Abstract
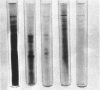
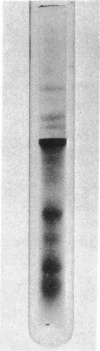
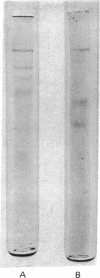
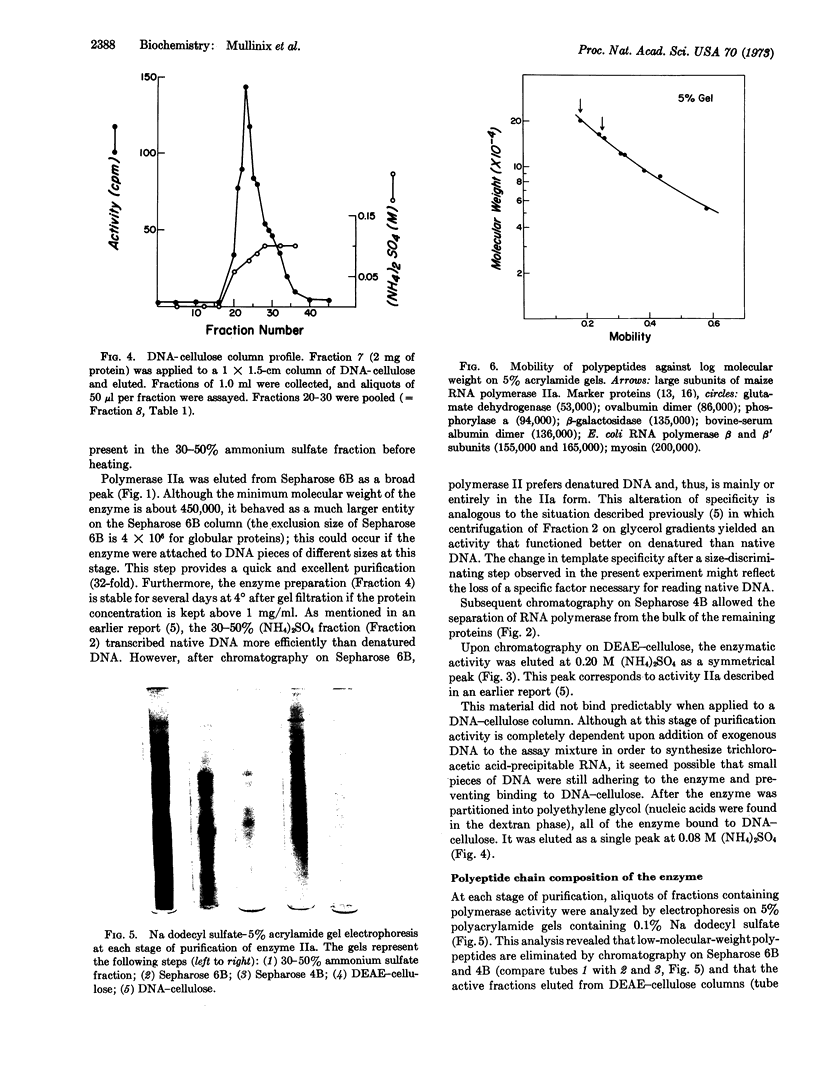
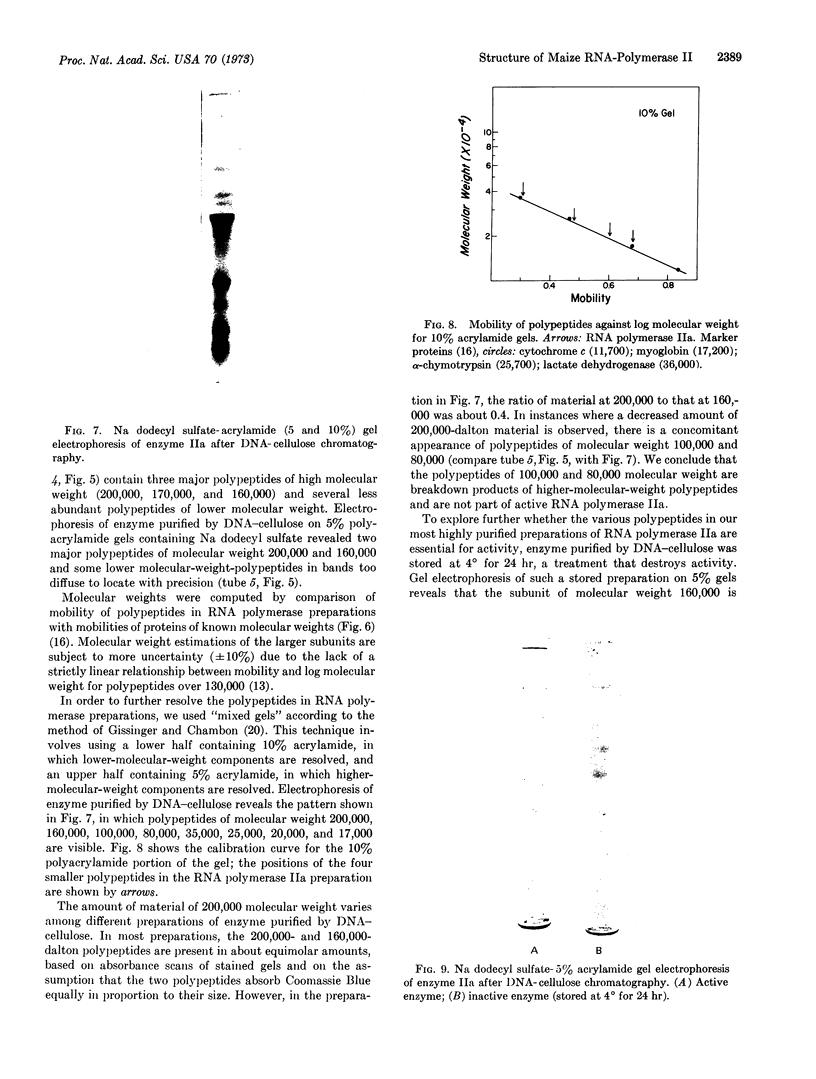
Nuclear DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II has been purified from leaves of Zea mays by a new procedure that improves enzyme stability and thus permits more manipulation during purification. The purification procedure includes a heating step, gel filtration on Sepharose 6B and 4B, and chromatography on DEAE- and DNA-celluloses. This method of purification yields an enzyme that exhibits maximal activity when denatured DNA is used as a template. Electrophoresis of highly purified enzyme on polyacrylamide gels containing sodium dodecyl sulfate indicates that maize RNA polymerase IIa is composed of several polypeptide subunits. The most highly purified preparations contain polypeptides with molecular weights of 200,000, 160,000, 35,000, 25,000, 20,000, and 17,000.
Keywords: polypeptide subunits
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts B. M., Amodio F. J., Jenkins M., Gutmann E. D., Ferris F. L. Studies with DNA-cellulose chromatography. I. DNA-binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:289–305. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Smith H. J., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: partial purification and properties of the chloroplast enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. Separation and characterization of the subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6168–6176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H.W. Purification of the rat liver form B DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gissinger F., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 2. Purification of calf-thymus AI enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):277–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01911.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 3. Purification of calf-thymus BI and BII enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gissinger F., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 1. Large-scale solubilization and separation of A and B calf-thymus RNA-polymerase activities. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jul 13;28(2):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01910.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORNSTEIN L. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. I. BACKGROUND AND THEORY. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:321–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polya G. M. Wheat leaf RNA polymerases. 3. Purification of the soluble RNA polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain G. C., Mullinix K. P., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: nuclear RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2647–2651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Blatti S. P., Rutter W. J. Molecular structures of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (II) from calf thymus and rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2994–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Studies on the stimulation by ammonium sulphate of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of isolated rat-liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):478–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]