Abstract
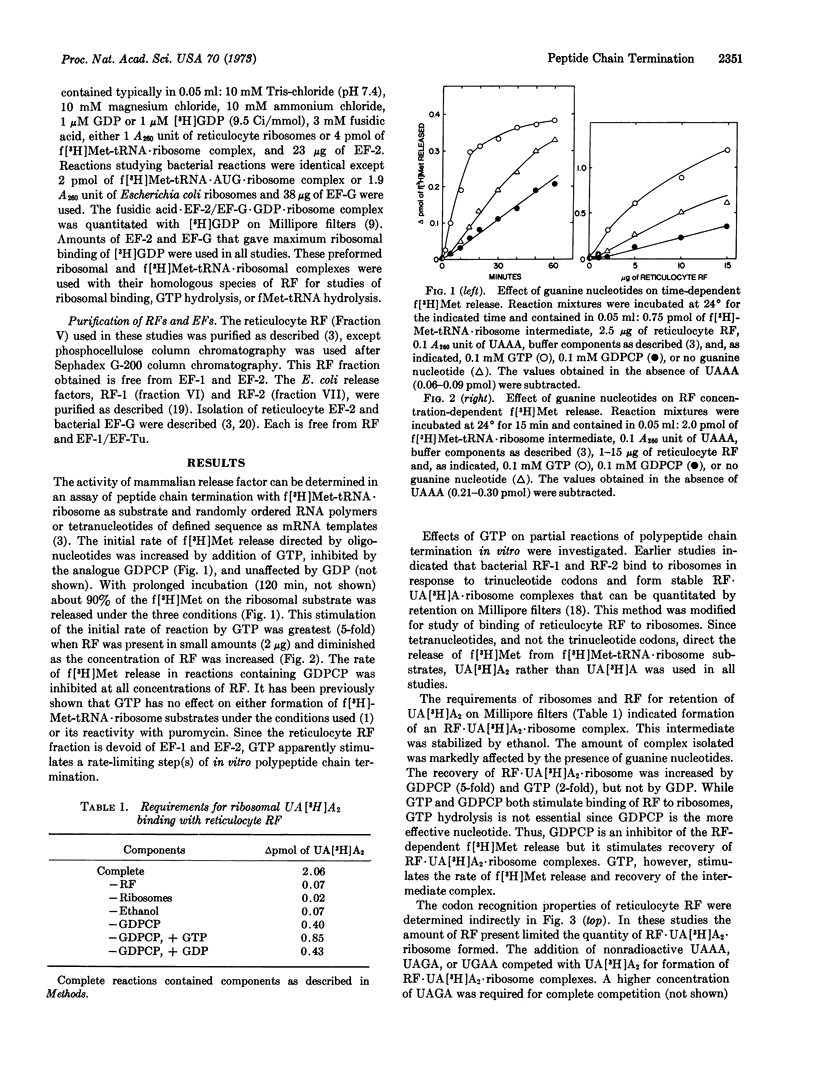
Release of formylmethionine from the reticulocyte ribosomal substrate, f[3H]Met-tRNA·ribosome, is promoted by reticulocyte release factor (RF). The initial rate of this reaction is stimulated by GTP but inhibited by GDPCP. Formation of an RF·UA[3H]A2·ribosome complex is a measure of the binding of reticulocyte RF to the ribosome, and the recovery of this complex is increased by GDPCP and, to a lesser extent, GTP. These studies suggest that GTP is involved in the initial association of RF with the ribosome and that hydrolysis of the γ-phosphate of the guanine nucleotide is required at a subsequent rate-limiting step. The ribosomal-dependent fMet-tRNA hydrolysis and GTPase activities of reticulocyte RF are inhibited when elongation factor (EF)-2 is bound to the respective ribosomal substrate in the presence of fusidic acid and GDP. When EF-G is bound to the f[3H]Met-tRNA·AUG·ribosome substrate with fusidic acid and GDP, the fMet-tRNA hydrolysis activity of Escherichia coli RF-1 and RF-2 is also inhibited. The binding of reticulocyte RF and E. coli RF-1 or RF-2 to their respective ribosomes is prevented when fusidic acid·EF-2/EF-G·GDP·ribosome complexes are used.
Keywords: reticulocyte, fusidic acid, peptide chain termination
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballesta J. P.G., Vazquez D. Reconstitution of the 50S ribosome subunit. Role of proteins L 7 and L 12 in the GTPase activities. Site of action of thiostrepton. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 15;28(3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Mammalian peptide chain termination. II. Codon specificity and GTPase activity of release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):619–624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Naaktgeboren N., Gubbens J., Voorma H. O. Recycling of initiation factors IF-1, IF-2 and IF-3. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):372–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Lin L., Salas M. L., Tao M. Studies on translocation V: Fusidic acid stabilization of a eukaryotic ribosome-translocation factor-GDP complex. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec;11(3):153–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80516-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Zieve F. J., Lin L. Studies on translocation. IV. The hydrolysis of a single round of guanosine triphosphate in the presence of fusidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5662–5667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Zieve F. J., Lin L., Zieve S. T. Formation of the ribosome-G factor-GDP complex in the presence of fusidic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90934-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodley J. W., Zieve F. J., Lin L., Zieve S. T. Studies on translocation. 3. Conditions necessary for the formation and detection of a stable ribosome-G factor-guanosine diphosphate complex in the presence of fusidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5656–5661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Spears C., Weissbach H. The formation of a complex containing ribosomes, transfer factor G and A guanosine nucleotide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Mar 31;34(6):843–848. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrer B., Vázquez D., Modolell J. Inhibition by elongation factor EF G of aminoacyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):733–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey C. T., Tompkins R., Scolnick E., Caryk T., Nirenberg M. Sequential translation of trinucleotide codons for the initiation and termination of protein synthesis. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):135–138. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Moon H. M., Maxwell E. S. Multiple forms and some properties of aminoacyltransferase I (elongation factor I) from rat liver. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4187–4194. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination with mammalian release factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):99–106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination: effect of protein S on ribosomal binding of release factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):537–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J., Milman G., Scolnick E., Caskey T. Peptide chain termination. VI. Purification and site of action of S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):430–437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highland J. H., Bodley J. W., Gordon J., Hasenbank R., Stöffler G. Identity of the ribosomal proteins involved in the interaction with elongation factor G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):147–150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibuki F., Moldave K. The effect of guanosine triphosphate, other nucleotides, and aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid on the activity of transferase I and on its binding to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):44–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood A. H., Sarkar P., Maitra U. Release of polypeptide chain initiation factor IF-2 during initiation complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3602–3605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin M., Lipmann F. Fusidic acid: inhibition of factor T2 in reticulocyte protein synthesis. Science. 1969 Apr 4;164(3875):71–72. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3875.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L. Elongation factors EF Tu and EF G interact at related sites on ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):752–755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Goldstein J., Scolnick E., Caskey T. Peptide chain termination. 3. Stimulation of in vitro termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):183–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Vazquez D. Inhibition by aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid of elongation factor G-dependent binding of guanosine nucleotide to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):488–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Sarkar S., Thach R. E. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in the initiation of peptide synthesis. 3. Binding of formylmethionyl-tRNA to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1638–1644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Skoultchi A., Waterson J., Lengyel P. Peptide chain elongation: GTP cleavage catalysed by factors binding aminoacyl-transfer RNA to the ribosome. Nature. 1969 May 17;222(5194):645–648. doi: 10.1038/222645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M. Demonstration of a guanosine triphosphate-dependent enzymatic binding of aminoacyl-ribonucleic acid to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1811–1816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman N., Bodley J. W. Ribosomes cannot interact simultaneously with elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):686–689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Inability of E. coli ribosomes to interact simultaneously with the bacterial elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1850–1856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Caskey C. T. Peptide chain termination. V. The role of release factors in mRNA terminator codon recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1235–1241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Moldave K. Characterization of the interaction of aminoacyltransferase II with ribosomes. Binding of transferase II and translocation of peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5354–5360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoultchi A., Ono Y., Waterson J., Lengyel P. Peptide chain elongation; indications for the binding of an amino acid polymerization factor, guanosine 5'-triphosphate--aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid complex to the messenger-ribosome complex. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 3;9(3):508–514. doi: 10.1021/bi00805a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kinoshita T., Masukawa H. Mechanism of protein synthesis inhibition by fusidic acid and related antibiotics. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Feb 15;30(3):278–283. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Redfield B., Yamasaki E., Davis R. C., Jr, Pestka S., Brot N. Studies on the ribosomal sites involved in factors Tu and G-dependent reactions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Mar;149(1):110–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosawa H., Inoue-Yokosawa N., Arai K. I., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine triphosphate hydrolysis in elongation factor Tu-promoted binding of aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid to ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):375–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



