Highlights
-
•
Retroperitoneal liposarcoma related pregnancy is rare.
-
•
Liposarcoma is sometimes positive for hormone receptor.
-
•
Additional therapy for liposarcoma is important to improve prognosis.
Keywords: Retroperitoneal liposarcoma, Estrogen receptor, Pregnancy
Abstract
Introduction
Liposarcoma is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas; however, early diagnosis is rare as the tumor remains difficult and unpalpable for a prolonged period of time.
Presentation of case
Here we report the first case of retroperitoneal liposarcoma associated with pregnancy and expression of estrogen receptor. A 34-year-old woman experienced persistent abdominal distension after her first delivery. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a large (40 cm ×35 cm), solid, palpable abdominal mass with fat attenuation displacing the ascending colon and the right kidney to the left. Laparotomy and an en-bloc resection of the tumor were performed; further, right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy were required. Histopathology showed a well-differentiated liposarcoma; approximately 10–20% of the tumor cells were ER-positive.
Discussion
Retroperitoneal liposarcoma associated with pregnancy is an extremely rare occurrence. Surgical resection is unquestionably the first choice of treatment, but complete resection is sometimes impossible due to the volume and depth of invasion of the tumor. In such cases, additional therapy for liposarcoma is important to improve prognosis. Thus, this report highlights the need for further research into hormone therapy.
Conclusion
Retroperitoneal liposarcoma has a high local recurrence rate due to the difficulty in complete surgical resection; therefore, additional hormone therapy is important for improving the prognosis.
1. Background
Liposarcoma is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas, yet early diagnosis is rare because the tumor remains difficult and unpalpable for a prolonged period of time. The peak incidence of liposarcoma occurs from 40 to 60 years of age with the preponderance of cases reported in men [1]. It is very rare in females of reproductive age, and the prognosis is better in pre-than in post-menopausal women [2]. Although some reports mention an association between steroid hormones and malignant soft tissue tumors including liposarcomas, a case of liposarcoma associated with pregnancy wherein hormone receptors have been investigated has not been previously reported. Here, we report the first case of retroperitoneal liposarcoma associated with pregnancy and ER expression and review the literature.
2. Case report
A 34-year-old woman experienced persistent abdominal distension for the duration of her pregnancy with no improvement even after delivery. She had a normal delivery eight months earlier, and her child displayed normal growth. Although no abnormalities were detected during the several routine transvaginal ultrasonographic examinations performed during pregnancy, at birth, and six months after delivery, contrast enhanced computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (fat suppression, T1WI) revealed a 40 cm × 35 cm solid mass with fat attenuation displacing the ascending colon and the right kidney to the left (Fig. 1A and B). Furthermore, this was accompanied by breathlessness due to restriction of diaphragmatic movement. Laboratory findings including tumor marker CA-125, alpha-fetoprotein, and carcino-embryogenic antigen levels were within the normal range. Laparotomy was performed under general anesthesia, and a mass was found to be wrapped in the retroperitoneum and pseudomembrane. The uterus, uterine tube and ovaries were normal. We performed an en-bloc resection of the tumor, along with right nephrectomy and adrenalectomy.
Fig. 1.
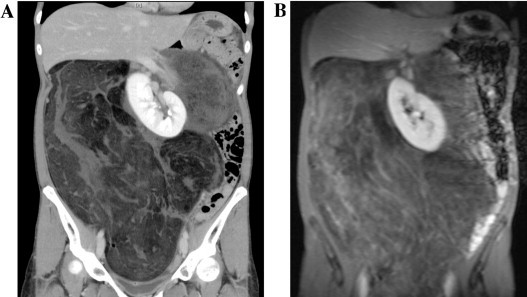
(A) contrast enhanced CT, (B) MRI (fat suppression, T1WI) A 40 × 35 cm solid mass with fat attenuation displacing ascending colon and right kidney to left.
The retroperitoneal mass weighed 7200 g and measured 43 cm × 40 cm × 13 cm (Fig. 2). Histopathological examination of the surgical specimen showed a well-differentiated liposarcoma (Fig. 3). Immunohistochemistry revealed approximately 10–20% of the tumor cells to be estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, with negative results for the progesterone receptor (PR) (Fig. 4). The patient recovered uneventfully and was discharged from the hospital on the 15th postoperative day. She and her husband were planning to try for another baby, so postoperative adjuvant therapy including hormone therapy was not undertaken. No recurrence was detected at the 3-year follow-up.
Fig. 2.
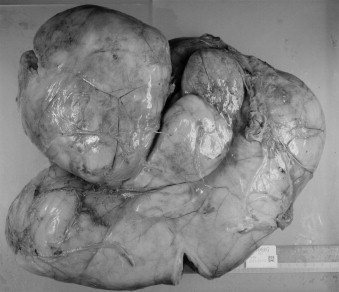
Gross appearance of the tumor. An elastic soft mass covered pseudocapsule weighed 7200 g and measured 43 cm × 40 cm × 13 cm with lobulations.
Fig. 3.
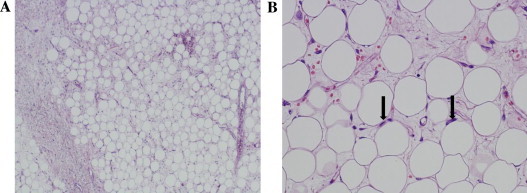
Hematoxylin and Eosin staining showing some lipoblasts with nuclear atypia (arrow) revealed a well-differentiated liposarcoma. A × 40, B × 200.
Fig. 4.
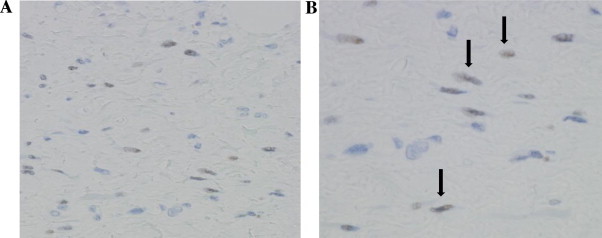
Immunostaining revealed resected specimen was ER positive (10 ∼ 20%) (arrow). A × 200, B × 400.
3. Discussion
Retroperitoneal sarcomas represent approximately 10–15% of all soft tissue sarcomas, which themselves are rare, accounting for only 1% of all malignancy [3]. The peak incidence of liposarcoma occurs from 40 to 60 years of age. The tumor is typically aggressive, with reported 5-year survival rates ranging from only 23% to 46% [4]. Lewis et al. [5] reported high local recurrence rates for retroperitoneal sarcoma, ranging from 40% to 80%. As the retroperitoneal space is easily distended by the enlarging tumor, the neoplasia remains inactive and unpalpable for prolonged period of time. A retroperitoneal mass may produce a wide range of signs and symptoms due to the compression and infiltration of the surrounding organs: localized pain associated with neurologic symptoms due to neuroplexus involvement, vomiting due to gastric compression, constipation, hydronephrosis, uremia due to renal disorder, and ureteric compression. Izumi et al. [6] reported that the most common symptom of retroperitoneal sarcomas is abdominal pain (25.8%), followed by abdominal distension and palpable mass, while 22.1% of the cases develop without symptoms. In the present case, the first symptoms were continuous abdominal distension and respiratory discomfort lasting throughout the pregnancy without improvement, suggesting that the mass existed and grew during the pregnancy. Ultrasonographic examinations performed as routine check-ups during the perinatal period did not detect the retroperitoneal tumor in this case. Hence, it is recommended that a transabdominal ultrasonographic examination (or MRI if necessary) be performed in cases where a pregnant woman complains of abdominal distention or respiratory discomfort.
We reviewed the literature on liposarcoma associated with pregnancy and found 16 cases including ours. Their clinical courses are summarized in Table 1 [1,3,7,8,10–18]. The mean age was 31 years (range, 15–44 years). Four cases of liposarcoma were discovered during the first trimester, 10 during the second or third trimester, and 2 within the 1 year postnatal period. Only 2 patients diagnosed in the first trimester were surgically treated during pregnancy; in all other cases, surgery was performed after delivery.
Table 1.
Clinicopathological characteristics of pregnancy-associated liposarcoma.
| Author | Age | complaint | Gestation at diagnosis (W) | Location | Surgery | Tumor subtype | Size (Weight) | Prognosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pierandrea D.J. et al. [1] | 41 | Weight loss | 34 | Retroperitoneum | 36 weeks of gestation concurrently with CS | Myxoid | 23 cm | Died after 8 months | ||
| Jeng C-J. et al. [3] | 33 | Unknown | 12 | Retroperitoneum | 36 weeks of gestation concurrently with CS | Myxoid | 25 × 20 cm | Recurrence after 4 months postop. | ||
| Matsuda S. et al. [7] | 28 | Pain in left thigh | 29 | Left thigh | 5 weeks after CS at 33 weeks of gestation | Myxoid | 15 × 10 × 5 cm | Free of disease 5 years postop. | ||
| 34 | Palpable mass | 20 | Right thigh | 7 weeks after ID at 33 weeks of gestation | Myxoid | 15 × 13 cm | Free of disease 4 years postop. | |||
| Tebes S. et al. [8] | 22 | Abdominal pain | 13 | Retroperitoneum | 3 weeks after VD at 29 weeks of gestation | Pleomorphic | 20 cm | Died after 2 months | ||
| Foruhan B. [10] | 28 | None | 28 | Retroperitoneum | 38 weeks of gestation concurrently with CS | Myxoid | 30 cm (2.678 kg) | Free of disease 18 months postop. | ||
| Yamamoto T. et al. [11] | 29 | Palpable mass | 29 | Right thigh | none (chemoradiotherapy after CS) | Myxoid | 8 × 8 × 5 cm | Remission 13 months postop. | ||
| 44 | Palpable mass | 22 | Left thigh | 6 weeks after CS at 32 weeks of gestation | Well-differentiated | 15 × 12 × 8 cm | Free of disease 5 years postop. | |||
| Kurogouchi A. et al. [12] | 30 | Palpable mass | 12 | Retroperitoneum | 13 weeks of gestation (CS at 37 weeks of gestation) | Myxoid | 34 × 14 × 14 cm | Alive 4 years lataer with operation for reccurence | ||
| Lopes R.I. et al. [13] | 33 | None | 13 | Retroperitoneum | 13 weeks of gestation (CS at 37 weeks of gestation) | Well-differentiated | 22 × 20 × 20cm(3.75 kg) | Free of disease 1 years postop. | ||
| Jafari K. et al. [14] | 15 | Chest pain | 31–32 | Mediastinum | none (chemoradiotherapy after VD) | Anaplastic | unknown | Remission | ||
| Carrol F. et al. [15] | 23 | Respiratory distress | 32–33 | Left pleura | 32–33 weeks of gestation concurrently with CS | Mixed-type | 29 × 15 × 15 + 21 × 12 × 8cm(4.46 kg) | Unknown | ||
| D-Garcia O.F. et al. [16] | 35 | Palpable mass | 36 | Retroperitoneum | after delivery (unspecified) | Well-differentiated | 52 × 40 × 35 cm (12.5 kg) | Free of disease 1 years postop. | ||
| Rouskova L. et al. [17] | 32 | Weight loss | 34 | Retroperitoneum | 3 days after delivery | Pleomorphic | unknown | Died after 1 month | ||
| Masuda T. et al. [18] | 34 | Unknown | Diagnosis at delivery | Retroperitoneum | 3 months after delivery | Myxoid | 7.5 × 7.0 × 7.1 cm | Free of disease 8 years postop. | ||
| Our case | 34 | Abdominal distension | 32weeks after delivery | Retroperitoneum | 9 months after delivery | Well-differentiated | 43 × 40 × 13cm(7.2 kg) | Free of disease 3 years postop. |
CS, cesarean section; ID, induced delivery; VD, vaginal delivery.
Liposarcoma is classified into five histological subtypes: well-differentiated, round-cell, myxoid, pleomorphic, and de-differentiated (WHO classification, 2002). There were 8 cases of myxoid type and 4 cases of well-differentiated type, both of which were classified as low-grade. Twelve cases were large tumors exceeding 15 cm in diameter. According to the reports, surgery was the only treatment given during pregnancy; however, radiotherapy to the lower extremity after delivery [7] and chemotherapy in combination of mesna, doxorubisin and ifosfamid after surgical excision [8] have been reported. In terms of prognosis, out of the 4 patients diagnosed in the first trimester, 2 survived following surgery under general anesthesia at 13th week of pregnancy. However, all patients for whom surgery was performed after delivery died. Therefore, surgical resection should be considered as soon as possible, even if the initial diagnosis is made during pregnancy.
The effect of pregnancy on tumors is a major concern. In our patient, a relationship existed between tumor growth and pregnancy, and immunostaining was ER-positive. Cantin and McNeer [2] determined that pregnancy does not adversely affect the prognosis of the tumor. However, they suggested that an estrogen–progesterone environment possibly has a favorable influence on the natural history of sarcoma, and the value of additive hormone therapy in the management of metastatic sarcoma should be explored. Matsuda et al. [7] reported that soft tissue sarcoma can grow rapidly during pregnancy. Xiao-Qiu Li et al. [9] who analyzed 120 soft tissue sarcomas including 31 liposarcomas for ER expression reported that neither gender nor age have a significant influence on the ER expression status, but further studies to assess the hormonal dependency of ER-positive mesenchymal neoplasms and potential therapeutic applications would be of clinicopathological significance. Retroperitoneal liposarcoma associated with pregnancy is an extremely rare occurrence, and no case investigating hormone receptors has been reported in the literature. Surgical resection is unquestionably the first choice of treatment for retroperitoneal liposarcoma, but a complete resection can sometimes be impossible due to the volume and depth of invasion of tumor. Therefore, additional therapy for liposarcoma is important to improve prognosis; thus, this report highlights the need for further research into hormone therapy.
Conflicts of interest
There are not any financial or other interests with regard to the submitted manuscript that might be construed as a conflict of interest.
Funding
There are not any sources of funding with regard to the submitted manuscript.
Ethical approval
This manuscript has been met ethical approval.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal on request.
Author contribution
Hiroaki Kasashima: writing the paper, doctor in charge.Yoshio Yamasaki: writing the paper, doctor in charge, guarantor.Yoshikazu Morimoto: data interpretation.Yusuke Akamaru; data interpretation.KeigoYasumasa: doctor with this patient’s surgery.Tsutomu Kasugai: pathological analysis.Yasuyuki Yoshida: pathological analysis.
Guarantor
The guarantor of this manuscript is Yoshio Yamasaki.
References
- 1.De Jaco P., Giorgio M., Zantedeschi B., Mazzoleni G., Marabini A. A case of retroperitoneal liposarcoma in pregnancy. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1993;72:122–124. doi: 10.3109/00016349309023425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cantin J., McNeer G.P. Effect of pregnancy on sarcoma of soft somatic tissues. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1967;125:28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jeng C.-J., Tzen C.-Y., Huang W.-C., Yang Y.-C., Shen J., Tzeng C.-R. Recurrent retroperitoneal myxoid liposarcoma during pregnancy: a case report and literature review. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 2005;15:1235–1238. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1438.2005.00180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bolin T.E., Bolin S.G., Wetterfors J. Retroperitoneal sarcomas: an analysis of 32 cases. Acta Chir. Scand. 1988;154:627–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.J.J. Lewis , D. Leung , J.M. Woodruff , M.F. Brennan, Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma, Analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution, Ann. Surg., 228, 355-365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Izumi H., Dowaki S., Matsuyama M., Yazawa N., Tobita K., Imaizumi T. Retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a case report (in Japanese with English abstract) Nihon Syokakibyo Gakkaizasshi. J. Gastroenterol. 2010;107:1505–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Matsuda S., Tanaka K., Harimaya K., Matsumoto Y., Sato H., Iwamoto Y. Treatment of myxoid liposarcoma in pregnancy. Clin. Orthopaedics Relat. Res. 2000;376:195–199. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200007000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tebes S., Cardosi R., Hoffman M. Liposarcoma complicating pregnancy. Gynecol. Oncol. 2001;83:610–612. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2001.6478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li X.-Q., Hisaoka M., Hashimoto H. Expression of estrogen rexeptors α and β in soft tissue sarcomas: immunohistochemical and molecular analysis. Pathol. Int. 2003;53:671–679. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2003.01543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Foruhan B. Retroperitoneal sarcomas obstructing delivery two case reports. Br. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1979;86:747–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb11280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yamamoto T., Marui T., Akisue T., Hitora T., Kawamoto T., Nagira K. Management of liposarcoma occurring in pregnant women. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:799–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kurogouchi A., Hyodo M., Sata H., Yamaguchi T., Niki T., Nagai H. Long-term survivor following resection of a retroperitoneal myxoid liposarcoma during pregnancy (in Japanese with English abstrac) Nihon Rinsyogeka Gakkaizasshi. Jpn. J. Surg. Assoc. 2011;72:2129–2133. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lopes R.I., Machado M., Paz C., Santos A.C., Reende W.W. Successful outcome of a surgically treated giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma during pregnancy. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2009;280:1067–1069. doi: 10.1007/s00404-009-1061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jafari K., Lash A.F., Webster A. Pregnancy and sarcoma. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1978;57:265–271. doi: 10.3109/00016347809154896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Carroll F., Kramer M.D., Acinapura A.J., Tietjen P.A., Wagner I., Oiseth S. Ann. Thorac. Sug. 1992;54:1212–1213. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(92)90102-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.D-Garcia O.F., D-Sotomayor M., R-Olvera H. Well differentiated giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma during the pregnancy. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2011;103:657–658. doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082011001200012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rouskova L., Melichar B., Nikolov D.H., Cerman J., Jr., Havel E., Megancova J. Fuluminant course of metastatic liposarcoma after delivery–case report. Eur. J. Gynaec. Oncol. 2007;28:67–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Masuda T., Inatsugi N., Yosikawa S., Takamura H., Enomoto H., Uchida H. An 8-year survival case of liposarcoma located in pararectal space (in Japanese with English abstract) Nihon Daichokoumonbyo Gakkaizasshi. J. Jpn. Soc. Coloproctol. 2011;72:2129–2133. [Google Scholar]


