Abstract
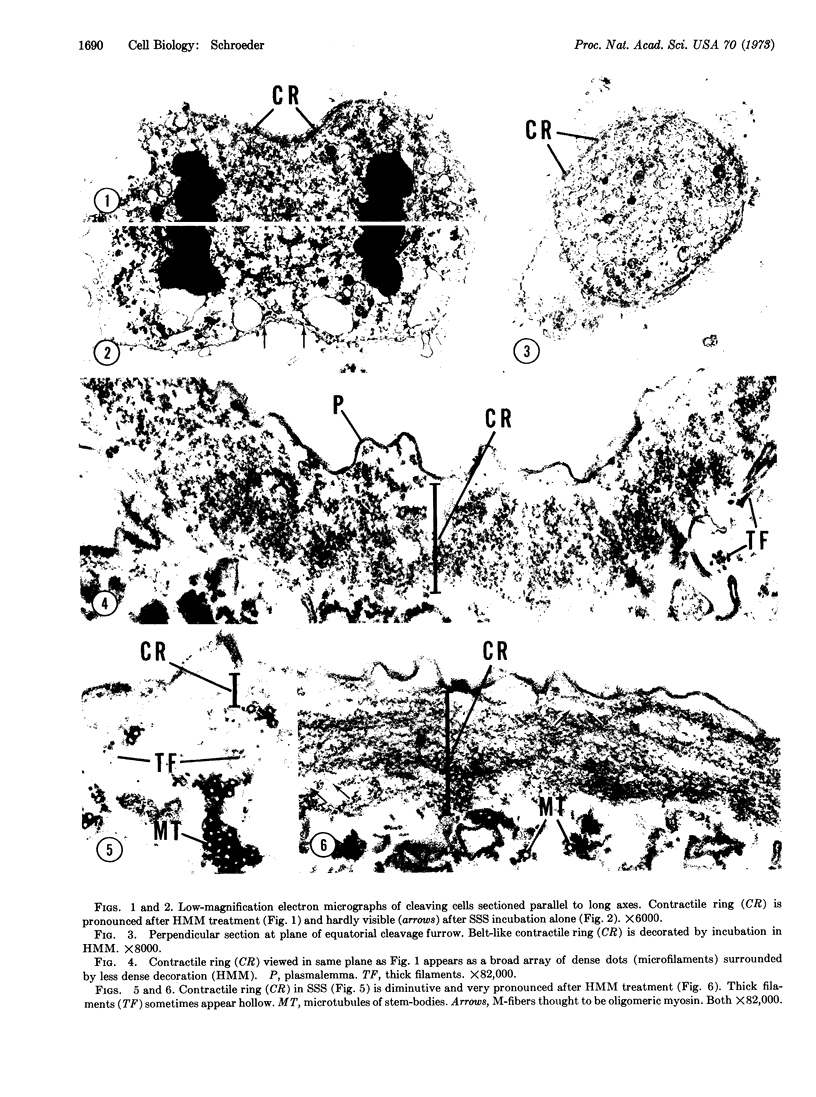
Many microfilaments and microtubules are well preserved after glycerol-extraction of HeLa cells at room temperature (22°). Incubation in heavy meromyosin from rabbit skeletal muscle results in conspicuous and characteristic “decoration” of microfilaments of the contractile ring. Decoration is completely prevented by 10 mM ATP or 2 mM pyrophosphate, and fails to occur if heavy meromyosin is either omitted or replaced by egg albumin, a nonspecific protein. Decorated microfilaments have a substructure consisting of polarized, repeating arrowheads 27-35 nm apart. The specificity of these results strongly suggests that microfilaments of the contractile ring in HeLa cells are closely related to muscle actin. Very thin undecorated strands among the microfilaments of the contractile ring possibly represent a myosin component. These findings are discussed in terms of: the actomyosin-like properties of the contractile ring as a mechanochemical organelle that causes cell cleavage; the probable universal occurrence of actin-like protein in all dividing animal cells; and the contractile ring's combined sensitivity to cytochalasin B and its affinity for heavy meromyosin, a combination unique among microfilamentous organelles.
Keywords: cell division, cytokinesis, cleavage, HeLa cells, microfilaments
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Pollard T. D., Kuehl W. M. Isolation and characterization of myosin and two myosin fragments from human blood platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson J. F. The use of fluorescein-labeled heavy meromyosin for the cytological demonstration of actin. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):293–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Forer A., Emmersen J. Actin in sperm tails and meiotic spindles. Nature. 1971 Dec 17;234(5329):408–410. doi: 10.1038/234408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke O., Kristensen B. I., Nielsen L. E. Electron microscopical observations on actinoid and myosinoid filaments in blood platelets. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Nov;37(3):351–369. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluemink J. G. Cytokinesis and cytochalasin-induced furrow regression in the first-cleavage zygote of Xenopus laevis. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;121(1):102–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00330921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Behnke O. An actin-like component in spermatocytes of a crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis Loew). I. The spindle. Chromosoma. 1972;39(2):145–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00319840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Behnke O. An actin-like component in spermatocytes of a crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis Loew). II. The cell cortex. Chromosoma. 1972;39(2):175–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00319841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Emmersen J., Behnke O. Cytochalasin B: does it affect actin-like filaments? Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):774–776. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawadi N. Actin in the mitotic spindle. Nature. 1971 Dec 17;234(5329):410–410. doi: 10.1038/234410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY H. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF NATURAL AND SYNTHETIC PROTEIN FILAMENTS FROM STRIATED MUSCLE. J Mol Biol. 1963 Sep;7:281–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M. G., Sheridan J. D., Estensen R. D. Cytochalasin B II: selective inhibition of cytokinesis in Xenopus laevis eggs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Apr;136(4):1158–1162. doi: 10.3181/00379727-136-35450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. B., Huxley H. E., DeRosier D. J. Three-dimensional reconstruction of F-actin, thin filaments and decorated thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):279–295. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T. Electron microscope observations on myosin from Physarum polycephalum. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):648–663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T., Huxley H. E. Electron microscope observations on actomyosin and actin preparations from Physarum polycephalum, and on their interaction with heavy meromyosin subfragment I from muscle myosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. Filament formation by purified Physarum myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2011–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. M., John H. A., Thomas N. S. Actin-like filaments in the cleavage furrow of newt egg. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):249–253. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. Cytokinesis in animal cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1971;31:169–213. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Holtzer H. Cytochalasin B: effects on cell morphology, cell adhesion, and mucopolysaccharide synthesis (cultured cells-contractile microfilaments-glycoproteins-embryonic cells-sorting-out). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. Cytokinesis: filaments in the cleavage furrow. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Oct;53(1):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90373-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. The contractile ring. I. Fine structure of dividing mammalian (HeLa) cells and the effects of cytochalasin B. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;109(4):431–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. The contractile ring. II. Determining its brief existence, volumetric changes, and vital role in cleaving Arbacia eggs. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):419–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selman G. G., Perry M. M. Ultrastructural changes in the surface layers of the newt's egg in relation to the mechanism of its cleavage. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jan;6(1):207–227. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Lin S. Cytochalasin B, its interaction with actin and actomyosin from muscle (cell movement-microfilaments-rabbit striated muscle). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ash J. F., Bradley M. O., Luduena M. A., Taylor E. L., Wrenn J. T., Yamada K. Microfilaments in cellular and developmental processes. Science. 1971 Jan 15;171(3967):135–143. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3967.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNT R. G., KOSHLAND D. E., Jr Properties of the O18 exchange reaction catalyzed by heavy meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1963 May;238:1708–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]