Abstract
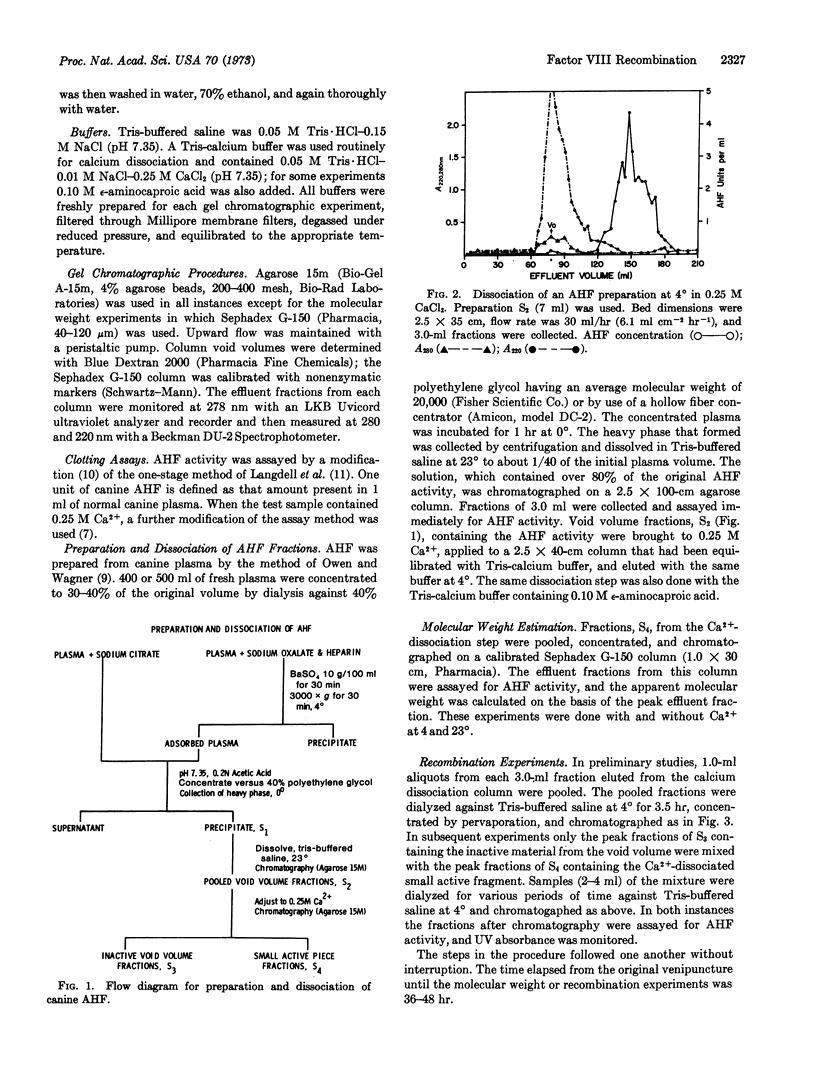
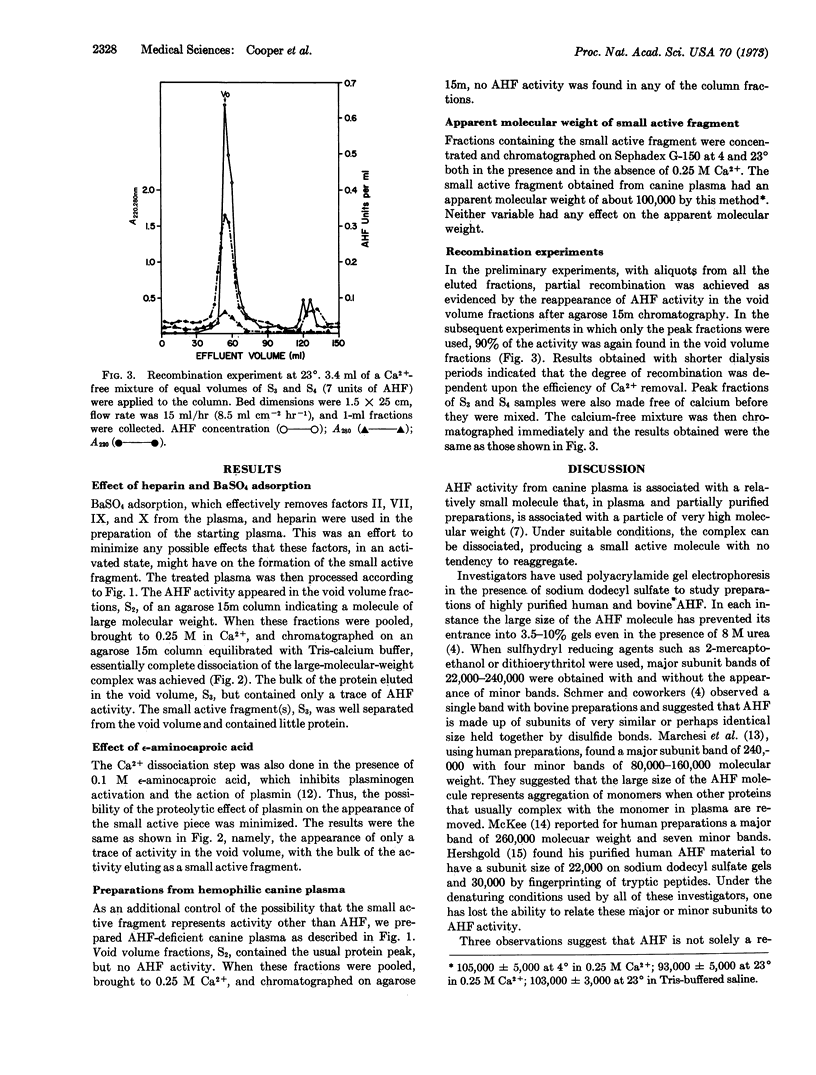
Factor VIII is a large protein molecule of molecular weight 2,000,000 or larger that elutes in the void volume on agarose gel chromatography. It has been shown previously that high concentrations of alkali halides and, more specifically, 0.25 M Ca2+ dissociate the molecule into a large carrier protein and a small fragment that retains the factor VIII activity. Factor VIII was prepared from normal canine plasma collected in sodium oxalate and heparin and adsorbed with BaSO4. Results with Ca2+ dissociation were the same as those obtained with fraction prepared from canine plasma collected in sodium citrate. The addition of 0.1 M ε-aminocaproic acid in the dissociation step had no effect. Fractionation of canine hemophilic plasma produced preparations without activity, and no activity was found when these inert preparations were dissociated with Ca2+. These results indicate that the Ca2+ dissociation is a true dissociation and not caused by enzymatic degradation by plasmin, thrombin, or activated factors VII, IX, or X. The apparent molecular weight of the small active fragment of factor VIII determined by gel chromatography was about 100,000. Finally, when the large carrier protein and the small active fragment of factor VIII were separated by gel chromatography, mixed, and dialyzed free of Ca2+, they recombined to form a large active molecule that appeared in the void volume on agarose gel chromatography.
Keywords: canine plasma fractions, antihemophilic factor, gel chromatography, molecular weight
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershgold E. J., Davison A. M., Janszen M. E. Isolation and some chemical properties of human factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Feb;77(2):185–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. The kaolin clotting time; a rapid one-stage method for diagnosis of coagulation defects. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):406–409. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Shulman N. R., Gralnick H. R. Studies on the purification and characterization of human factor 8. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2151–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI107022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D., Kass L., Lang P. D. Studies on the purification of antihemophilic factor (factor VIII). II. Separation of partially purified antihemophilic factor by gel filtration of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):957–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI106055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmer G., Kirby E. P., Teller D. C., Davie E. W. The isolation nd characterization of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2512–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THELIN G. M., WGNER R. H. Sedimentation of plasma antihemophilic factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Oct;95:70–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Phillips L. L., Rosner W. Separation of sub-units of antihemophilic factor (AHF) by agarose gel chromatography. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Mochtar I. A. Purification of human antihemophilic factor (factor VIII) by gel chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):677–679. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90247-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



