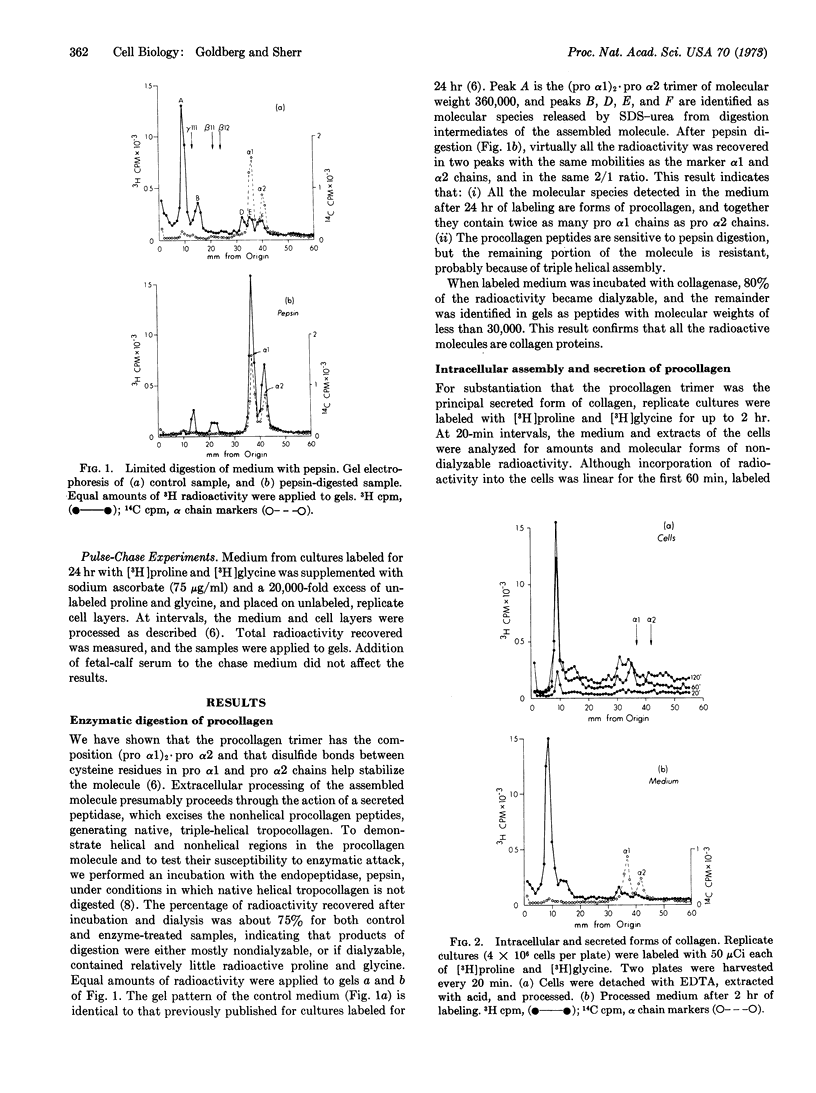
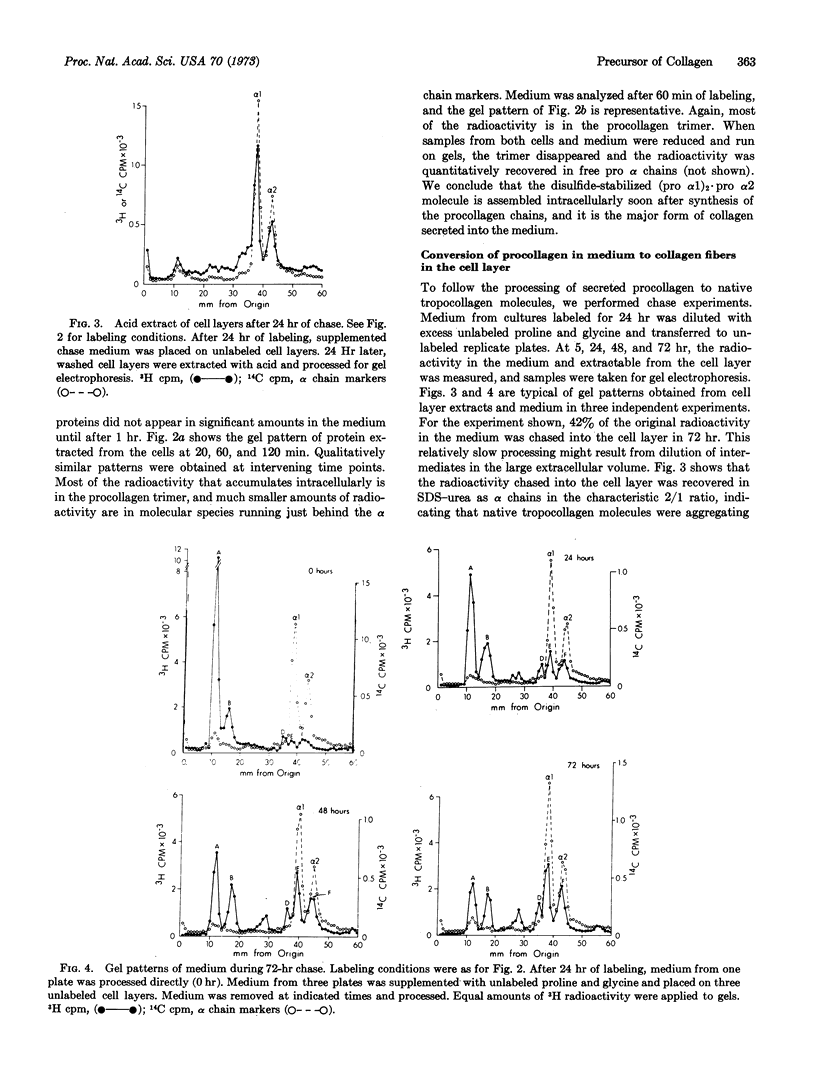
Abstract
Cultures of human diploid fibroblasts were labeled with radioactive proline and glycine, and the precursor of collagen (procollagen) in cells and medium was characterized by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A covalently assembled molecule with the composition (pro α1)2·pro α2 (approximate molecular weight, 360,000) appeared intracellularly soon after synthesis of the constituent chains, and could be detected in the medium after 60 min of labeling. The molecule was stabilized by disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in the amino-terminal procollagen peptide sequences of the three chains. Collagenase digested the molecule to peptides of 30,000 molecular weight or less. Limited digestion with pepsin excised nonhelical procollagen peptides, yielding native, triple-helical tropocollagen. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that a peptidase in the medium sequentially excised the nonhelical peptides from the molecule, generating tropocollagen molecules that aggregated as fibers in the cell layer. The excised, nonhelical procollagen peptides contained little or no proline or glycine. Intramolecular bonds of the lysyl aldehyde type were not detected in the secreted molecule, as reduction of the medium always resulted in quantitative recovery of free pro α chains in dodecyl sulfate-urea. Lysyl-derived, covalent bonds appeared to form between tropocollagen molecules aggregating in the cell layer. We suggest the term “pro-tropocollagen” for the assembled, secreted precursor of collagen.
Keywords: isotopic labeling, pulse-chase, pepsin digestion, gel electrophoresis
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellamy G., Bornstein P. Evidence for procollagen, a biosynthetic precursors of collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Ehrlich H. P., Wyke A. W. Procollagen: conversion of the precursor to collagen by a neutral protease. Science. 1972 Feb 4;175(4021):544–546. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4021.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Von der Mark K., Wyke A. W., Ehrlich H. P., Monson J. M. Characterization of the pro- 1 chain of procollagen. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2808–2813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Jimenez S. A., Olsen B. R., Prockop D. J. A transport form of collagen from embryonic tendon: electron microscopic demonstration of an NH 2 -terminal extension and evidence suggesting the presence of cystine in the molecule (chick embryo-tropocollagen-gel filtration). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Bornstein P. Further characterization of procollagen: the identification of a pro- 2 chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1750–1756. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Characterization of collagen peptides by sodium dodecylsulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jun;41(2):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG B., GREEN H. AN ANALYSIS OF COLLAGEN SECRETION BY ESTABLISHED MOUSE FIBROBLAST LINES. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jul;22:227–258. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg B., Epstein E. H., Jr, Sherr C. J. Precursors of collagen secreted by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., McGoodwin E. B., Martin G. R. The nature of the collagen synthesized by cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):454–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. K., McGoodwin E., Martin G. R. Studies on protocollagen: identification of a precursor of proto alpha 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell S. R., Martin G. R. The cross-linking of collagen and elastin: enzymatic conversion of lysine in peptide linkage to alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde (allysine) by an extract from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):708–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN A. L., PFAHL D., SPEAKMAN P. T., DAVISON P. F., SCHMITT F. O. Tropocollagen: significance of protease-induced alterations. Science. 1963 Jan 4;139(3549):37–39. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3549.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



