Abstract
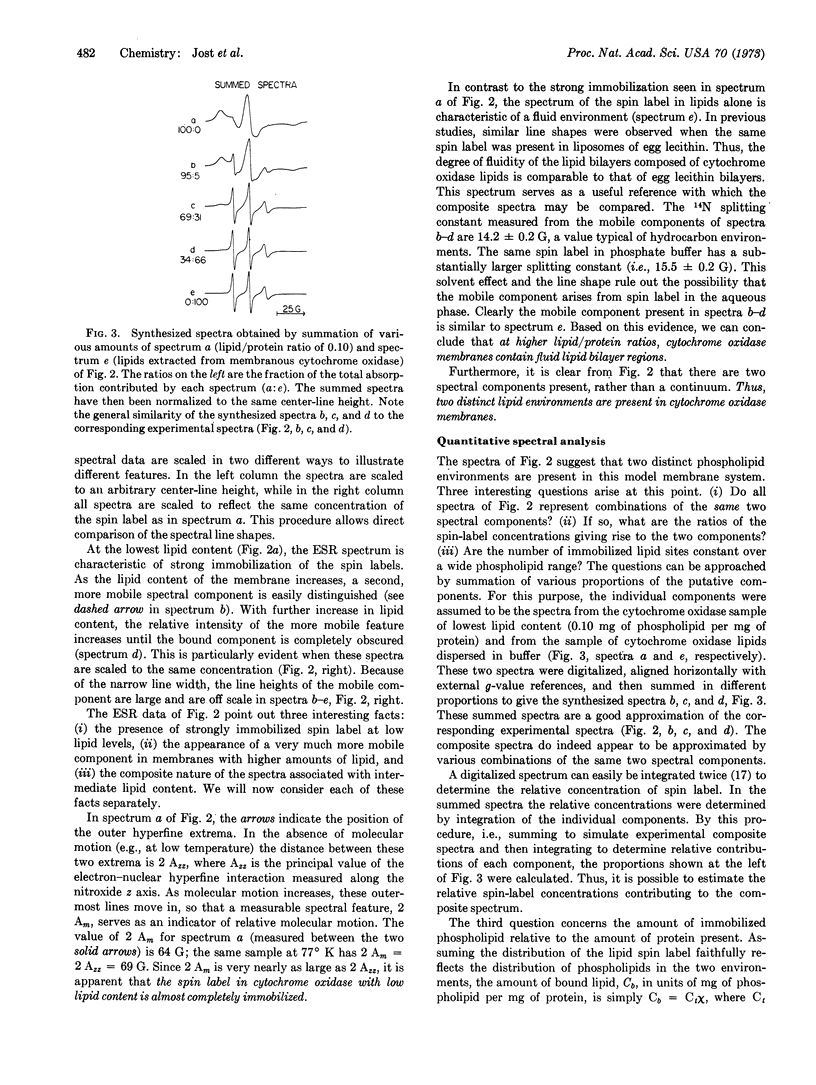
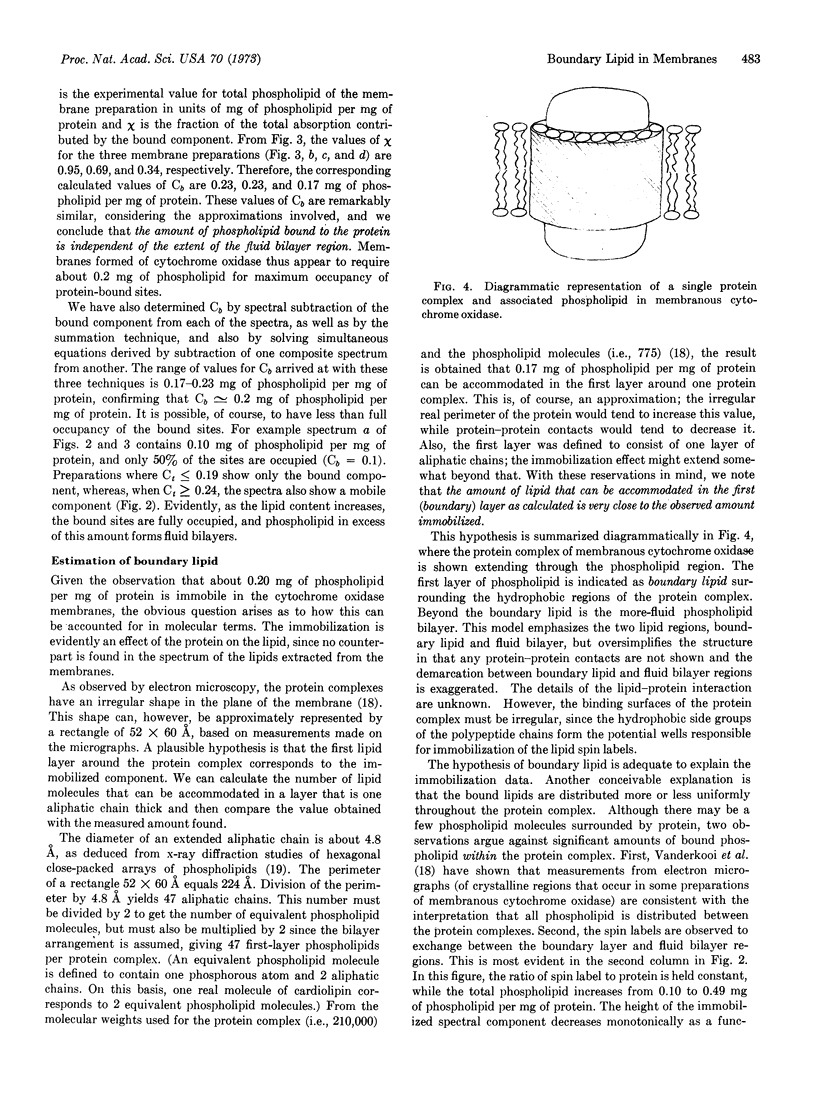
Cytochrome oxidase (EC 1.9.3.1) isolated from beef-heart mitochondria with an appropriate phospholipid content forms vesicular structures. Lipid-protein interactions in this model membrane system were studied with the lipid spin label, 16-doxylstearic acid. As the phospholipid/protein ratio is varied, two spectral components are observed. At low phospholipid/protein ratios (≤0.19 mg of phospholipid per mg of protein) the lipid spin label is highly immobilized. At higher phospholipid content an additional component characteristic of fluid lipid bilayers is evident. By summation of digitalized spectra and subsequent integration it was shown that all composite spectra could be approximated by assuming only two components are present, and that the amount of phospholipid bound to the protein is independent of the extent of the fluid bilayer region. The experimentally determined amount of phospholipid for maximum occupancy of protein-bound sites is about 0.2 mg of phospholipid per 1.0 mg of protein. Calculations show that this ratio is consistent with a single layer of phospholipid surrounding the protein complex. The data are interpreted as evidence for a boundary of immobilized lipid between the hydrophobic protein and adjacent fluid bilayer regions in this membrane model system.
Keywords: membranous cytochrome oxidase, spin label, electron spin resonance
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown L., Frank R., Fox L., Voekler R., York R., Sontag E. Effects of interval payment, task choice and high rate reinforcement contingencies on the production rate of trainable level retarded and severely emotionally disturbed students. Train Sch Bull (Vinel) 1974 Nov;71(3):195–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., GLENN J. L., GREEN D. E. Studies on the electron transfer system. IV. The electron transfer particle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Dec;22(3):475–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Green D. E. Membrane proteins and membrane structure. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Hayashi H. The polypeptide composition of cytochrome oxidase from beef heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 1;26(1):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80587-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M. Lipid bilayer structure in the membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90238-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. C., Kim J. J., Racker E. Ion transport and respiratory control in vesicles formed from cytochrome oxidase and phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1338–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasàitis A. A., Nemecek I. B., Severina I. I., Skulachev V. P., Smirnova S. M. Membrane potential generation by two reconstituted mitochondrial systems: liposomes inlayed with cytochrome oxidase or with ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 20;275(3):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Tillack T. W., Jackson R. L., Segrest J. P., Scott R. E. Chemical characterization and surface orientation of the major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1445–1449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell H. M., McFarland B. G. Physics and chemistry of spin labels. Q Rev Biophys. 1970 Feb;3(1):91–136. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000442x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steim J. M., Tourtellotte M. E., Reinert J. C., McElhaney R. N., Rader R. L. Calorimetric evidence for the liquid-crystalline state of lipids in a biomembrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):104–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun F. F., Prezbindowski K. S., Crane F. L., Jacobs E. E. Physical state of cytochrome oxidase. Relationship between membrane formation and ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 May 28;153(4):804–818. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi G. Molecular architecture of biological membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Jun 20;195:6–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi G., Senior A. E., Capaldi R. A., Hayashi H. Biological membrane structure. 3. The lattice structure of membranous cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):38–48. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. N., Jr A METHOD FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS QUANTITATIVE ESTIMATION OF CYTOCHROMES A, B, C1, AND C IN MITOCHONDRIA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Sep;107:537–543. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90313-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins M. H., Blaurock A. E., Engelman D. M. Bilayer structure in membranes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):72–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio230072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]