Abstract
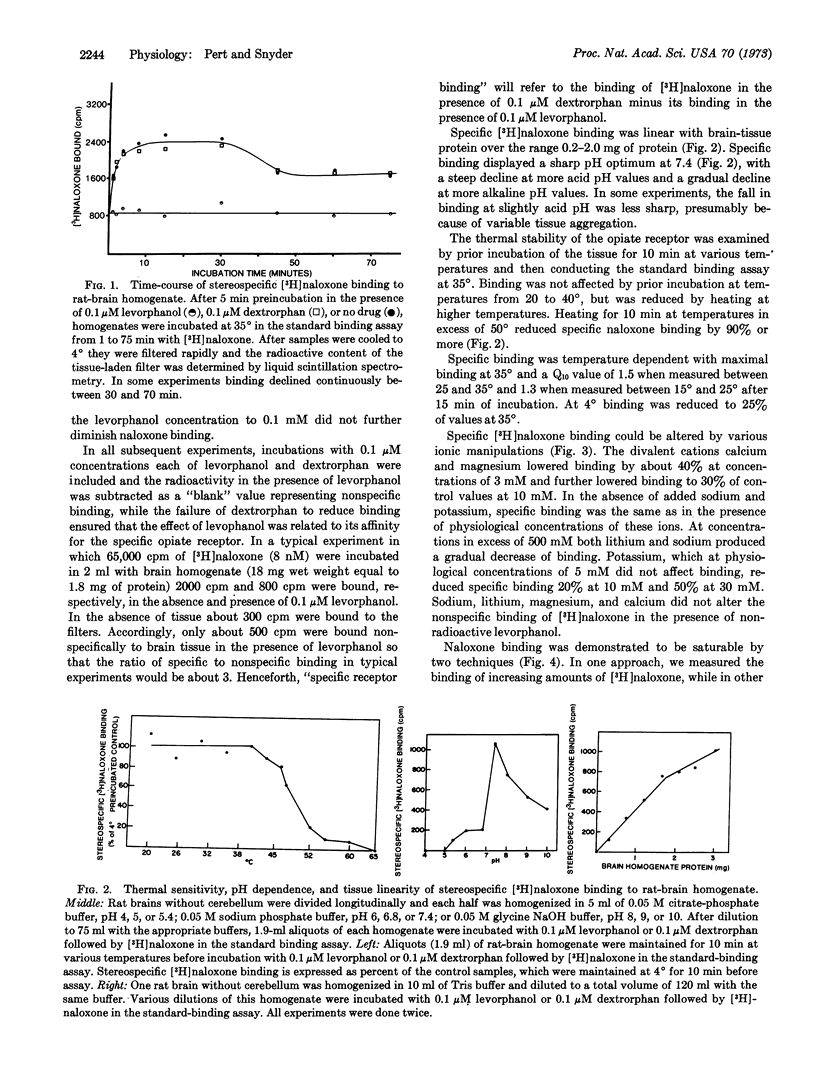
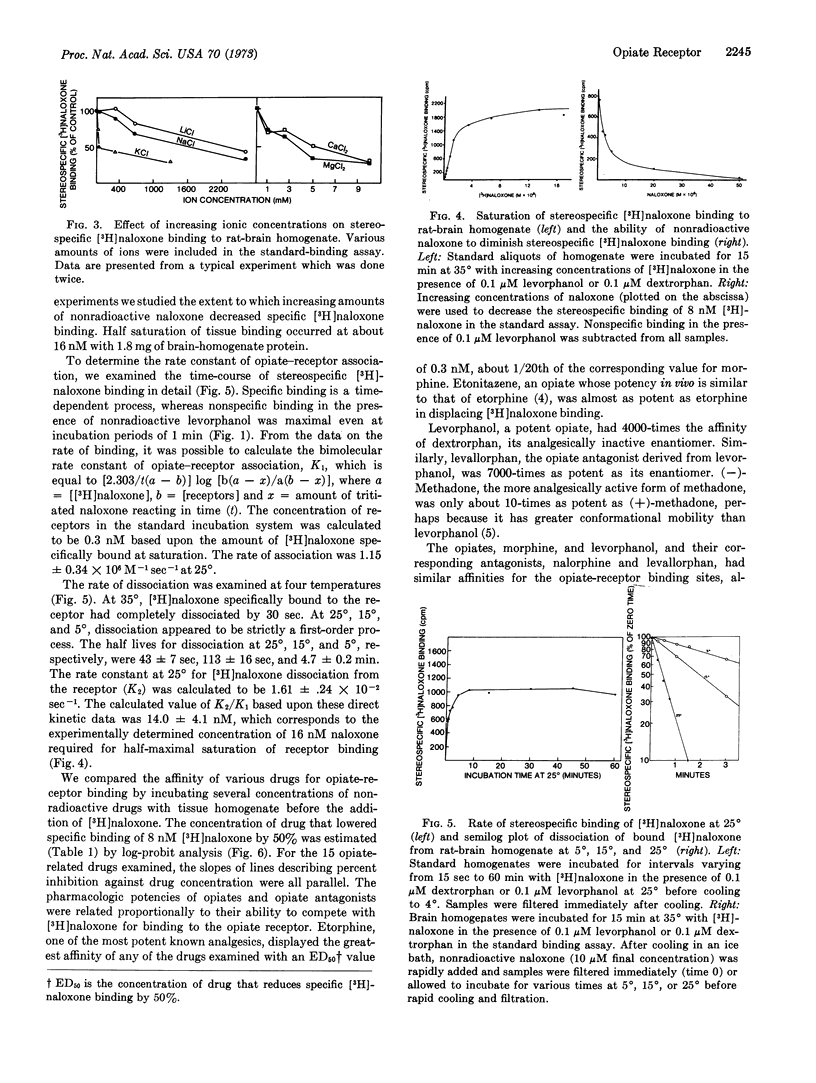
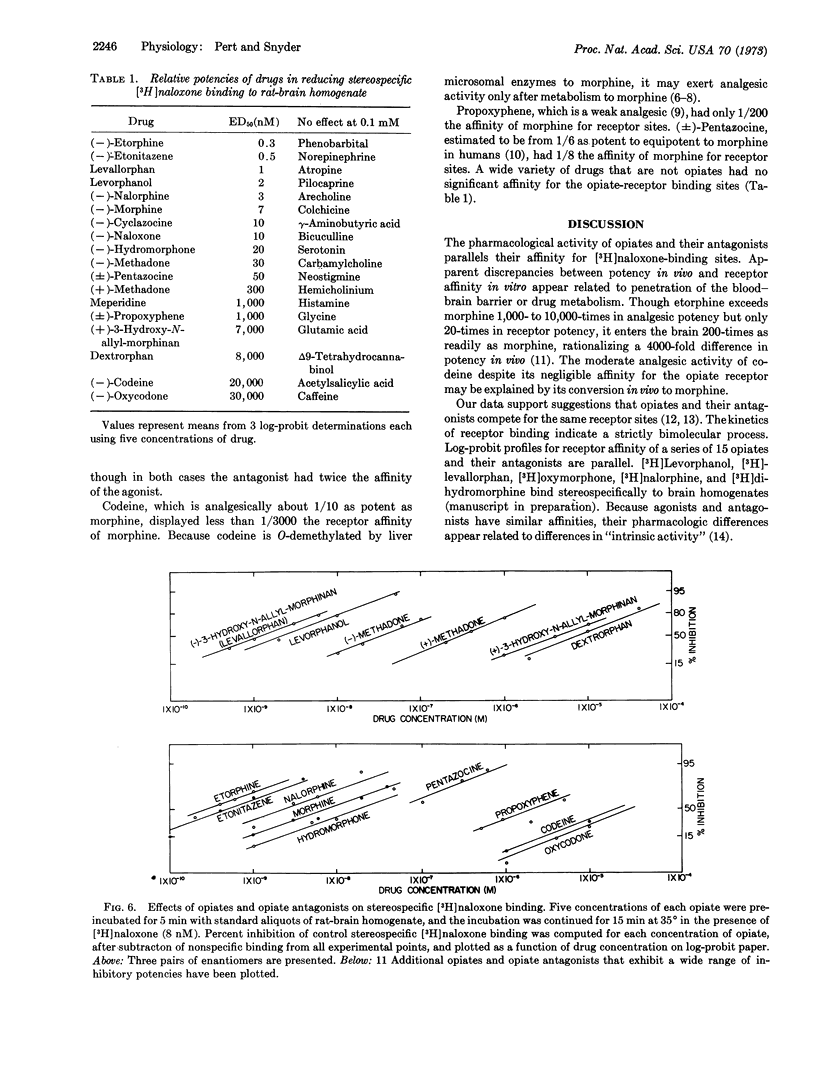
[3H]Naloxone, a potent opiate antagonist, binds stereospecifically to opiate-receptor sites in rat-brain tissue. The binding is time, temperature, and pH dependent and saturable with respect to [3H]naloxone and tissue concentration. The [3H]naloxone-receptor complex formation is bimolecular with a dissociation constant of 20 nM. 15 Opiate agonists and antagonists compete for the same receptors, whose density is 30 pmol/g. Potencies of opiates and their antagonists in displacing [3H]naloxone binding parallel their pharmacological potencies.
Keywords: naloxone, opiate antagonist
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER T. K. Comparative potencies of codeine and its demethylated metabolites after intraventricular injection in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 May;140:155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COX B. M., WEINSTOCK M. QUANTITATIVE STUDIES OF THE ANTAGONISM BY NALORPHINE OF SOME OF THE ACTIONS OF MORPHINE-LIKE ANALGESIC DRUGS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Weinstock M. The effect of analgesic drugs on the release of acetylcholine from electrically stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 May;27(1):81–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lowney L. I., Pal B. K. Stereospecific and nonspecific interactions of the morphine congener levorphanol in subcellular fractions of mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1742–1747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumbach L., Chernov H. I. The analgesic effect of opiate-opiate antagonist combinations in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Sep;149(3):385–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug C. C., Jr, Oka T. Uptake of dihydromorphine-3H by synaptosomes. Life Sci I. 1971 Feb 15;10(4):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90249-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHANNESSON T., SCHOU J. MORPHINE AND NORMORPHINE IN THE BRAINS OF RATS GIVEN IDENTICALLY ANALGAESIC DOSES OF MORPHINE, CODEINE OR NORMORPHINE. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1963;20:165–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1963.tb01733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASAGNA L. THE CLINICAL EVALUATION OF MORPHINE AND ITS SUBSTITUTES AS ANALGESICS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Mar;16:47–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R. Opioid antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Dec;19(4):463–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navon S., Lajtha A. Uptake of morphine in particulate fractions from rat brain. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 18;24(3):534–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portoghese P. S. Stereochemical factors and receptor interactions associated with narcotic analgesics. J Pharm Sci. 1966 Sep;55(9):865–887. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600550902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODS L. A. The pharmacology of nalorphine (N-allylnormorphine). Pharmacol Rev. 1956 Jun;8(2):175–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



