Abstract
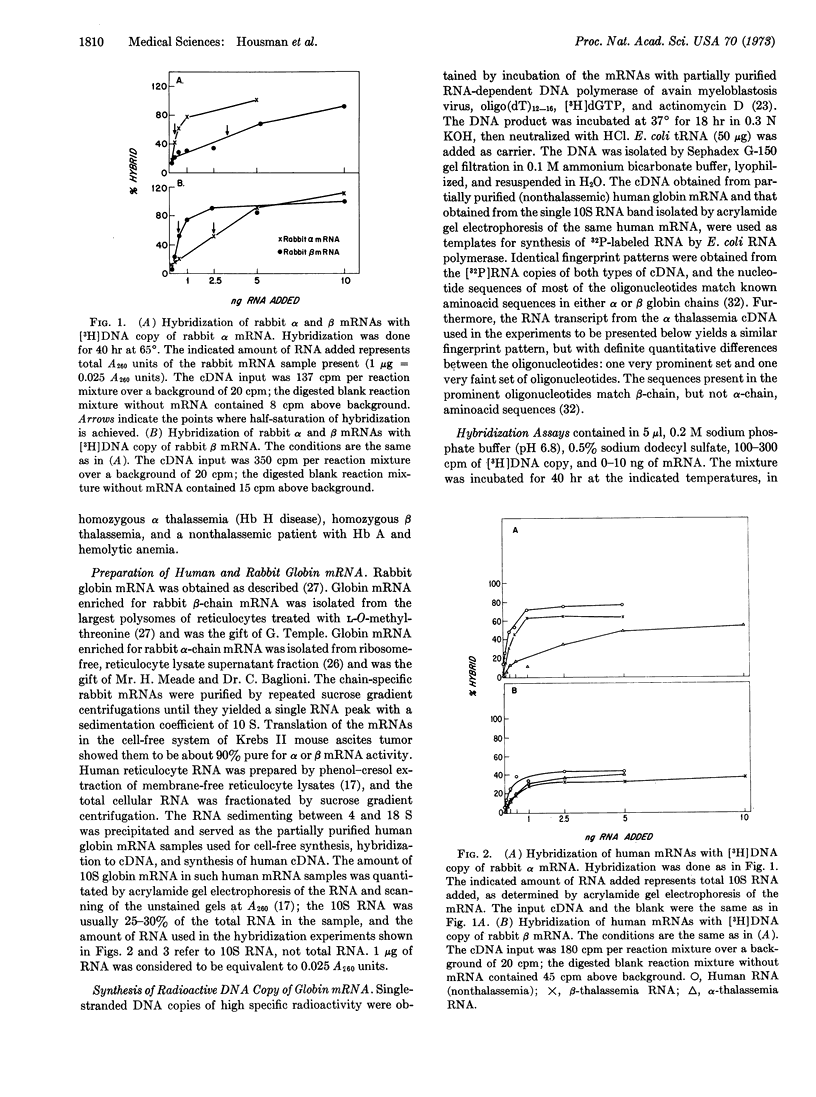
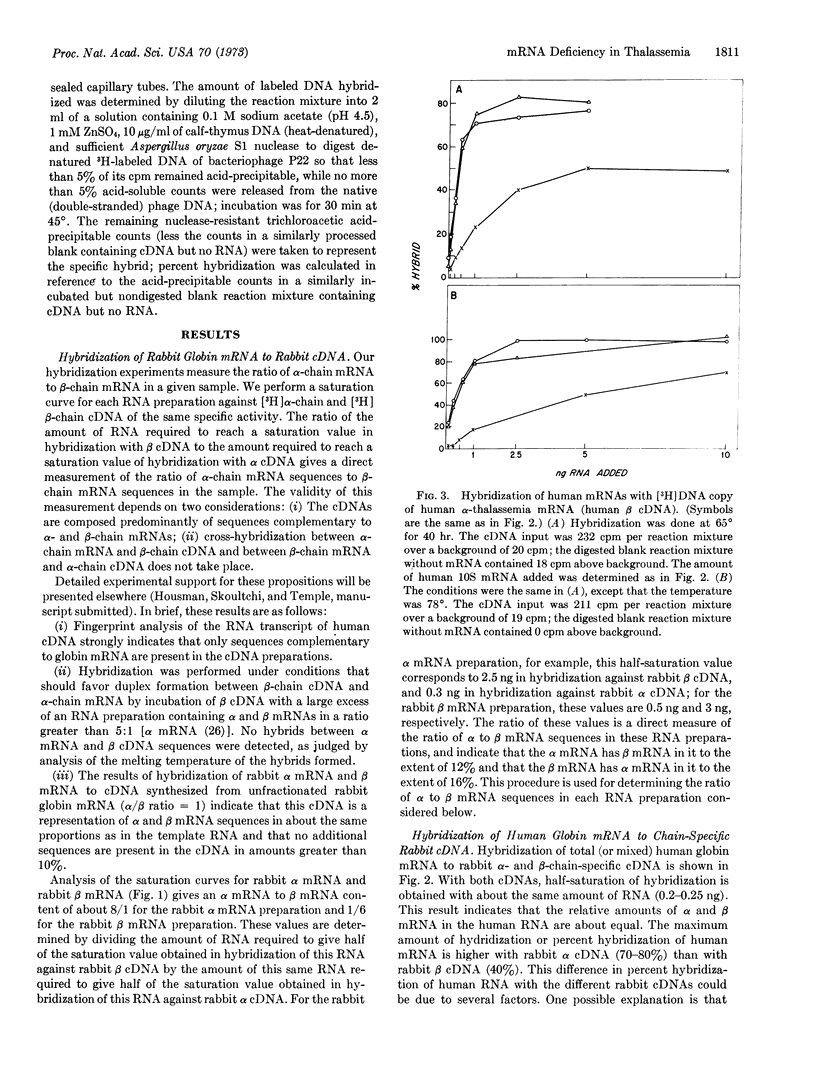
A hybridization assay procedure was devised that makes possible quantitation of the ratio of mRNA of alpha to mRNA of beta globin chains in an RNA sample. The assay uses the radioactive synthetic DNA copies obtained by incubation of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus with rabbit globin mRNA that is 80-90% enriched in mRNA specific for synthesis of alpha or beta globin chains. The rabbit alpha-chain mRNA is obtained from the postribosomal supernatant of rabbit reticulocyte lysates; the rabbit beta-chain mRNA is obtained from the largest polysomes of rabbit reticulocytes treated with L-O-methylthreonine. Sufficient homology exists between rabbit and human globin chains and globin mRNAs that the synthetic DNA copies of chain-specific rabbit globin mRNA hybridize with human globin mRNA. Applied to the study of globin mRNA isolated from reticulocytes of humans with alpha and beta thalassemia, the technique revealed marked quantitative deficiency of alpha-chain mRNA relative to beta-chain mRNA in alpha thalassemia and similar deficiency of beta-chain mRNA relative to alpha-chain mRNA in beta thalassemia. The thalassemia syndromes are therefore characterized by true quantitative deficiency of the mRNA specific for the affected globin chain.
Keywords: RNA-DNA hybridization, RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, mouse ascites tumor cell-free system
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T. A nuclease specific for heat-denatured DNA in isolated from a product of Aspergillus oryzae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Campana T. Alpha-chain and globin: intermediates in the synthesis of rabbit hemoglobin. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):480–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. F. Association of an endoribonuclease with the avian myeloblastosis virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7282–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank A., Marks P. A. Protein synthesis in a cell free human reticulocyte system: ribosome function in thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):330–336. doi: 10.1172/JCI105347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank A., Terada M., Metafora S., Dow L., Marks P. A. In vitro synthesis of DNA components of human genes for globins. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):167–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio235167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Jr, Forget B. G. Defect in messenger RNA for human hemoglobin synthesis in beta thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2755–2760. doi: 10.1172/JCI106778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum N., Maleknia M., Schapira G. Alpha- et bêta-globines libres et biosynthèse de l'hémoglobine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):236–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum N., Maleknia N., Schapira G. Alpha-hémoglobine libre et biosynthèse de l'hémoglobine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;179(2):448–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman A. S., Bank A. Changing rates of globin chain synthesis during erythroid cell maturation in thalassemia. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90486-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Na-Nakorn S., Wasi P. Haemoglobin synthesis in beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):664–668. doi: 10.1038/220664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi F., Rowley P. T., Del Senno L., Pontremoli S., Volpato S. Induction of -globin synthesis in the -thalassaemia of Ferrara. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):83–87. doi: 10.1038/newbio238083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus J. C., Labie D., Vibert M., Conconi F. An attempt at demonstrating the existence of a nonsense mutation in -thalassemia. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May 23;27(2):291–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Thornton A. G., Nienhuis A. W., Anderson W. F. Cell-free hemoglobin synthesis in beta-thalassemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1854–1861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard E., Terada M., Dow L. W., Bank A. Decreased globin messenger RNA activity associated with polyribosomes in thalassaemia. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 14;241(111):209–211. doi: 10.1038/newbio241209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYWOOD J. D., KARON M., WEISSMAN S. AMINO ACIDS: INCORPORATION INTO ALPHA- AND BETA-CHAINS OF HEMOGLOBIN BY NORMAL AND THALASSEMIC RETICULOCYTES. Science. 1964 Oct 23;146(3643):530–531. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3643.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood D., Karon M., Weissman S. Asymmetrical incorporation of amino acids in the alpha and beta chains of hemoglobin synthesized by thalassemic reticulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Sep;66(3):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES R. T., SCHROEDER W. A. CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION AND SUBUNIT HYBRIDIZATION OF HUMAN HEMOGLOBIN H AND ASSOCIATED COMPOUNDS. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1357–1367. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C. Messenger RNA for globin in the postribosomal supernatant of rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1425–1428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. G., Lodish H. F., Kan Y. W., Housman D. Beta thalassemia and translation of globin messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nienhuis A. W., Anderson W. F. Isolation and translation of hemoglobin messenger RNA from thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, and normal human reticulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1971 Nov;50(11):2458–2460. doi: 10.1172/JCI106745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nienhuis A. W., Laycock D. G., Anderson W. F. Translation of rabbit haemoglobin messenger RNA by thalassaemic and non-thalassaemic ribosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 16;231(24):205–208. doi: 10.1038/newbio231205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder R. F. Translation of -globin m-RNA in -thalassemia and the S and C hemoglobinopathies. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):364–372. doi: 10.1172/JCI106822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Aviv H., Scolnick E., Leder P. In vitro synthesis of DNA complementary to purified rabbit globin mRNA (RNA-dependent DNA polymerase-reticulocyte-hemoglobin-density gradient centrifugation-oligo(dT) primer). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):264–268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley P. T., Kosciolek B. Distinction between two types of beta-thalassaemia by inducibility of the cell-free synthesis of beta-chains by nonthalassaemic soluble fraction. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):234–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio239234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. Heterozygous Beta thalassemia: balanced globin synthesis in bone marrow cells. Science. 1970 Mar 13;167(3924):1513–1514. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3924.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaeffer J. R. Evidence for soluble alpha-chains as intermediates in hemoglobin synthesis in the rabbit reticulocyte. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):647–652. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaeffer J. R., Trostle P. K., Evans R. F. Inhibition of the biosynthetic completion of rabbit hemoglobin by isolated human hemoglobin chains. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4284–4291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D. A crude nuclease preparation suitable for use in DNA reassociation experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 29;240(4):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple G. F., Housman D. E. Separation and translation of the mRNAs coding for and chains of rabbit globin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1574–1577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Meuth N. L., Bromfeld E., Manly K. F., Baltimore D. Covalently linked RNA-DNA molecule as initial product of RNA tumour virus DNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):131–134. doi: 10.1038/newbio233131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Temple G. F., Fan H., Baltimore D. In vitro synthesis of DNA complementary to rabbit reticulocyte 10S RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):163–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio235163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A. Globin synthesis in thalassaemia: an in vitro study. Nature. 1965 Dec 11;208(5015):1061–1065. doi: 10.1038/2081061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



