Abstract
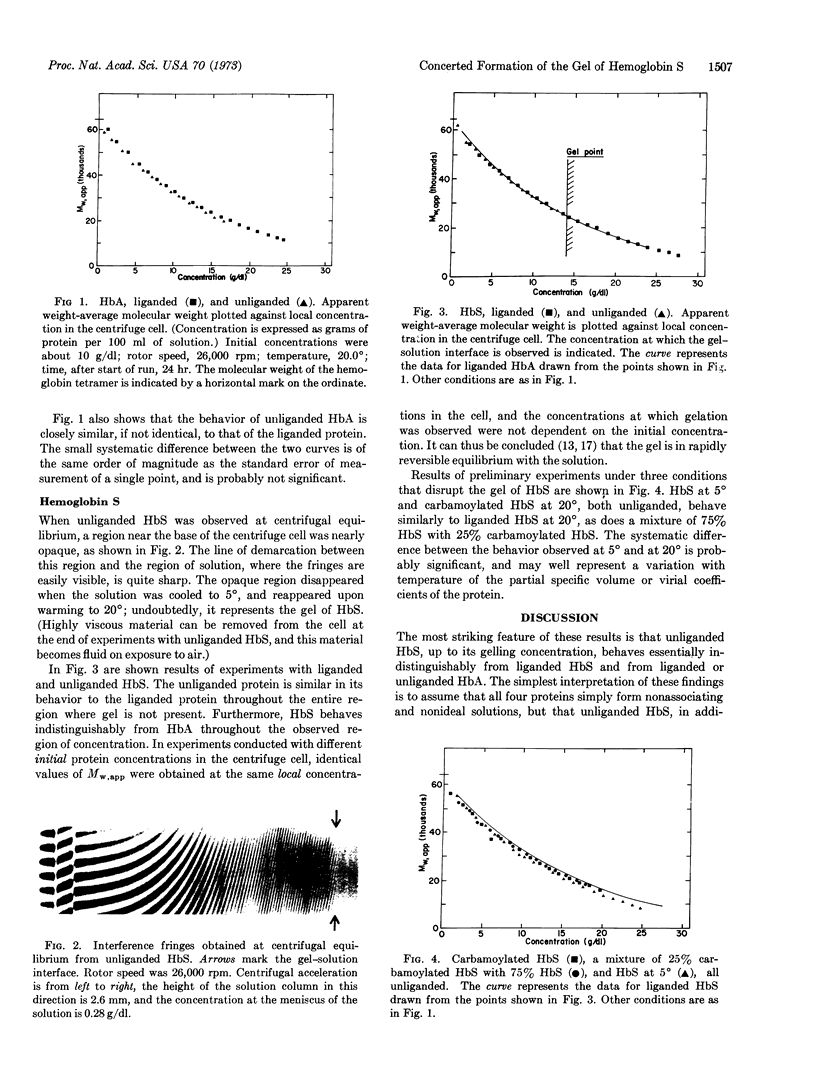
Apparent weight-average molecular weights of hemoglobin A and hemoglobin S were measured at high concentrations by equilibrium ultracentrifugation. Carbonmonoxy-hemoglobin S appears to exist as a solution of unassociated molecules, as do carbonmonoxy-and deoxy-hemoglobin A. Deoxy-hemoglobin S, however, exists in a gel-like state at concentrations above 14 g/dl, but no aggregates smaller than the gel were observed in solutions that were in equilibrium with the gel. Carbamoylation of hemoglobin S produced a solution of unaggregated molecules, as did cooling of uncarbamoylated hemoglobin S to 5°. It is concluded that the gel of hemoglobin S is formed in a stoichiometrically concerted manner, and that the size of the smallest stable aggregate is greater than 20 hemoglobin molecules.
Keywords: hemoglobin A, sickle-cell anemia, ultracentrifugation, protein association
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C. Properties of sickle-cell haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1957 Feb;65(2):212–219. doi: 10.1042/bj0650212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansevin A. T., Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Improved ultracentrifuge cells for high-speed sedimentation equilibrium studies with interference optics. Anal Biochem. 1970 Mar;34:237–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENESCH R., MACDUFF G., BENESCH R. E. DETERMINATION OF OXYGEN EQUILIBRIA WITH A VERSATILE NEW TONOMETER. Anal Biochem. 1965 Apr;11:81–87. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BESSIS M., NOMARSKI G., THIERY J. P., BRETON-GORIUS J. Etude sur la falciformation des globules rouges au microscope polarisant et au microscope électronique. II. L'intérieru du globule; comparaison avec les cristaux intra-globulaires. Rev Hematol. 1958 Apr-Jun;13(2):249–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertles J. F., Rabinowitz R., Döbler J. Hemoglobin interaction: modification of solid phase composition in the sickling phenomenon. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):375–377. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Manning J. M. Potassium cyanate as an inhibitor of the sickling of erythrocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1180–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. W. Studies on the destruction of red blood cells. VIII. Molecular orientation in sickle cell hemoglobin solutions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Oct;75(1):197–201. doi: 10.3181/00379727-75-18144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett G. L., Schachman H. K. Dissociation of hemoglobin into subunits. Monomer formation and the influence of ligands. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magdoff-Fairchild B., Swerdlow P. H., Bertles J. F. Intermolecular organization of deoxygenated sickle haemoglobin determined by x-ray diffraction. Nature. 1972 Sep 22;239(5369):217–219. doi: 10.1038/239217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama M. Molecular mechanism of red cell "sickling". Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):145–149. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., ITANO H. A. Sickle cell anemia a molecular disease. Science. 1949 Nov 25;110(2865):543–548. doi: 10.1126/science.110.2865.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERUTZ M. F., MITCHISON J. M. State of haemoglobin in sickle-cell anaemia. Nature. 1950 Oct 21;166(4225):677–679. doi: 10.1038/166677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERUTZ R. R., LIQUORI A. M., EIRICH F. X-ray and solubility studies of the haemoglobin of sickle-cell anaemia patients. Nature. 1951 Jun 9;167(4258):929–931. doi: 10.1038/167929a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F., Lehmann H. Molecular pathology of human haemoglobin. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):902–909. doi: 10.1038/219902a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roark D. E., Yphantis D. A. Studies of self-associating systems by equilibrium ultracentrifugation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Nov 7;164(1):245–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINER R. F. Reversible association processes of globular proteins. I. Insulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Aug;39(2):333–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90344-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINHARDT J., ZAISER E. M. Hydrogen ion equilibria in native and denatured proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1955;10:151–226. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Holde K. E., Rossetti G. P. A sedimentation equilibrium study of the association of purine in aqueous solutions. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):2189–2194. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. The fine structure of sickled hemoglobin in situ. Blood. 1968 May;31(5):561–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willimas R. C., Jr A laser light source for the analytical ultracentrifuge. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




