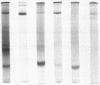
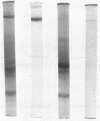
Abstract
Two antigens that exist in high frequency in tumor tissues of patients with Hodgkin's disease have been obtained in relatively concentrated form. Extracts of Hodgkin's spleen tumor tissue, when subjected to chromatography on Sephadex G-200, separate into three major protein peaks of which only the first (peak I) possesses the predominant antigenic activities associated with the disease. Antigenic analysis performed with hyperimmune rabbit antisera obtained after repeated immunizations with peak I proteins demonstrated that this fraction contained both F and S antigens associated with Hodgkin's disease and small contaminant amounts of an antigen associated with normal lymphocytes. The tissue distribution patterns of the Hodgkin's disease tumor-associated antigens suggest that they both originate in lymphoid tissues and that the F antigen may represent a product of reactive lymphocytes while the S antigen may be a dedifferentiation antigen expressed in very immature lymphocytes.
Keywords: spleen, lymph nodes, fetal liver, F and S antigens
Full text
PDF
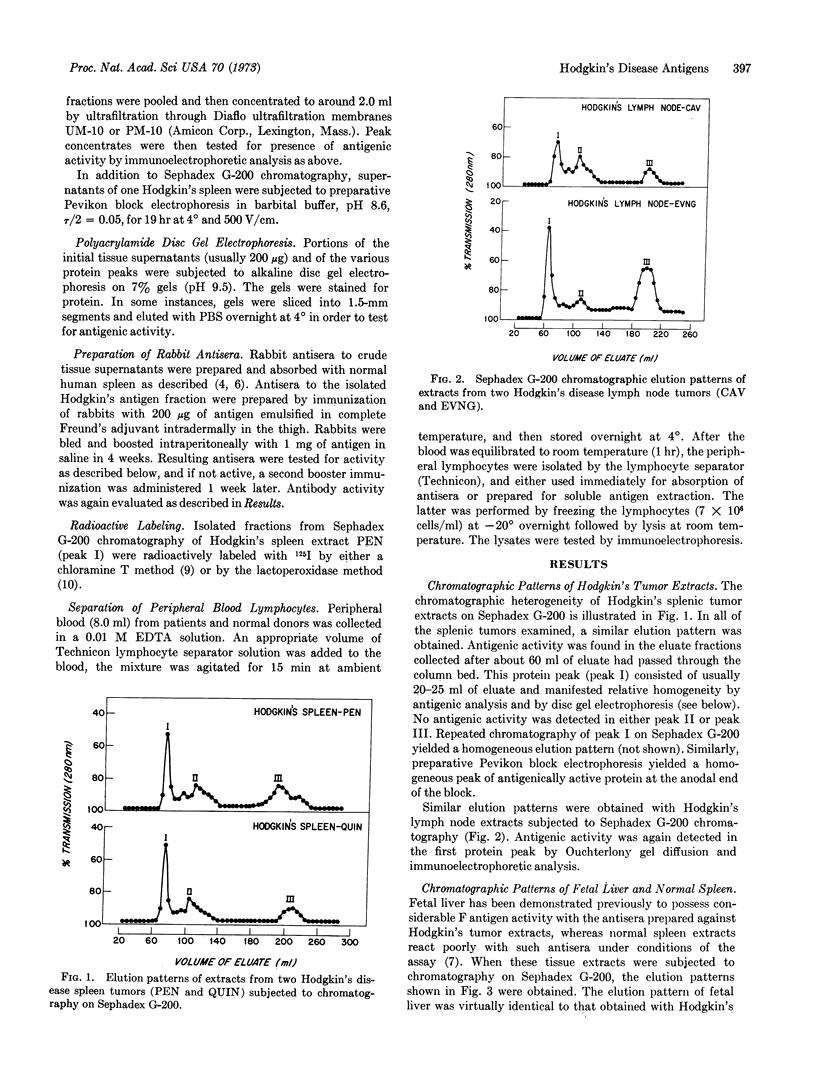
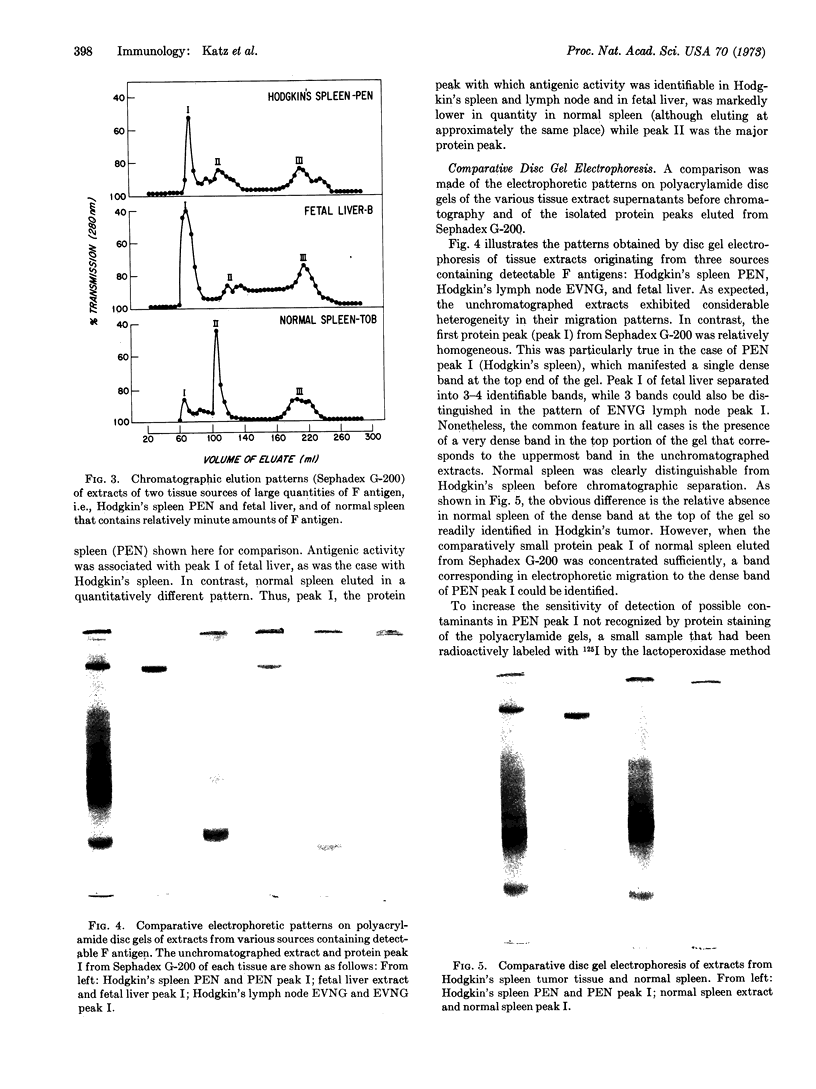

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casazza A. R., Duvall C. P., Carbone P. P. Summary of infectious complications occurring in patients with Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Res. 1966 Jun;26(6):1290–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GENDEL B. R., ENDE M., NORMAN S. L. Cryptococcosis; a review with special reference to apparent association with Hodgkin's disease. Am J Med. 1950 Sep;9(3):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90430-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Order S. E., Chism S. E., Hellman S. Studies of antigens associated with Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1972 Nov;40(5):621–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Order S. E., Porter M., Hellman S. Hodgkin's disease: evidence for a tumor-associated antigen. N Engl J Med. 1971 Aug 26;285(9):471–474. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197108262850901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]