Abstract
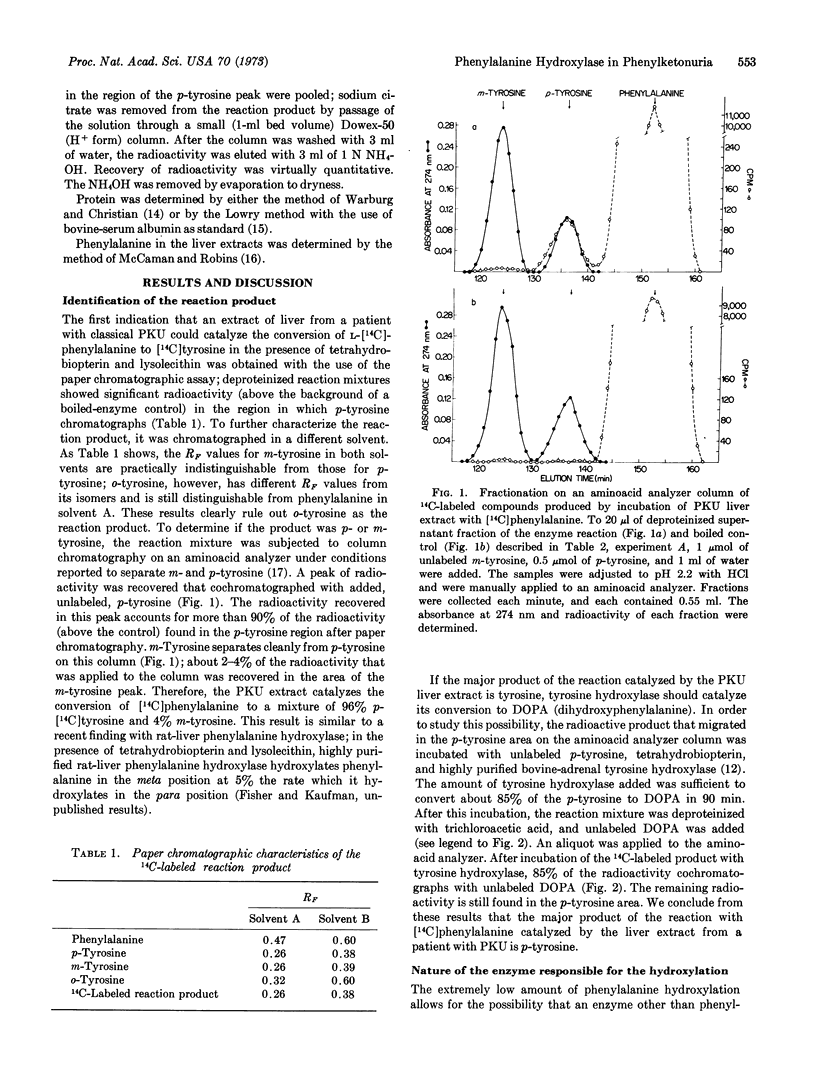
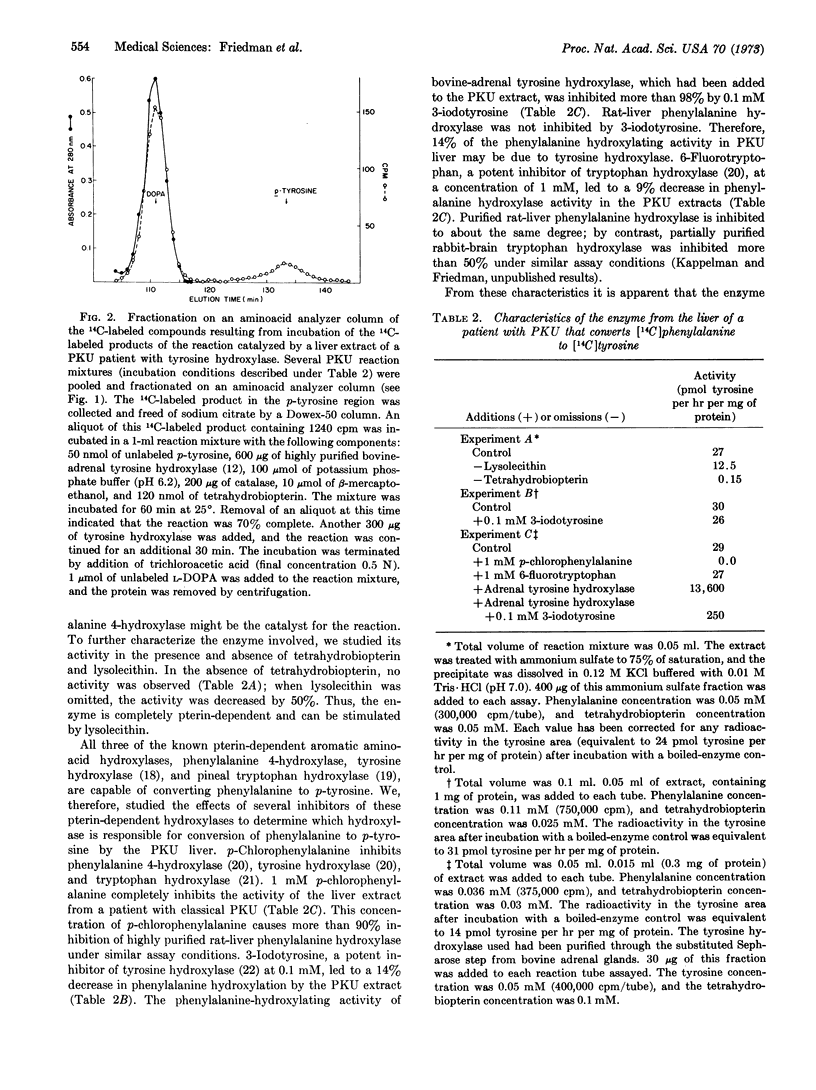
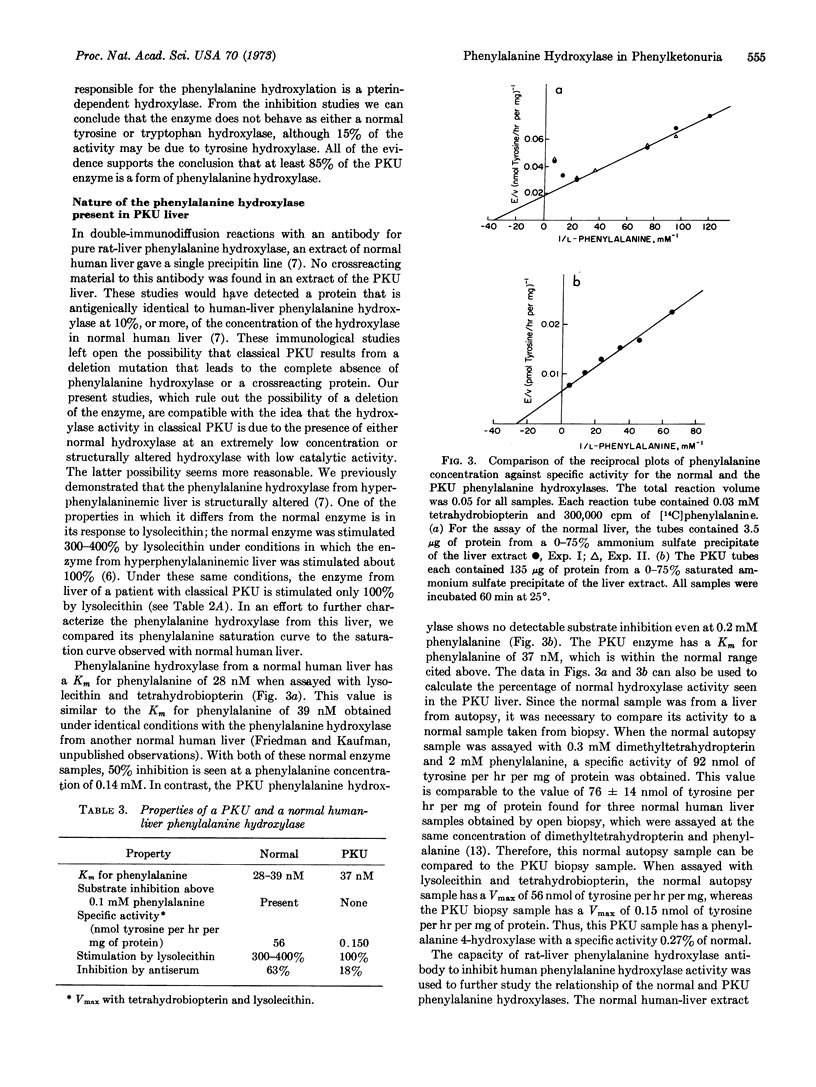
An extract from a liver biopsy of a patient with classical phenylketonuria contains phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.3.1) with a specific activity 0.27% of the normal activity of the hydroxylase. This enzyme from a patient with phenylketonuria is a structurally altered form of phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase that probably results from a mutation in the gene coding for the hydroxylase.
Keywords: genetic disease, tetrahydrobiopterin, lysolecithin
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fisher D. B., Kaufman S. The stimulation of rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase by phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2250–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. B., Kirkwood R., Kaufman S. Rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase, an iron enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5161–5167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kaufman S., Kang E. S. Nature of the molecular defect in phenylketonuria and hyperphenylalaninaemia. Nature. 1972 Nov 17;240(5377):157–159. doi: 10.1038/240157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm U., Knapp A., Tischer W., Schlenzka K. Phenylalaninhydroxylase-Aktivität bei Hyperphenylalaninämie und klassischer Phenylketonurie. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1972;28(3):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gál E. M., Roggeveen A. E., Millard S. A. DL-[2-14C]p-chlorophenylalanine as an inhibitor of tryptophan 5-hydroxylase. J Neurochem. 1970 Aug;17(8):1221–1235. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IKEDA M., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. HYDROXYLATION OF PHENYLALANINE BY PURIFIED PREPARATIONS OF ADRENAL AND BRAIN TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 17;18:482–488. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90778-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERVIS G. A. Phenylpyruvic oligophrenia deficiency of phenylalanine-oxidizing system. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Mar;82(3):514–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jequier E., Robinson D. S., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Further studies on tryptophan hydroxylase in rat brainstem and beef pineal. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 May;18(5):1071–1081. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice P., O'Flynn M. E., Hsia D. Y. Phenylalanine-hydroxylase activity in hyperphenylalaninaemia. Lancet. 1967 Apr 29;1(7496):928–929. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. Phenylalanine hydroxylation cofactor in phenylketonuria. Science. 1958 Dec 12;128(3337):1506–1508. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3337.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang E. S., Kaufman S., Gerald P. S. Clinical and biochemical observations of patients with atypical phenylketonuria. Pediatrics. 1970 Jan;45(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. A protein that stimulates rat liver phenylalanine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4751–4759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S., Fisher D. B. Purification and some physical properties of phenylalanine hydroxylase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S. Phenylalanine hydroxylase of human liver: assay and some properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Oct;134(1):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg W., Jequier E., Sjoerdsma A. Tryptophan hydroxylation: measurement in pineal gland, brainstem, and carcinoid tumor. Science. 1967 Jan 13;155(3759):217–219. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3759.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITOMA C., AULD R. M., UDENFRIEND S. On the nature of enzymatic defect in phenylpyruvic oligophrenia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Apr;94(4):634–635. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong J. H., D'Iorio A., Benoiton N. L. Formation of meta-tyrosine form L-phenylalanine by beef adrenal medulla. A new biosynthetic route to catecholamines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):229–236. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Zaltzman-Nirenberg P., Nagatsu T. Inhibitors of purified beef adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE H. W., MOLDAVE K., MEISTER A. Studies on conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine in phenylpyruvic oligophrenia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Apr;94(4):632–633. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



