0.0056 (8) | −0.0085 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0451 (9) | 0.0680 (13) | 0.0511 (9) | 0.0025 (9) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0074 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0402 (8) | 0.0628 (13) | 0.0621 (10) | 0.0075 (8) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0067 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0396 (8) | 0.0516 (11) | 0.0481 (8) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0101 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C13 | 1.7474 (18) | C8—C9 | 1.378 (2) |
| O1—C1 | 1.218 (2) | C10—C15 | 1.366 (2) |
| O2—N2 | 1.2118 (19) | C10—C11 | 1.375 (2) |
| O3—N2 | 1.2245 (19) | C11—C12 | 1.389 (3) |
| O4—C2 | 1.4016 (17) | C12—C13 | 1.360 (3) |
| O4—C10 | 1.3891 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.363 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.335 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.386 (2) |
| N1—C3 | 1.469 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9800 |
| N2—C9 | 1.464 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.531 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.560 (2) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.505 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.387 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C9 | 1.404 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.370 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.377 (3) | ||
| C2—O4—C10 | 116.71 (11) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.42 (18) |
| C1—N1—C3 | 96.38 (13) | C11—C12—C13 | 119.89 (18) |
| O2—N2—O3 | 122.79 (14) | Cl1—C13—C14 | 119.24 (15) |
| O2—N2—C9 | 118.87 (13) | Cl1—C13—C12 | 119.92 (14) |
| O3—N2—C9 | 118.34 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.82 (17) |
| O1—C1—N1 | 132.86 (15) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.57 (17) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 135.24 (15) | C10—C15—C14 | 120.02 (16) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 91.90 (12) | O4—C2—H2 | 112.00 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 132.00 | C1—C2—H2 | 112.00 |
| C3—N1—H1 | 132.00 | C3—C2—H2 | 112.00 |
| O4—C2—C1 | 118.81 (12) | N1—C3—H3 | 112.00 |
| O4—C2—C3 | 114.90 (12) | C2—C3—H3 | 112.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 85.17 (11) | C4—C3—H3 | 112.00 |
| N1—C3—C2 | 85.85 (11) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 116.85 (14) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 114.34 (14) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 123.94 (14) | C7—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.12 (14) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.00 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 115.94 (14) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.75 (16) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.68 (18) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.63 (18) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.33 (16) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.00 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 116.69 (14) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C4—C9—C8 | 122.66 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| N2—C9—C4 | 120.65 (13) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.00 |
| C11—C10—C15 | 120.23 (15) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.00 |
| O4—C10—C11 | 123.40 (14) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| O4—C10—C15 | 116.34 (13) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.00 |
| C10—O4—C2—C3 | 156.31 (12) | C2—C3—C4—C9 | −70.06 (19) |
| C2—O4—C10—C11 | 32.5 (2) | C3—C4—C9—N2 | 1.0 (2) |
| C2—O4—C10—C15 | −149.62 (14) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | −179.81 (15) |
| C10—O4—C2—C1 | −105.11 (15) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.68 (17) |
| C3—N1—C1—C2 | 6.71 (14) | C9—C4—C5—C6 | −1.2 (2) |
| C3—N1—C1—O1 | −173.8 (2) | C5—C4—C9—N2 | −178.08 (14) |
| C1—N1—C3—C2 | −6.60 (14) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | 1.1 (2) |
| C1—N1—C3—C4 | 111.06 (16) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.3 (3) |
| O3—N2—C9—C4 | 158.62 (14) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.8 (3) |
| O2—N2—C9—C8 | 158.71 (15) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.9 (3) |
| O3—N2—C9—C8 | −20.7 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | −0.1 (2) |
| O2—N2—C9—C4 | −22.0 (2) | C7—C8—C9—N2 | 179.17 (15) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −6.30 (14) | O4—C10—C11—C12 | 178.78 (18) |
| N1—C1—C2—O4 | −122.13 (15) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 1.0 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—O4 | 58.4 (3) | O4—C10—C15—C14 | −177.37 (15) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 174.2 (2) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.6 (3) |
| O4—C2—C3—N1 | 125.34 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −2.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—N1 | 5.73 (12) | C11—C12—C13—Cl1 | −179.60 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −109.51 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 2.2 (4) |
| O4—C2—C3—C4 | 10.09 (19) | Cl1—C13—C14—C15 | −178.84 (15) |
| N1—C3—C4—C9 | −168.11 (14) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 108.95 (17) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.8 (3) |
| N1—C3—C4—C5 | 10.9 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 is the centroid of the nitrobenzene ring (C4–C9).
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.936 (2) | 166 |
| C8—H8···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.53 | 3.307 (2) | 142 |
| C15—H15···O2iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.338 (2) | 149 |
| C3—H3···Cg2iv | 0.98 | 2.70 | 3.5118 (19) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) x, y−1, z; (iv) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB7322).
References
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Butcher, R. J., Akkurt, M., Jarrahpour, A. & Badrabady, S. A. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1101–o1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cossio, F. P., Lecea, B. & Palomo, C. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 1743–1744.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Jarrahpour, A. & Zarei, M. (2007). Molecules, 12, 2364–2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jarrahpour, A. & Zarei, M. (2008). Synth. Commun. 38, 1837–1845.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322fig1.tif
View of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms drawn at the 30% probability level.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989014025845/hb7322fig2.tif
View of the hydrogen bonding of the title compound along b axis. Only H atoms involved in H bonding are shown.
CCDC reference: 1036035
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


