Abstract
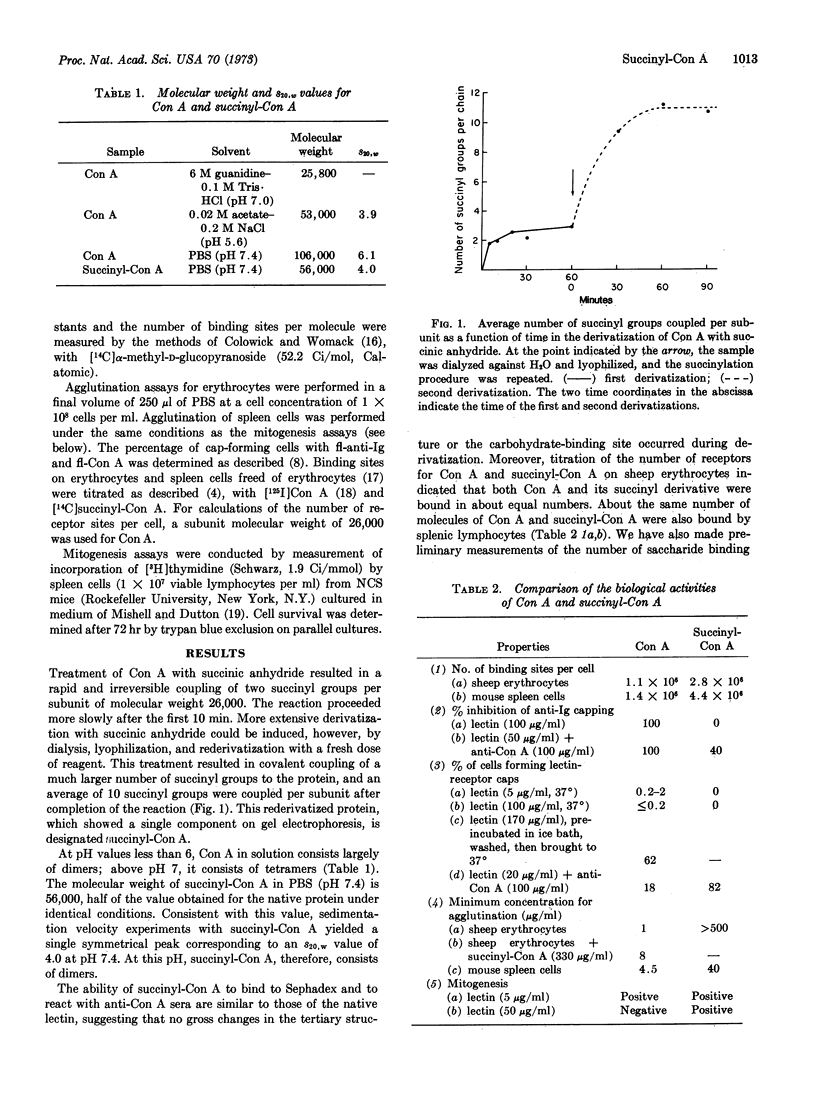
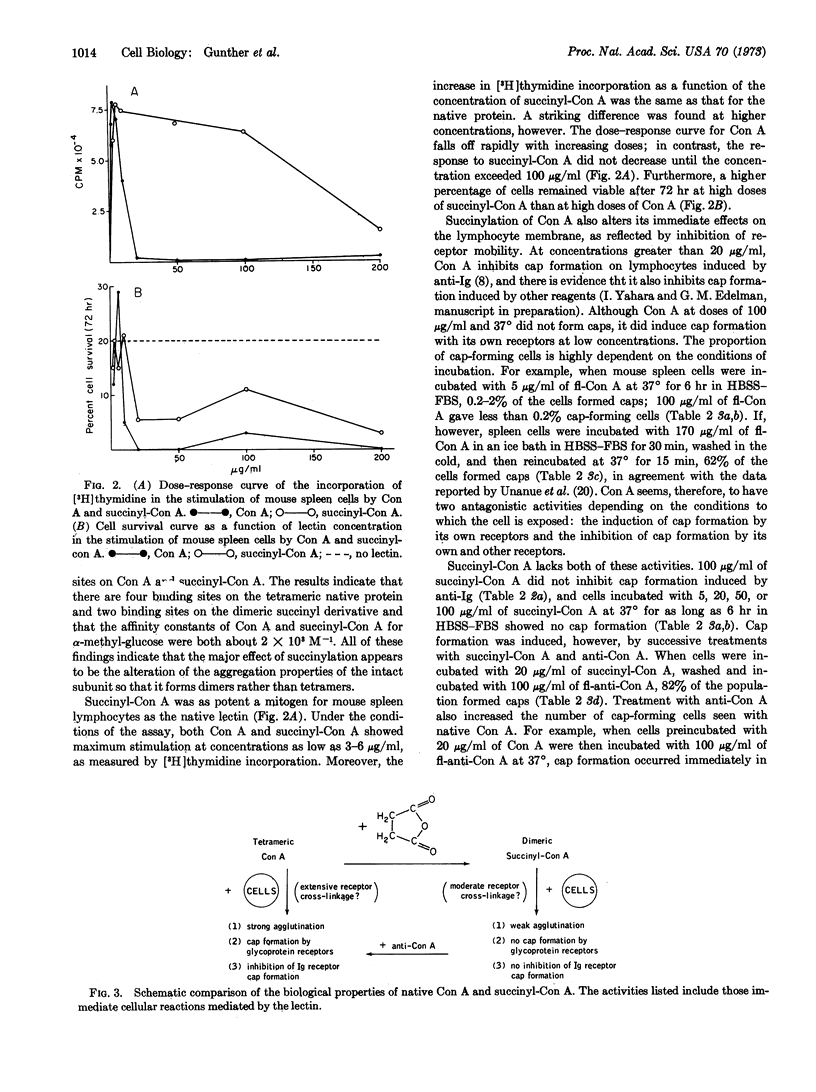
Chemical derivatization of tetrameric concanavalin A (Con A) with succinic anhydride or acetic anhydride converts the protein to a dimeric molecule without altering its carbohydrate-binding specificity. At low concentrations, the dose-response curves for the mitogenic stimulation of mouse spleen cells by native Con A and succinyl-Con A are similar. Above lectin concentrations of 10 μg/ml, however, the response to Con A is diminished, while that for succinyl-Con A does not decrease until much higher doses are reached. We have attributed this difference mainly to the higher rate of cell death induced by the native Con A molecule. Con A also shows a greater capacity than succinyl-Con A to agglutinate sheep erythrocytes and to inhibit cap formation by immunoglobulin receptors on spleen cells. Moreover, at low concentrations, Con A induced its glycoprotein receptors to form caps, but succinyl-Con A did not induce cap formation. Addition of antibodies directed against Con A to succinyl-Con A bound on cells restored the properties of agglutination, inhibition of immunoglobulin receptor cap formation, and induction of cap formation by Con A receptors. Similar results have been obtained for acetyl-Con A. These data suggest that the altered biological activities of succinyl-Con A and acetyl-Con A are attributable to their reduced valence.
Keywords: lectins, lymphocyte stimulation, membrane receptors
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berlin R. D. Effect of concanavalin A on phagocytosis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):44–45. doi: 10.1038/newbio235044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin R. D., Ukena T. E. Effect of colchicine and vinblastine on the agglutination of polymorpho-nuclear leucocytes by concanavalin A. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):120–122. doi: 10.1038/newbio238120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Goldstein G. Chromatographic purification of tetramethylrhodamine-immune globulin conjugates and their use in the cellular localization of rabbit gamma-globulin polypeptide chains. J Immunol. 1965 Aug;95(2):230–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colowick S. P., Womack F. C. Binding of diffusible molecules by macromolecules: rapid measurement by rate of dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Pflumm M. N., Edelman G. M. Isolation and proteolytic cleavage of the intact subunit of concanavalin A. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 15;11(17):3233–3239. doi: 10.1021/bi00767a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Reeke G. N., Jr, Becker J. W., Waxdal M. J., Wang J. L. The covalent and three-dimensional structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Millette C. F. Molecular probes of spermatozoan structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2436–2440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Hart D. A., Wells J. V., Nisonoff A. Requirement for cross-linkage in the stimulation of transformation of rabbit peripheral lymphocytes by antiglobulin reagents. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1484–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Easten A. The relationship between antigenic structure and the requirement for thymus-derived cells in the immune response. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):103–119. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Interaction of the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A with normal and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOWSKY D. S., ROSENAU W., MOON H. D. ISOLATION OF IMMUNOLOGICALLY COMPETENT LYMPHOCYTES FROM SENSITIZED MOUSE SPLEENS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Jan;115:77–79. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milthorp P., Forsdyke D. R. Inhibition of lymphocyte activation at high ratios of concanavalin A to serum depends on complement. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1351–1352. doi: 10.1038/2271351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Katchalski E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by concanavalin A and its reversion by methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell A. E., Leon M. A. Reversible interaction of human lymphocytes with the mitogen concanavalin A. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Oct;62(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. Structural changes in membranes of transformed lymphocytes demonstrated by freeze-etching. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao D. D., Lumry R., Rajender S. Modification of protein properties by change in charge. Succinylated chymotrypsinogen. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 18;29(2):377–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Perkins W. D., Karnovsky M. J. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. I. Analysis by immunofluorescence and ultrastructural radioautography. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):885–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Unusual fragments in the subunit structure of concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1130–1134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxdal M. J., Wang J. L., Pflumm M. N., Edelman G. M. Isolation and order of the cyanogen bromide fragments of concanavalin A. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3343–3347. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Reid B., James K. Effect of antilymphocytic antibody and antibody fragments on human lymphocytes in vitro. Nature. 1967 Aug 5;215(5101):591–594. doi: 10.1038/215591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



