Abstract
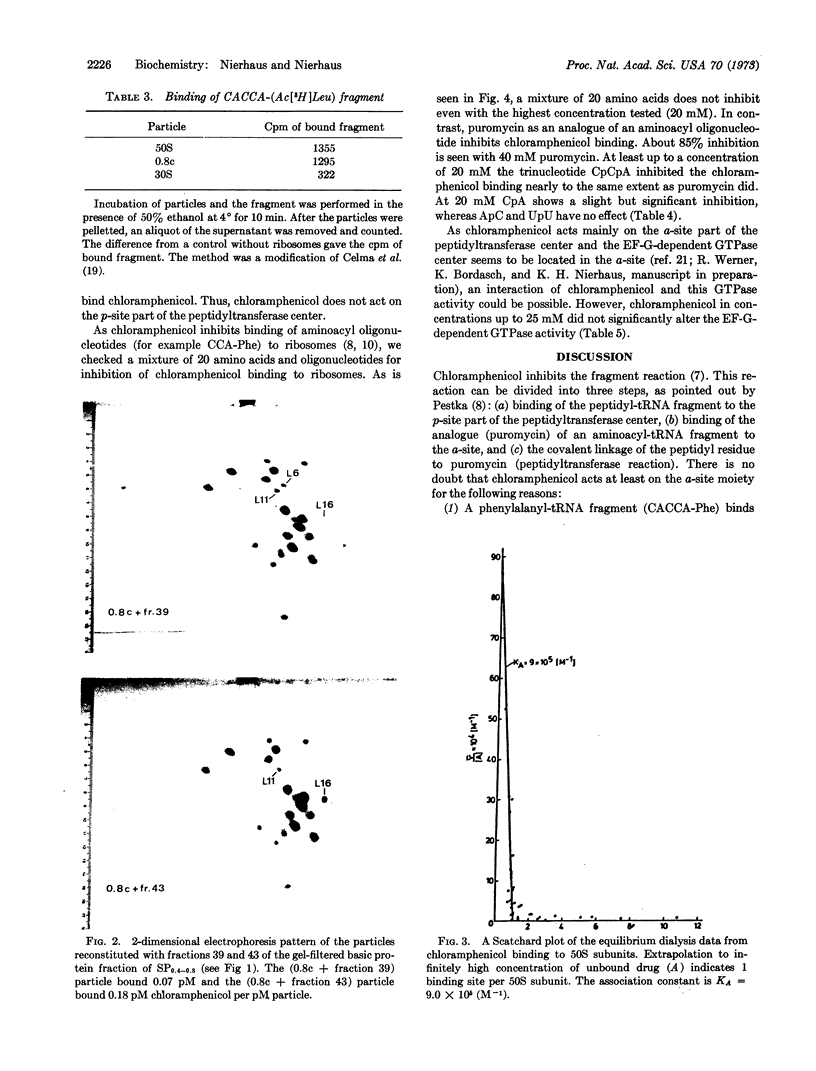
50S-derived cores were prepared by treatment of 50S subunits with 0.4 M Licl (0.4c core) and 0.8 M Licl (0.8c core), respectively. 0.4c cores bind chloramphenicol whereas 0.8c cores do not. The split proteins obtained during the transitions 0.4c → 0.8c were separated by DEAE-cellulose chromatography and Sephadex G-100 gel filtration. Reconstitution experiments with the fractionated proteins demonstrated that protein L16 is involved in chloramphenicol binding.
In contrast to chloramphenicol, the CACCA-(N-acetyl-leucyl) fragment is bound by the 0.8c core, i.e., this core contains the intact p-site moiety of the peptidyltransferase center.
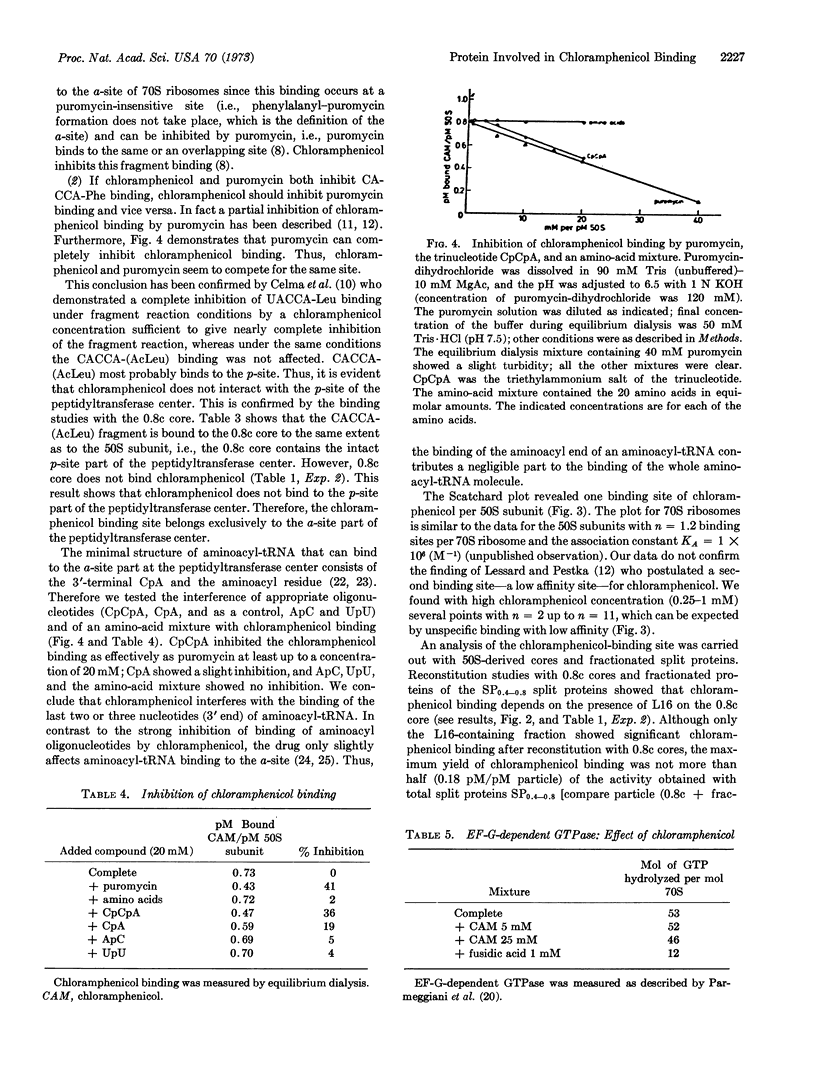
Puromycin can inhibit chloramphenicol binding completely. In the concentration range tested (up to 20 mM) the trinucleotide CCA inhibits chloramphenicol binding as effectively as puromycin, whereas an aminoacid mixture shows no inhibition. It is concluded that chloramphenicol acts exclusively on the a-site part of the peptidyltransferase center interfering with the binding of the last two or three nucleotides (3′ end) of aminoacyl-tRNA.
Keywords: LiCl 50S cores, ribosomal split proteins, equilibrium dialysis, chloramphenicol action
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1970 Feb 16;6(3):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes: Binding of UACCA-Leu to 50 S subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Mar 16;13(4):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80546-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Vazquez D., Modolell J. Failure of fusidic acid and siomycin to block ribosomes in the pretranslocated state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1240–1246. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90844-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutsogeorgopoulos C. Inhibitors of the reaction between puromycin and polylysyl-RNA in the presence of ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 7;27(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutsogeorgopoulos C. On the mechanism of action of chloramphenicol in protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 24;129(1):214–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Goldstein A., Kanner L. C. Inhibition by chlorampenicol of the growth of nascent protein chains in Escherichia coli. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Mar;2(2):158–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Monro R. E., Torres-Pinedo R., Vazquez D. Substrate- and antibiotic-binding sites at the peptidyl-transferase centre of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Studies on the chloramphenicol. lincomycin and erythromycin sites. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C., Braun C. B. Measurement of binding of chloramphenicol by intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1671–1676. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1671-1676.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessard J. L., Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 23. Chloramphenicol, aminoacyl-oligonucleotides, and Escherichia coli ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6909–6912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Staehelin T., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. The peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:357–368. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 8. Survey of the effect of antibiotics of N-acetyl-phenylalanyl-puromycin formation: possible mechanism of chloramphenicol action. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XI. Antibiotic effects on phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):709–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H., Harris R. J., Clarke L. P., Wheldrake J. F., Elliott W. H. Structural requirements of inhibition of polyphenylalanine synthesis by aminoacyl and nucleotidyl analogues of puromycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;179(1):248–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ D. ANTIBIOTICS WHICH AFFECT PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: THE UPTAKE OF 14C-CHLORAMPHENICOL BY BACTERIA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:409–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Monro R. E. Effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis on the binding of aminoacyl tRNA to ribosomal subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):155–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. The binding of chloramphenicol by ribosomes from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFE A. D., HAHN F. E. MODE OF ACTION OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. IX. EFFECTS OF CHLORAMPHENICOL UPON A RIBOSOMAL AMINO ACID POLYMERIZATION SYSTEM AND ITS BINDING TO BACTERIAL RIBOSOME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan 11;95:146–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukioka M., Morisawa S. Enhancement of the phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to the peptidyl recognition center of ribosomal peptidyltransferase and inhibition of the chloramphenicol binding to ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 16;254(2):304–315. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90839-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukioka M., Morisawa S. Reversibility of chloramphenicol inhibition of the poly U directed polyphenylalanine synthesis by G factor and GTP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 30;40(6):1331–1339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





