Abstract
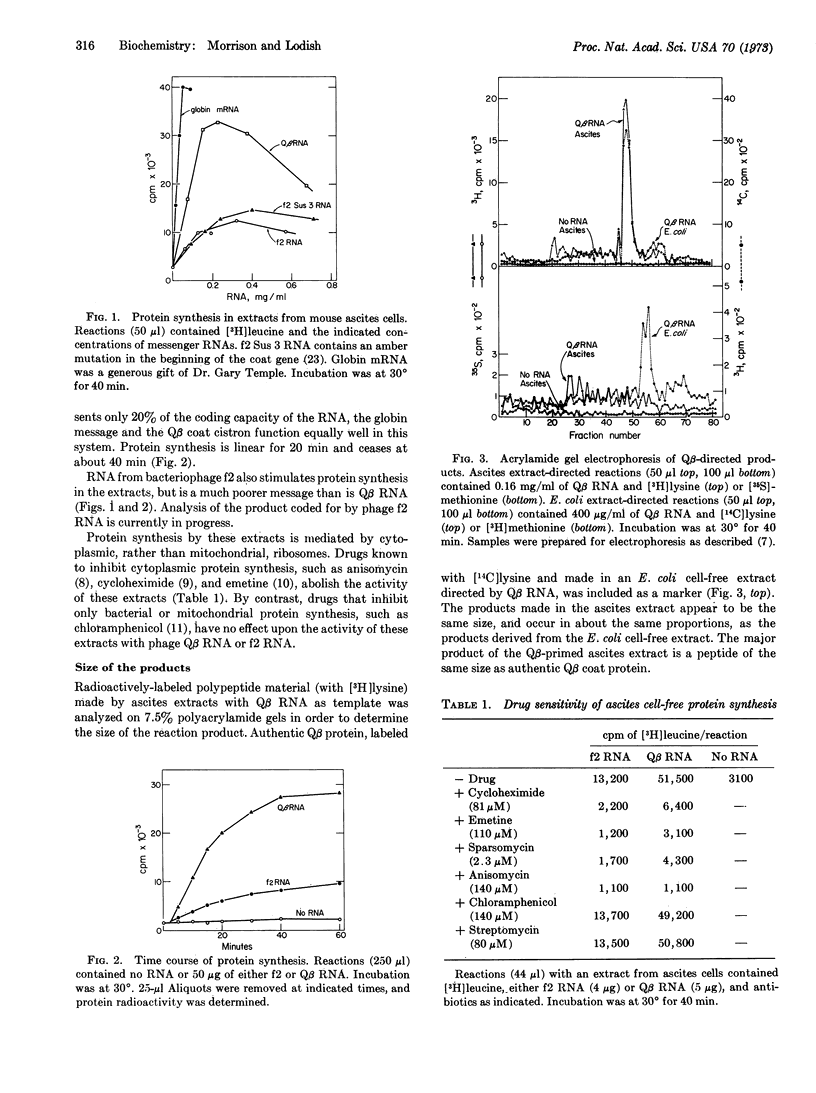
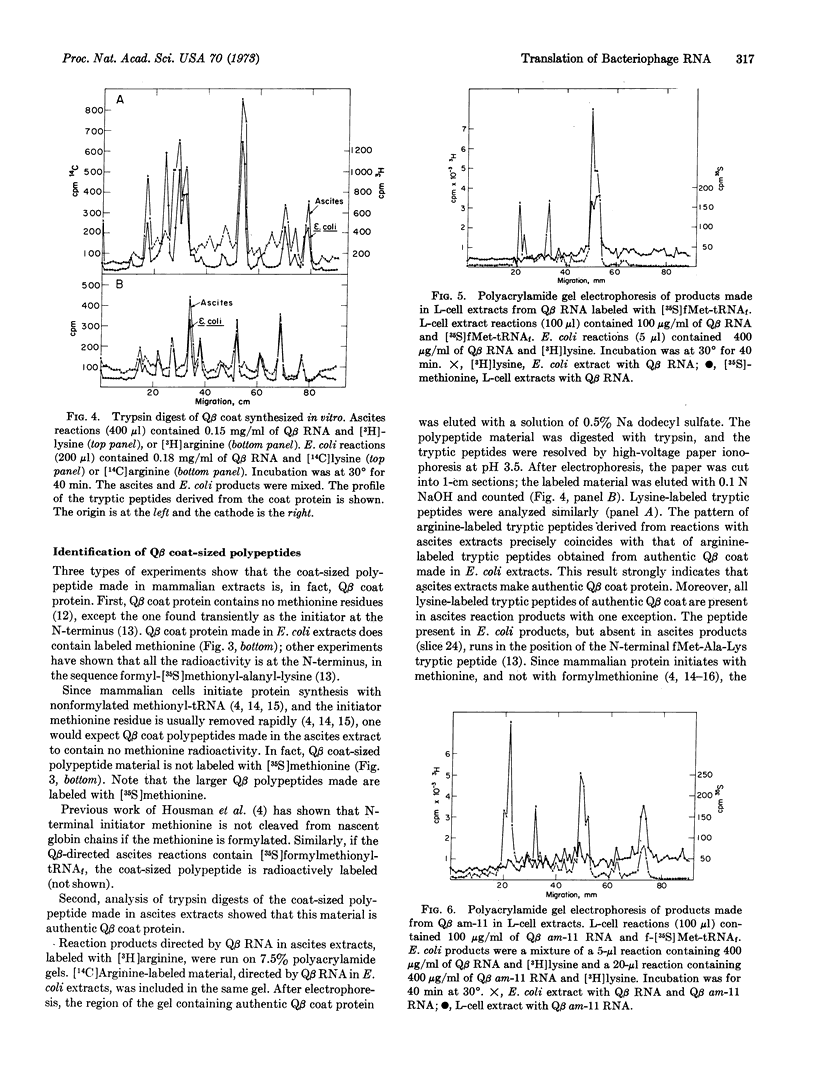
Cytoplasmic extracts from Krebs II mouse ascites cells and from L cells translate messenger RNA from coliphage Qβ with fidelity to produce products that migrate on polyacrylamide gels with those products directed by Qβ RNA in an Escherichia coli cell-free system. The mammalian cell extracts correctly initiate and terminate Qβ coat protein synthesis, as shown by: (i) [3H]lysine-and [3H]arginine-labeled tryptic peptides derived from the coat-sized product resemble these from authentic Qβ coat protein, (ii) Qβ coat (which contains methionine only at the N-terminal end) can be radioactively labeled with methionine only if the methionine is formylated, and (iii) L cell extracts directed by Qβ am-11 (an amber mutant in the coat protein) RNA make no completed coat-sized material, but do make a peptide the size of the authentic amber coat fragment.
Keywords: L cells, Krebs ascites cells, coat protein, tryptic peptides, N-formylmethionine
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. M., Capecchi M. R. N-formylmethionyl-sRNA as the initiator of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):147–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Initiation of E. coli proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1517–1524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhardt D. L., Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Amber mutants and polarity in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1967 Oct 14;29(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman E., Lodish H. F. Inhibition of replication of ribonucleic acid bacteriophage f2 by superinfection with bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):417–429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.417-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Inhibitors of protein biosynthesis. II. Mode of action of anisomycin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3226–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grollman A. P. Structural basis for inhibition of protein synthesis by emetine and cycloheximide based on an analogy between ipecac alkaloids and glutarimide antibiotics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1867–1874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi K., Webster R. E., Matsuhashi S. Gene products of bacteriophage Q beta. Virology. 1971 Aug;45(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90343-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Jacobs-Lorena M., Rajbhandary U. L., Lodish H. F. Initiation of haemoglobin synthesis by methionyl-tRNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):913–918. doi: 10.1038/227913a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R., Hunter T. Role of methionine in the initiation of haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):672–676. doi: 10.1038/227672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb A. J., Clark-Walker G. D., Linnane A. W. The biogenesis of mitochondria. 4. The differentiation of mitochondrial and cytoplasmic protein synthesizing systems in vitro by antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 23;161(2):415–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Mosteller R. D., Hardesty B. The mechanism of sodium fluoride and cycloheximide inhibition of hemoglobin biosynthesis in the cell-free reticulocyte system. J Mol Biol. 1966 Oct 28;21(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Bacteriophage f2 RNA: control of translation and gene order. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):345–350. doi: 10.1038/220345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Robertson H. D. Regulation of in vitro translation of bacteriophage f2 RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:655–673. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Secondary structure of bacteriophage f2 ribonucleic acid and the initiation of in vitro protein biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 28;50(3):689–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. An in vitro protein synthesizing system from mouse L fibroblasts infected with reovirus. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):724–733. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K., Villa-Komaroff L., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus messenger RNAs synthetesized in vitro into reovirus polypeptides by several mammalian cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2649–2653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K., Lodish H. F. Amino terminal peptides of RNA phage proteins synthesized in the cell free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):748–756. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T., Dixon G. H. Transient incorporation of methionine at the N-terminus of protamine newly synthesized in trout testis cells. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):676–680. doi: 10.1038/227676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Dintzis H. M. Protein chain initiation in rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1282–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., McDowell M. J., Joklik W. K. Essential and nonessential noncapsid reovirus proteins. Virology. 1971 Sep;45(3):716–723. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



