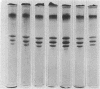
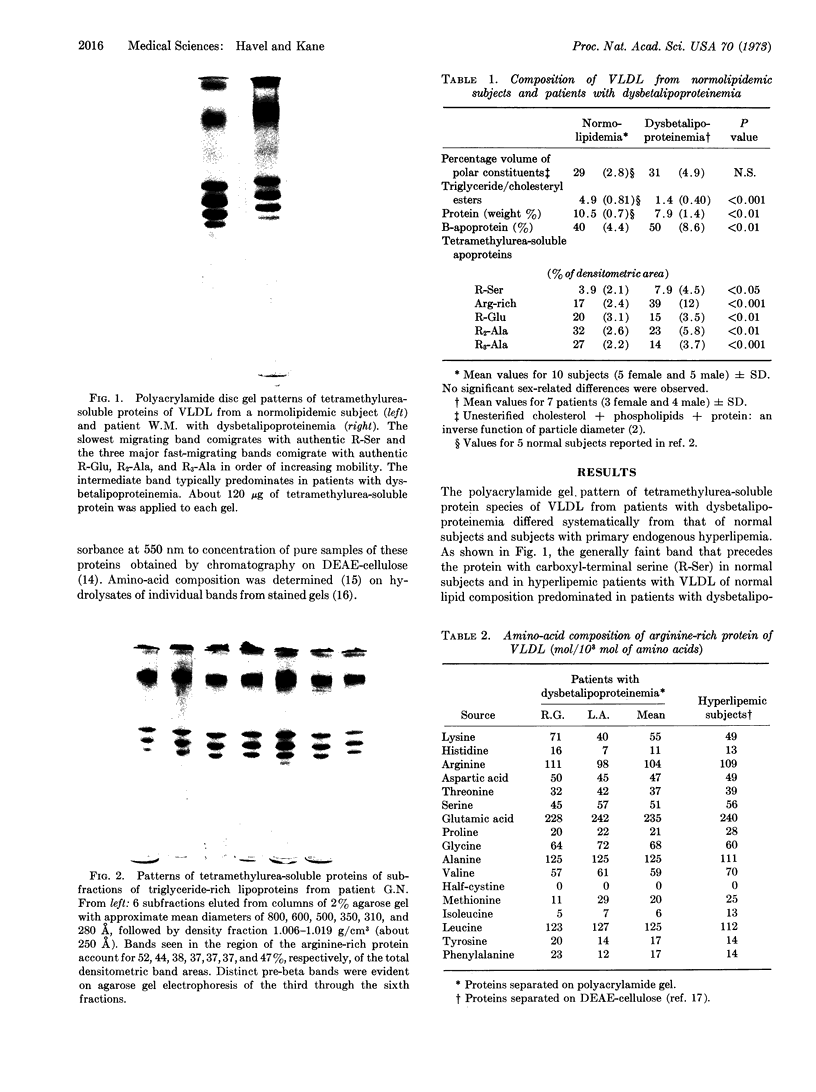
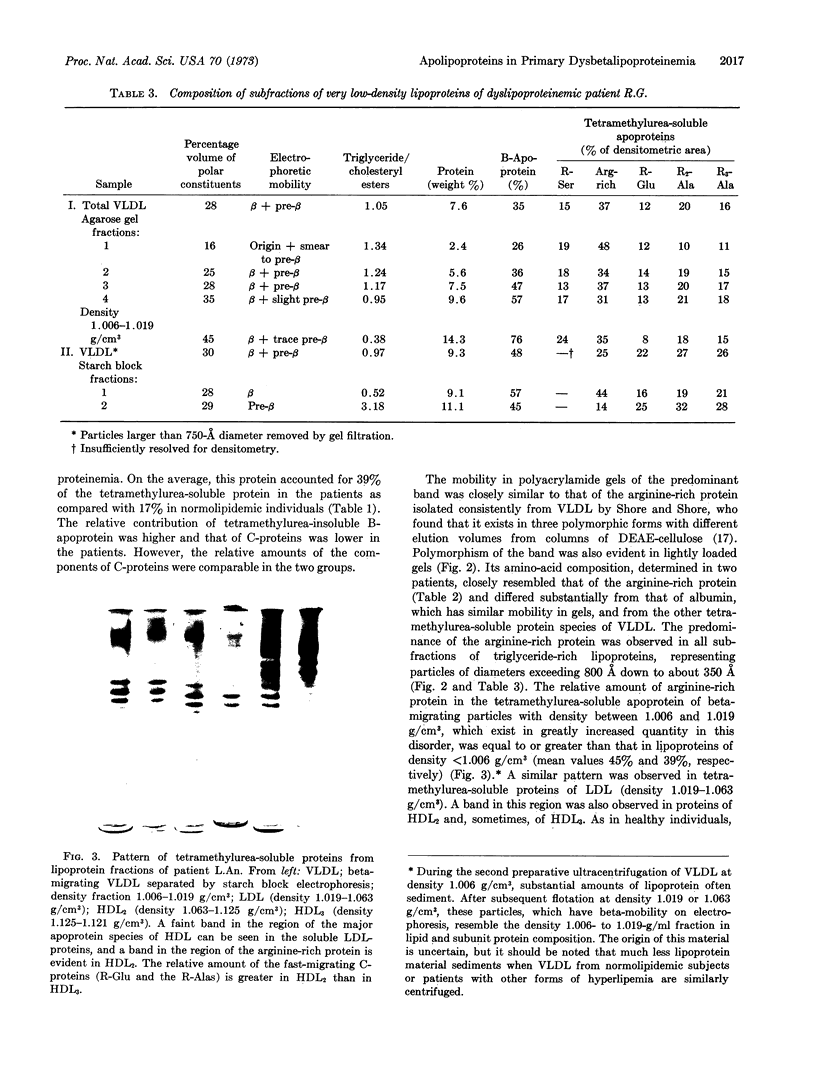
Abstract
Lipoproteins of very low density that are unusually rich in cholesteryl esters accumulate in blood plasma in a characteristic primary form of human hyperlipoproteinemia. These lipoproteins, which are thought to be products of the initial catabolic step in the metabolism of normal triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, have beta rather than pre-beta mobility on electrophoresis, presumably because they have lost certain protein components from their surface. In this study, we have used polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of apoprotein components that are soluble in tetramethylurea to show that the very low-density lipoprotein fraction of blood serum from seven patients with hyperlipoproteinemia contains unusually large amounts of an arginine-rich protein. Pre-beta migrating, very low-density lipoproteins separated from serum of post-absorptive patients and chylomicrons obtained after a fat-rich meal contain normal amounts of this arginine-rich protein, but beta-migrating, very low-density lipoproteins and chylomicron-like particles separated from serum of post-absorptive patients contain more than twice as much. These apparently partially degraded lipoproteins also contain more tetramethylurea-insoluble protein and smaller amounts of the other soluble protein components than their normal counterparts.
Keywords: chylomicrons, very low-density lipoproteins, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, tetramethylurea
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J. Early effects of fat ingestion on lipids and lipoproteins of serum in man. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jun;36(6 Pt 1):848–854. doi: 10.1172/JCI103491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Mechanisms of hyperlipoproteinemia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;26(0):57–70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7547-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Lindgren F. T., Bierman E. L. Very low density lipoprotein subfractions in a subject with broad-beta disease (Type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia) and a subject with endogenous lipemia (Type IV). Chemical composition and electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90122-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Abnormal lipid composition of chylomicrons in broad-beta disease (type 3hyperlipoproteinemia). J Clin Invest. 1970 Oct;49(10):1853–1858. doi: 10.1172/JCI106403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L. Amino acid analysis of stained bands from polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TRAUTMAN R. The alpha2 lipoproteins of human serum; correlation of ultracentrifugal and electrophoretic properties. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jun;35(6):641–648. doi: 10.1172/JCI103320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. On thelipoprotein abnormality in type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):754–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI106546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Estrich D. L., Wood P. D., Kinsell L. W. Evaluation of gel chromatography for plasma lipoprotein fractionation. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jul;11(4):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Isolation and characterization of polypeptides of human serum lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B. Heterogeneity of human plasma very low density lipoproteins. Separation of species differing in protein components. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):502–507. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]