Abstract
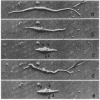
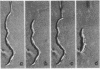
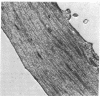
The contraction of isolated smooth-muscle cells has been correlated with evagination of the cell membrane, a marked change in myofilament orientation, and a decrease in cellular volume. Both localized and full contractions have been elicited in the same cell by varying the intensity of electrical stimulation. These results may be explained by a model of the smooth-muscle cell in which the contractile apparatus extends between attachment sites on the cell membrane that are relatively closely spaced.
Keywords: cell volume, cell membrane, myofilaments, contractile mechanism
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLINKS J. R. INFLUENCE OF OSMOTIC STRENGTH ON CROSS-SECTION AND VOLUME OF ISOLATED SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:42–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby R. M., Young A. M., Dotson R. S., Fisher B. A., McKinnon K. Contraction of single smooth muscle cells from Bufo marinus stomach. Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):351–352. doi: 10.1038/234351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. H., Fay F. S. Thick myofilaments in contracted and relaxed mammalian smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1972;71(2):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Huxley A. F., Julian F. J. The variation in isometric tension with sarcomere length in vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):170–192. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. E., Rice R. V. Ultrastructural studies on the contractile mechanism of smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Sep;42(3):683–694. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane B. P. Alterations in the cytologic detail of intestinal smooth muscle cells in various stages of contraction. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):199–213. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., MOLINARI S. Electron microscopy of muscular arteries; pial vessels of43 the cat and monkey. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Jun;3:447–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBLUTH J. SMOOTH MUSCLE: AN ULTRASTRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE DYNAMIC OF ITS CONTRACTION. Science. 1965 Jun 4;148(3675):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3675.1337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Squire J. M. Structural basis of contraction in vertebrate smooth muscle. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 14;67(1):117–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90390-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]