Abstract
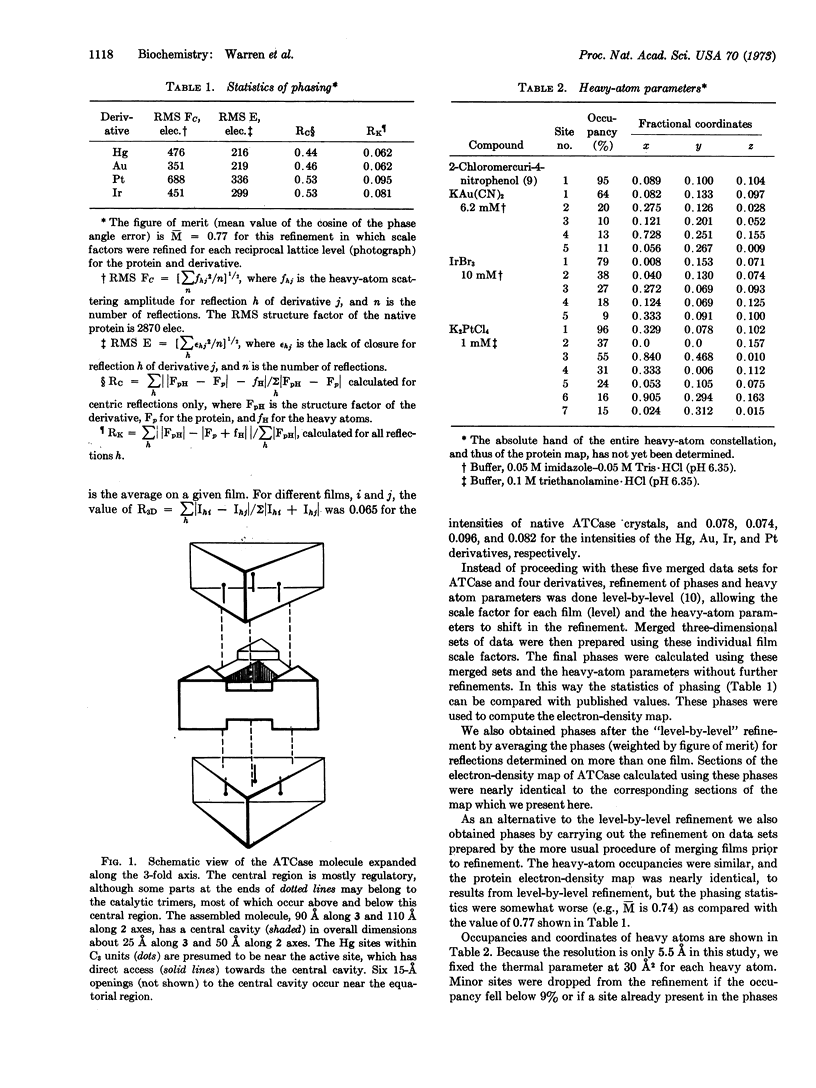
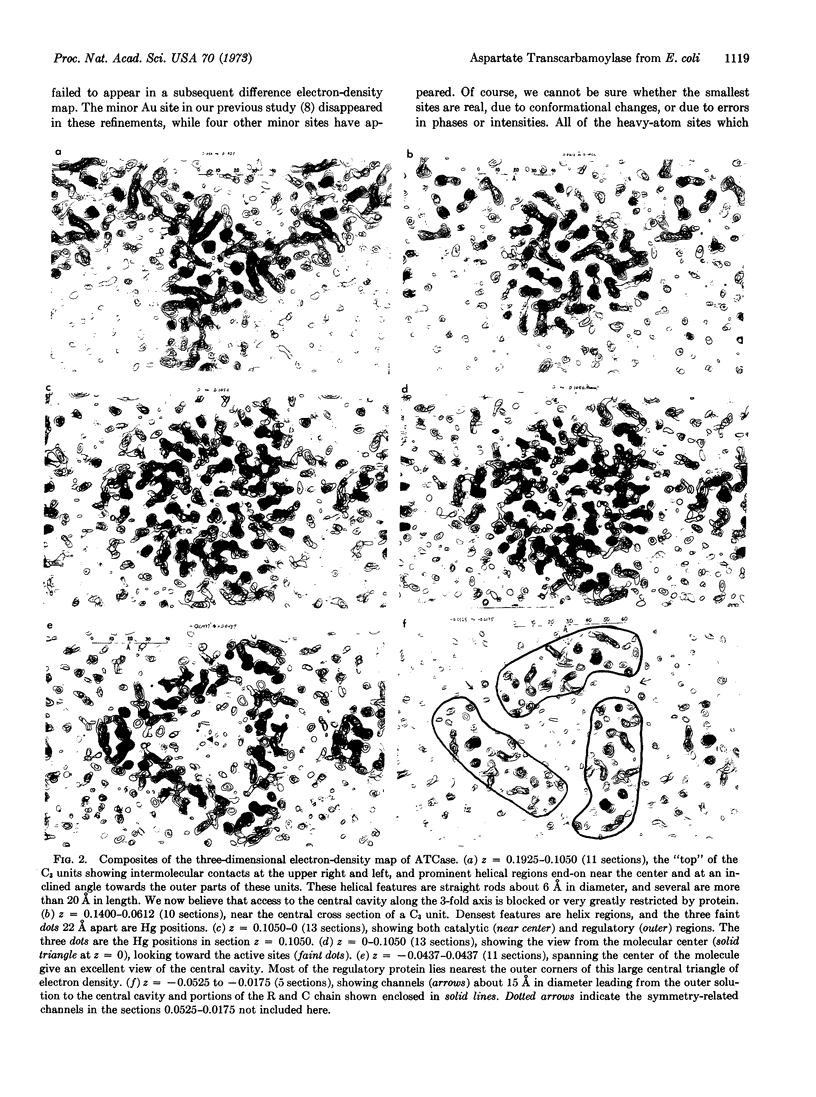
The allosteric enzyme, aspartate transcarbamoylase (EC 2.1.3.2), has previously been shown in our x-ray diffraction studies to have D3-32 symmetry. There are six catalytic (C) and six regulatory (R) chains in the molecular complex (R6C6). Our three-dimensional x-ray diffraction study of this enzyme (R32, a = 131 Å, c = 200 Å) at 5.5 Å resolution shows a spatial arrangement of the two catalytic trimers C3 above and below an equatorial belt of three regulatory dimers R2. The molecule is about 110 × 110 × 90 Å in largest dimensions, and is shown here to contain a large central aqueous cavity about 50 × 50 × 25 Å in size. Location of the single sulfhydryl of each catalytic chain, and correlation of its reactivity with enzymatic activity in the molecule, suggests that the nearby active sites are most probably accessible from the central cavity, but probably not directly from the external solution. The most obvious access to the central cavity consists of six channels, each about 15 Å in diameter, near the regulatory region. A component of the regulatory mechanism may be modulation of access of substrates through these channels.
Keywords: enzyme activity, allosteric enzyme, x-ray diffraction, crystallography
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans D. R., McMurray C. H., Lipscomb W. N. The thiol group in the catalytic chains of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3638–3642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHART J. C., PARDEE A. B. The enzymology of control by feedback inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. Distinct subunits for the regulation and catalytic activity of aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. W., Sigler P. B., Henderson R., Blow D. M. Three-dimensional structure of tosyl-alpha-chymotrypsin. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):652–656. doi: 10.1038/214652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelbach M. E., Pigiet V. P., Jr, Gerhart J. C., Schachman H. K. A role for zinc in the quaternary structure of aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 1;11(3):315–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00753a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARDEE A. B., YATES R. A. Control of pyrimidine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli by a feed-back mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1956 Aug;221(2):757–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards K. E., Williams R. C. Electron microscopy of aspartate transcarbamylase and its catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3393–3395. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P., Weber K. Localization of the zinc binding site of aspartate transcarbamoylase in the regulatory subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1019–1023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. New structural model of E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase and the amino-acid sequence of the regulatory polypeptide chain. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1116–1119. doi: 10.1038/2181116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., McMurray C. H., Edwards B. F., Franks W. A., Lipscomb W. N. The 5.5 Angstrom resolution structure of the regulatory enzyme, asparate transcarbamylase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:285–290. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystallographic determination of symmetry of aspartate transcarbamylase. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1119–1121. doi: 10.1038/2181119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]