Abstract
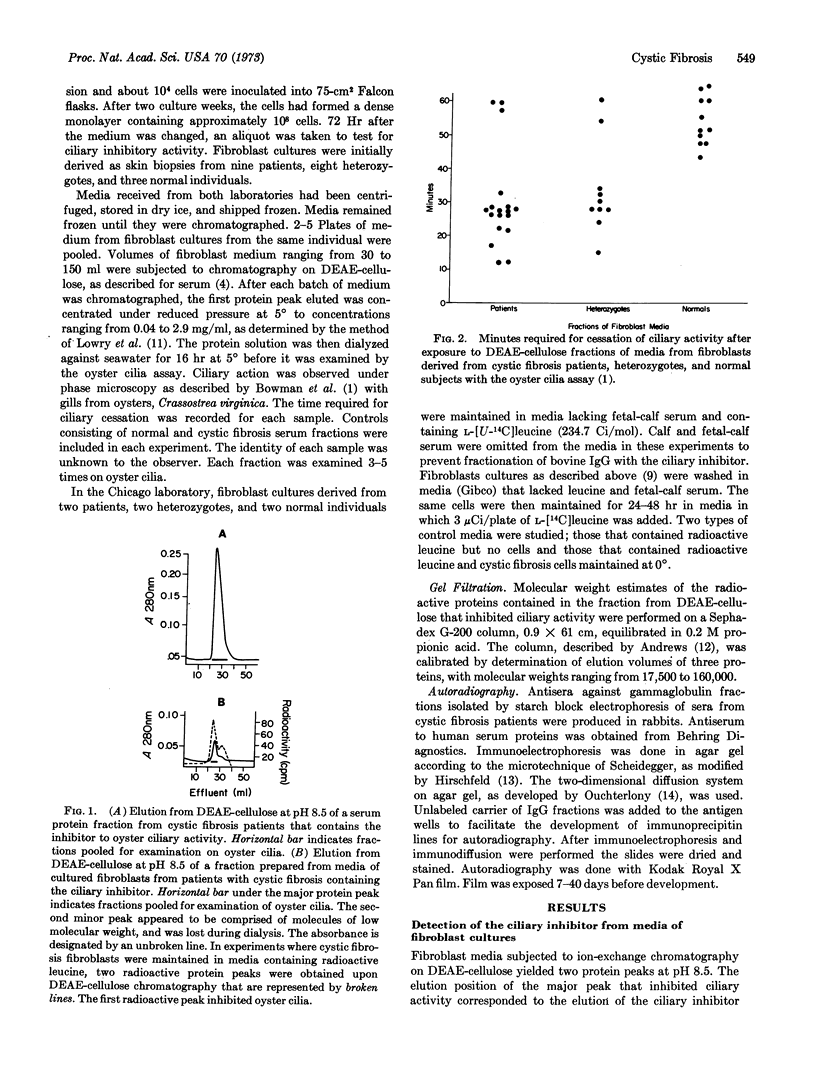
A chromatographic fraction has been identified in media from fibroblast cultures derived from 15 of 18 cystic fibrosis patients and 8 of 10 heterozygotes that inhibits ciliary activity, as judged by the oyster gill assay. The analogous fraction of media from cultures of fibroblasts derived from 11 normal individuals did not inhibit ciliary activity under the experimental conditions used. The chromatographic fractions containing the ciliary inhibitory activity from both fibroblast media and sera of cystic fibrosis patients and heterozygotes eluted in the same position from diethylaminoethyl-cellulose at pH 8.5.
Although the serum ciliary inhibitor had consistently been detected in a fraction that contained predominantly immunoglobulin G, results of the fractionation of fibroblast media demonstrate that the ciliary inhibitor is present in a protein fraction containing three species of different molecular weight and in which IgG cannot be detected by the techniques used.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis, cilia, fibroblast, oyster
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besley G. T., Patrick A. D., Norman A. P. Inhibition of the motility of gill cilia of Dreissensia by plasma of cystic fibrosis patients and their parents. J Med Genet. 1969 Sep;6(3):278–280. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.3.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. H., Lockhart L. H., McCombs M. L. Oyster ciliary inhibition by cystic fibrosis factor. Science. 1969 Apr 18;164(3877):325–326. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3877.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. H., McCombs M. L., Lockhart L. H. Cystic fibrosis: characterization of the inhibitor to ciliary action in oyster gills. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):871–873. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S., Bearn A. G. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. A study in cell culture. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):775–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S., Bearn A. G. Oyster ciliary inhibition by cystic fibrosis culture medium. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHFELD J. Immune-electrophoretic demonstration of qualitative differences in human sera and their relation to the haptoglobins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb04844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. Acid mucopolysaccharides in cultured fibroblasts of cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 30;33(6):954–958. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90405-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matalon R., Dorfman A. Hurler's syndrome: biosynthesis of acid mucopolysaccharides in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1310–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spock A., Heick H. M., Cress H., Logan W. S. Abnormal serum factor in patients with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. Pediatr Res. 1967 May;1(3):173–177. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196705000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



