Abstract
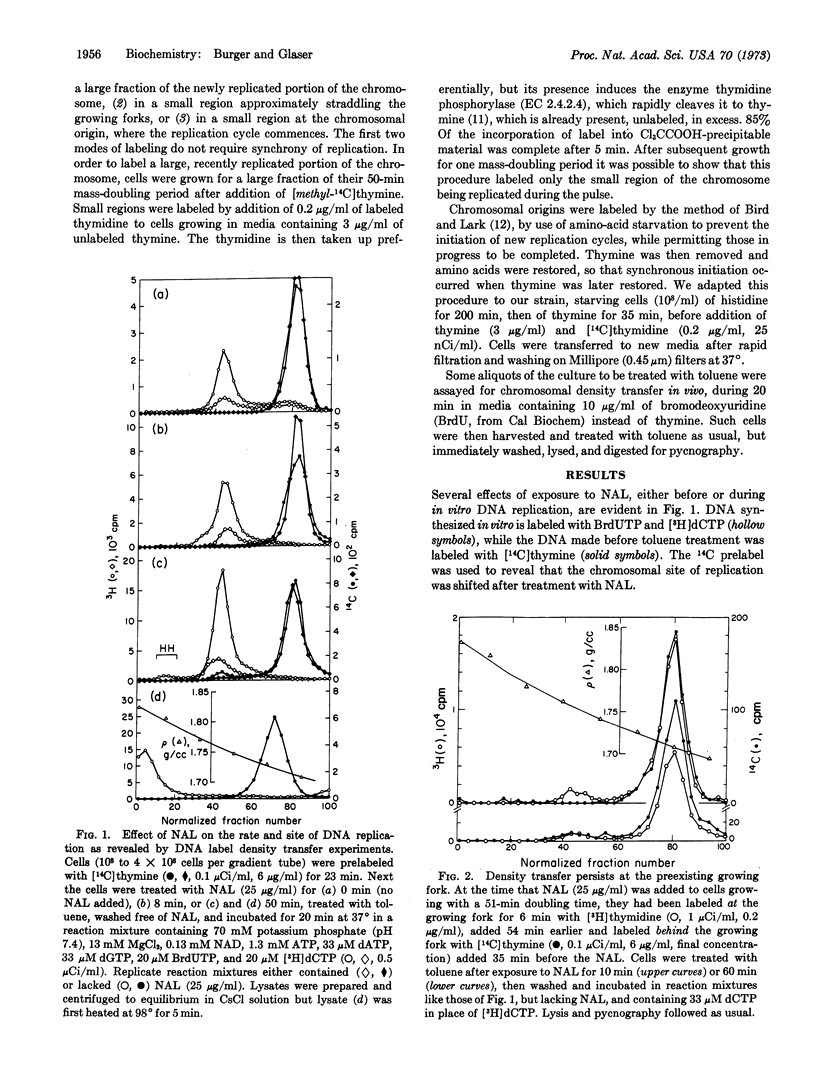
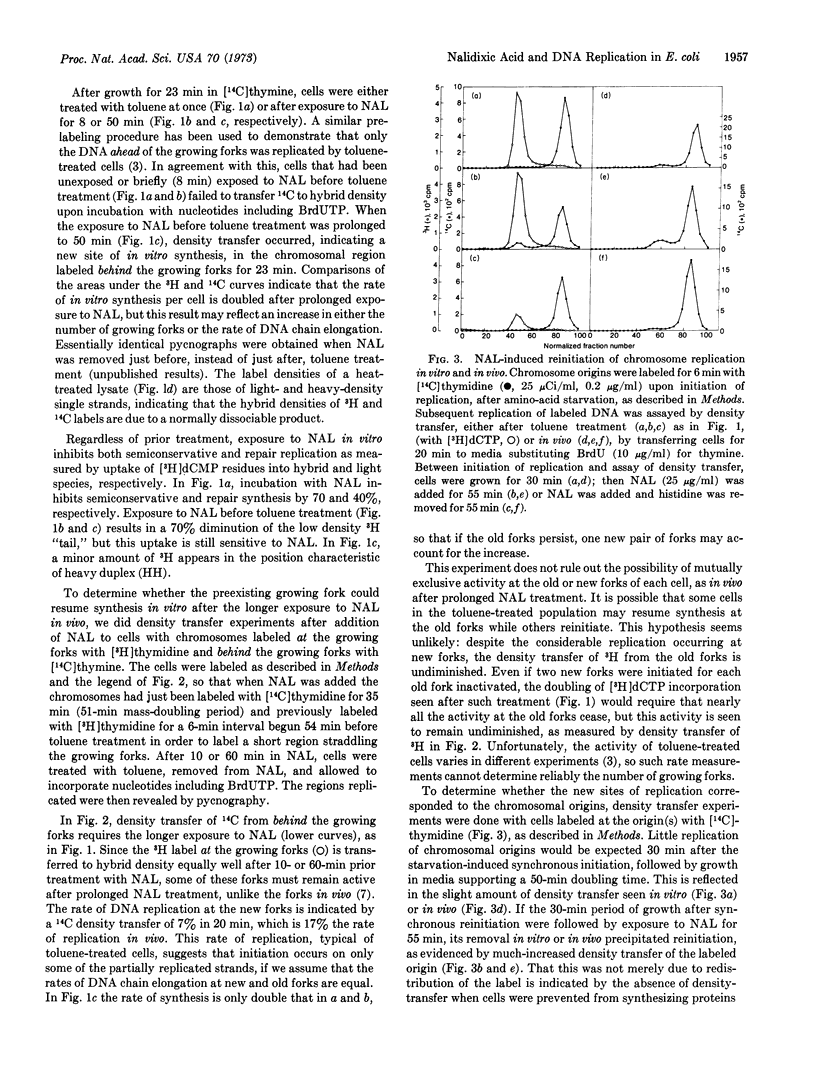
Nalidixic acid inhibits DNA synthesis in toluene-treated E. coli, strain B/r, as it is well known to do in vivo. Both semiconservative and repair syntheses are affected, though to different degrees. Density-transfer experiments indicate that chromosomal replication is reinitiated when nalidixic acid is removed from toluene-treated cells after exposure to the acid for one generation in vivo. For cells in vivo or after toluene-treatment, reinitiation is not seen in asynchronous cultures exposed briefly to nalidixic acid or in cells prevented from synthesizing proteins during their exposure to the acid. Reinitiation occurs at the chromosomal origin but, unlike the effect seen in vivo, replication at the old site persists.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird R., Lark K. G. Initiation and termination of DNA replication after amino acid starvation of E. coli 15T-. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:799–808. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger R. M. Toluene-treated Escherichia coli replicate only that DNA which was about to be replicated in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2124–2126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSS W. A., DEITZ W. H., COOK T. M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF NALIDIXIC ACID ON ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1112-1118.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koiyama M., Kolber A. R. Temperature sensitive mutant of the DNA replication system in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1157–1160. doi: 10.1038/2281157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita T., White K. P., Sueoka N. Chromosom replication in toluenized Bacillus subtilis cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):111–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio232111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordoh J., Hirota Y., Jacob F. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli. V. Incorporation of deoxynucleoside triphosphates by DNA thermosensitive mutants of Escherichia coli also lacking DNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):773–778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses R. E., Richardson C. C. Replication and repair of DNA in cells of Escherichia coli treated with toluene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):674–681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OISHI M., YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. SYNCHRONOUS AND DICHOTOMOUS REPLICATIONS OF THE BACILLUS SUBTILIS CHROMOSOME DURING SPORE GERMINATION. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1069–1073. doi: 10.1038/2041069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrini A. M., Geroldi D., Siccardi A., Falaschi A. Studies on the mode of action of nalidixic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACHMELER M., GERHART J., ROSNER J. Limited thymidine uptake in Escherichia coli due to an inducible thymidine phosphorylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 29;49:222–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90888-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. B., Glaser D. A. Control of initiation of DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli B-r. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):255–262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. B., Hane M. W., Glaser D. A. Synchronous reinitiation of chromosome replication in E. coli B-r after nalidixic acid treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):365–369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



