Abstract
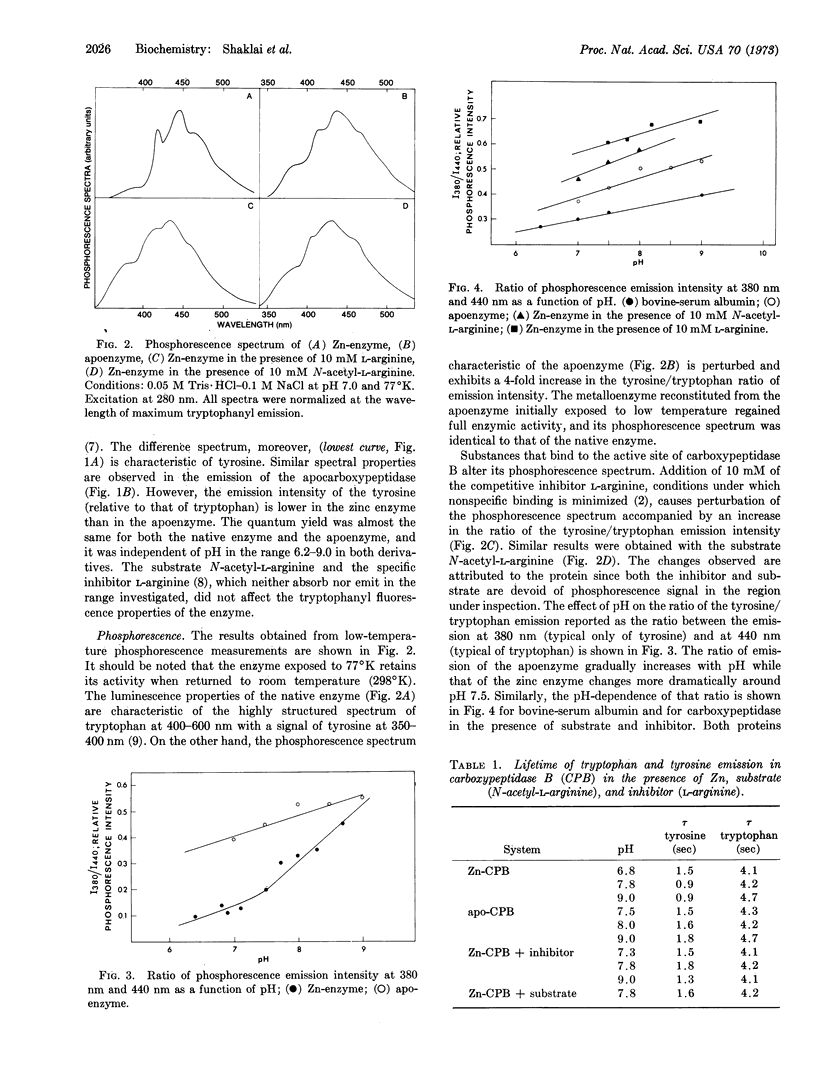
The luminescence spectra of carboxypeptidase B indicate specific differences between the zinc and apoenzyme due to the state of tyrosyl residues presumably at the active site. These differences disappear when enzyme-substrate or enzyme-inhibitor complexes are formed, suggesting that they may reflect the interaction of a tyrosyl residue in the native enzyme with the catalytically essential zinc atom. An interpretation of the role of that tyrosyl residue in the mechanism of action of carboxypeptidase B is presented.
Keywords: fluorescence, phosphorescence, enzyme mechanism
Full text
PDF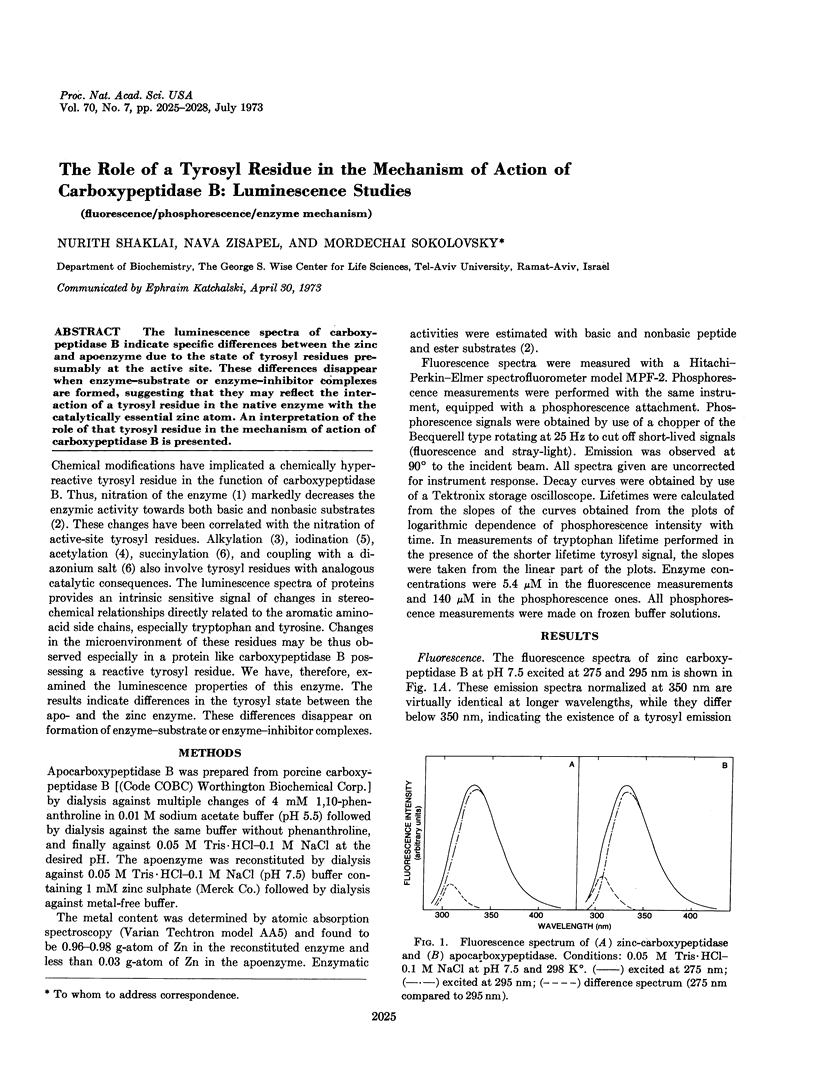


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUGENSTEIN L., NAG-CHAUDHURI J. ENERGY TRANSFER IN PROTEINS. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1145–1147. doi: 10.1038/2031145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Femfert U., Pfleiderer G. The tyrosyl residues at the active site of aminopeptidase M modifications by tetranitromethane. FEBS Lett. 1969 Aug;4(4):262–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen J. T., Vallee B. L. Differences between the conformation of arsanilazotyrosine 248 of carboxypeptidase A in the crystalline state and in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2532–2535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longworth J. W. Techniques for measuring fluorescence and phosphorescence of biological materials. Photochem Photobiol. 1968 Dec;8(6):589–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1968.tb05901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAG-CHAUDHURI J., AUGENSTEIN L. EFFECT OF THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT ON EXCITED STATES OF AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS. Biopolym Symp. 1964;13:441–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr Isolation and sequence of peptides at the active center of bovine carboxypeptidase B. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5246–5253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Lawson W. B. Evidence for tyrosine at the active center of bovine carboxypeptidase B. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 10;241(7):1648–1650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roholt O. A., Pressman D. The sequence around the active-center tyrosyl of porcine carboxypeptidase B. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan 1;18(1):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M., Eisenbach L. Porcine carboxypeptidase B. Arsanilazocarboxypeptidase, spectral and functional consequences of modification of tyrosine-"248". Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb;25(3):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolovsky M. Porcine carboxypeptidase B. Nitration of the functional tyrosyl residue with tetranitromethane. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong T., Bersohn R., Brumer P., Luk C. K., Tao T. Effect of pH on the phosphorescence of tryptophan, tyrosine, and proteins. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2979–2985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF E. C., SCHIRMER E. W., FOLK J. E. The kinetics of carboxypeptidase B activity. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3094–3099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeargers E., Bishai F. R., Augenstein L. On the nature of tyrosine phosphorescence from proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90768-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisapel N., Sokolovsky M. Porcine carboxypepticase B: multiple substrates binding modes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):357–363. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


