Abstract
Lyme disease or Lyme borreliosis, which is caused by three groups of the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi, is transmitted in North America, Europe, and Asia by ticks of the Ixodes ricinus complex. The primary areas around the world that are now affected by Lyme disease are near the terminal moraine of the glaciers 15,000 years ago. The emergence of Lyme disease in the United States in this century is thought to have occurred because of ecological conditions favorable for deer. From 1982 through 1991, 40,195 cases occurring in 47 states were reported to the Centers for Disease Control, but enzootic cycles of B. burgdorferi have been identified in only 19 states. During the last several decades, the disease has spread to new areas and has caused focal outbreaks, including locations near Boston, New York, and Philadelphia. Lyme disease is like syphilis in its multisystem involvement, occurrence in stages, and mimicry of other diseases. Diagnosis of late neurologic abnormalities of the disorder has created the most difficulty. A recent phenomenon is that a number of poorly understood conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome or fibromyalgia, are misdiagnosed as "chronic Lyme disease." Part of the reason for misdiagnosis is due to problems associated with diagnostic tests. The various manifestations of Lyme disease can usually be treated successfully with oral doxycycline or amoxicillin, except for objective neurologic manifestations, which seem to require intravenous therapy. Vector control of thick-borne diseases has been difficult and, therefore, reduction of the risk of infection has been limited primarily to personal protection measures.
Full text
PDF

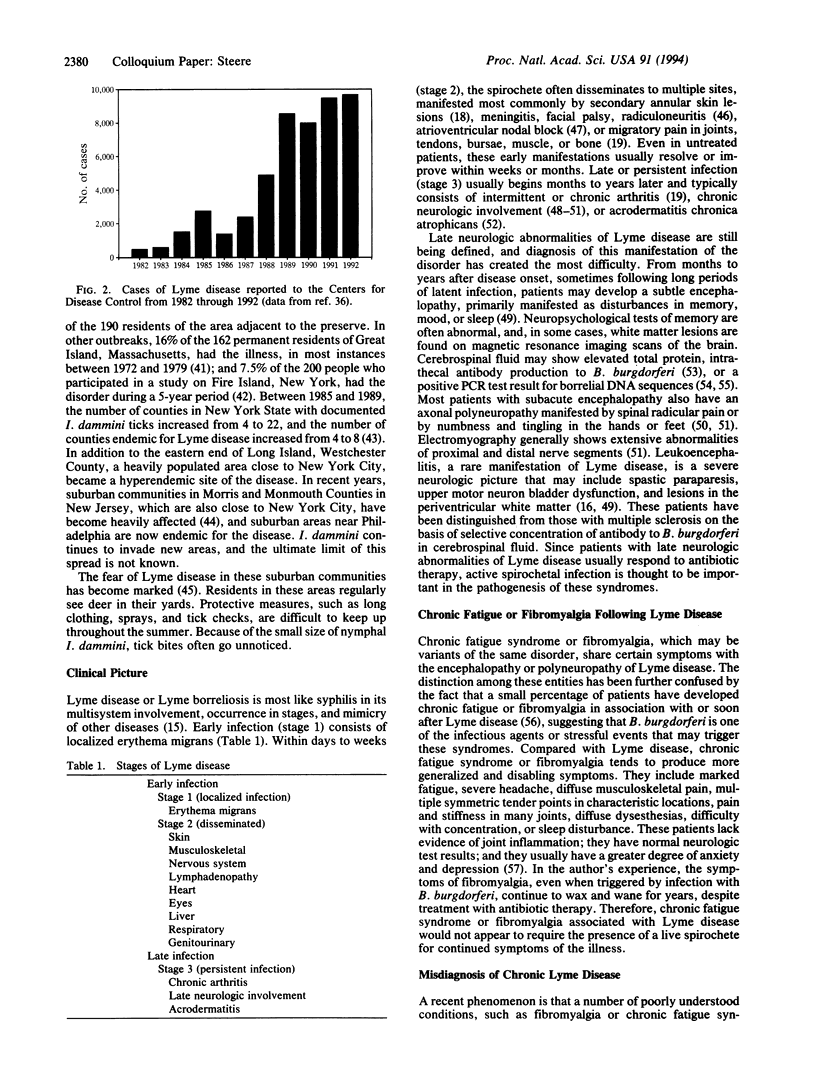



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann R., Kabatzki J., Boisten H. P., Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Hartung S., Runne U. Spirochäten-Atiologie der Erythema-chronicum-migrans-Krankheit. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1984 Jan 20;109(3):92–97. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann R., Rehse-Küpper B., Gollmer E., Schmidt R. Chronic neurologic manifestations of erythema migrans borreliosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:16–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ai C. X., Hu R. J., Hyland K. E., Wen Y. X., Zhang Y. G., Qiu Q. C., Li D. Y., Liu X. D., Shi Z. X., Zhao J. H. Epidemiological and aetiological evidence for transmission of Lyme disease by adult Ixodes persulcatus in an endemic area in China. Int J Epidemiol. 1990 Dec;19(4):1061–1065. doi: 10.1093/ije/19.4.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Brehmer-Andersson E., Hovmark A. Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans--a spirochetosis. Clinical and histopathological picture based on 32 patients; course and relationship to erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius. Am J Dermatopathol. 1986 Jun;8(3):209–219. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198606000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Early and late cutaneous manifestations in Ixodes-borne borreliosis (erythema migrans borreliosis, Lyme borreliosis). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:4–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakken L. L., Case K. L., Callister S. M., Bourdeau N. J., Schell R. F. Performance of 45 laboratories participating in a proficiency testing program for Lyme disease serology. JAMA. 1992 Aug 19;268(7):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranton G., Postic D., Saint Girons I., Boerlin P., Piffaretti J. C., Assous M., Grimont P. A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;42(3):378–383. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-3-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Fish D. The biological and social phenomenon of Lyme disease. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1610–1616. doi: 10.1126/science.8503006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Coleman L. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from erythema migrans lesions and perilesional skin. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):359–361. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.359-361.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Ormiston B. G., Coleman J. L., Hanrahan J. P., Benach J. L. Prevalence of the Lyme disease spirochete in populations of white-tailed deer and white-footed mice. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. N., Lane R. S. Lyme disease in California: a novel enzootic transmission cycle of Borrelia burgdorferi. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1439–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.1604318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Lane R. S., Barbour A. G., Gresbrink R. A., Anderson J. R. The western black-legged tick, Ixodes pacificus: a vector of Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Sep;34(5):925–930. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canica M. M., Nato F., du Merle L., Mazie J. C., Baranton G., Postic D. Monoclonal antibodies for identification of Borrelia afzelii sp. nov. associated with late cutaneous manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1993;25(4):441–448. doi: 10.3109/00365549309008525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Conaty S. M., Platkin S. P., Luft B. J. Amoxycillin plus probenecid versus doxycycline for treatment of erythema migrans borreliosis. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1404–1406. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93103-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Conaty S. M., Platkin S. P., Luft B. J. Amoxycillin plus probenecid versus doxycycline for treatment of erythema migrans borreliosis. Lancet. 1990 Dec 8;336(8728):1404–1406. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93103-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekonenko E. J., Steere A. C., Berardi V. P., Kravchuk L. N. Lyme borreliosis in the Soviet Union: a cooperative US-USSR report. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):748–753. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinerman H., Steere A. C. Lyme disease associated with fibromyalgia. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 15;117(4):281–285. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-4-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler F., Whalen J. A., Reinhardt B. N., Steere A. C. Western blotting in the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):392–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Flavell R. A. Protection of mice against the Lyme disease agent by immunizing with recombinant OspA. Science. 1990 Oct 26;250(4980):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2237407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Telford S. R., 3rd, Barthold S. W., Kantor F. S., Spielman A., Flavell R. A. Elimination of Borrelia burgdorferi from vector ticks feeding on OspA-immunized mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5418–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M. D., Schwartz B. S., Friedmann C., Maccarillo B., Borbi M., Tuccillo R. Lyme disease in New Jersey outdoor workers: a statewide survey of seroprevalence and tick exposure. Am J Public Health. 1990 Oct;80(10):1225–1229. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.10.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman J. L., Jurkovich P., Kramber J. M., Johnson R. C. Molecular detection of persistent Borrelia burgdorferi in the urine of patients with active Lyme disease. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.269-278.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin J. J., Little B. W., Coyle P. K., Dattwyler R. J. Lyme disease: cause of a treatable peripheral neuropathy. Neurology. 1987 Nov;37(11):1700–1706. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.11.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperin J. J., Luft B. J., Anand A. K., Roque C. T., Alvarez O., Volkman D. J., Dattwyler R. J. Lyme neuroborreliosis: central nervous system manifestations. Neurology. 1989 Jun;39(6):753–759. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanrahan J. P., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Bosler E. M., Morse D. L., Cameron D. J., Edelman R., Kaslow R. A. Incidence and cumulative frequency of endemic Lyme disease in a community. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):489–496. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R. F., Meadows M. E., Vincent L. C., Logigian E. L., Steere A. C. Memory impairment and depression in patients with Lyme encephalopathy: comparison with fibromyalgia and nonpsychotically depressed patients. Neurology. 1992 Jul;42(7):1263–1267. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.7.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata M., Baba S., Iguchi K., Yamaguti N., Russell H. Lyme disease in Japan and its possible incriminated tick vector, Ixodes persulcatus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):854–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller T. L., Halperin J. J., Whitman M. PCR detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of Lyme neuroborreliosis patients. Neurology. 1992 Jan;42(1):32–42. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krampitz H. E. In vivo isolation and maintenance of some wild strains of European hard tick spirochetes in mammalian and arthropod hosts. A parasitologist's view. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):21–28. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastavica C. C., Wilson M. L., Berardi V. P., Spielman A., Deblinger R. D. Rapid emergence of a focal epidemic of Lyme disease in coastal Massachusetts. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 19;320(3):133–137. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901193200301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebech A. M., Hansen K. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in urine samples and cerebrospinal fluid samples from patients with early and late Lyme neuroborreliosis by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jul;30(7):1646–1653. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.7.1646-1653.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Wilson M. L., Spielman A. Mice as reservoirs of the Lyme disease spirochete. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Mar;34(2):355–360. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebling M. R., Nishio M. J., Rodriguez A., Sigal L. H., Jin T., Louie J. S. The polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in human body fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 May;36(5):665–675. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Kaplan R. F., Steere A. C. Chronic neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Nov 22;323(21):1438–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011223232102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logigian E. L., Steere A. C. Clinical and electrophysiologic findings in chronic neuropathy of Lyme disease. Neurology. 1992 Feb;42(2):303–311. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Lubke L., Hauglum W., Garon C. F. Species-specific identification of and distinction between Borrelia burgdorferi genomic groups by using 16S rRNA-directed oligonucleotide probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Mar;30(3):628–632. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.3.628-632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massarotti E. M., Luger S. W., Rahn D. W., Messner R. P., Wong J. B., Johnson R. C., Steere A. C. Treatment of early Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1992 Apr;92(4):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90270-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Duffy D. C., Campbell S. R. An unexpected result from burning vegetation to reduce Lyme disease transmission risks. J Med Entomol. 1993 May;30(3):642–645. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Ribeiro J. M., Spielman A. Lyme disease and babesiosis: acaricide focused on potentially infected ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):609–614. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather T. N., Ribeiro J. M., Spielman A. Lyme disease and babesiosis: acaricide focused on potentially infected ticks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 May;36(3):609–614. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuschka F. R., Spielman A. The emergence of Lyme disease in a changing environment in North America and central Europe. Exp Appl Acarol. 1986 Dec;2(4):337–353. doi: 10.1007/BF01193900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melski J. W., Reed K. D., Mitchell P. D., Barth G. D. Primary and secondary erythema migrans in central Wisconsin. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Jun;129(6):709–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocton J. J., Dressler F., Rutledge B. J., Rys P. N., Persing D. H., Steere A. C. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA by polymerase chain reaction in synovial fluid from patients with Lyme arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jan 27;330(4):229–234. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199401273300401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachner A. R., Steere A. C. The triad of neurologic manifestations of Lyme disease: meningitis, cranial neuritis, and radiculoneuritis. Neurology. 1985 Jan;35(1):47–53. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Rys P. N., Dodge D. E., White T. J., Malawista S. E., Spielman A. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi DNA in museum specimens of Ixodes dammini ticks. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1420–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.2402635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister H. W., Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schielke E., Sörgel F., Einhäupl K. M. Randomized comparison of ceftriaxone and cefotaxime in Lyme neuroborreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):311–318. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G., Pfister H. W., Einhäupl K. Repeated isolation of spirochetes from the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with meningoradiculitis Bannwarth. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;3(6):564–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02013623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahn D. W., Malawista S. E. Lyme disease: recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Mar 15;114(6):472–481. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-6-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck C. E., Snoddy E. L., Spielman A. Pressurized sprays of permethrin or deet on military clothing for personal protection against Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1986 Jul 28;23(4):396–399. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/23.4.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze T. L., Taylor G. C., Vasvary L. M., Simmons W., Jordan R. A. Effectiveness of an aerial application of carbaryl in controlling Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) adults in a high-use recreational area in New Jersey. J Med Entomol. 1992 May;29(3):544–547. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/29.3.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Goldstein M. D., Ribeiro J. M., Schulze T. L., Shahied S. I. Antibody testing in Lyme disease. A comparison of results in four laboratories. JAMA. 1989 Dec 22;262(24):3431–3434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro E. D., Gerber M. A., Holabird N. B., Berg A. T., Feder H. M., Jr, Bell G. L., Rys P. N., Persing D. H. A controlled trial of antimicrobial prophylaxis for Lyme disease after deer-tick bites. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 17;327(25):1769–1773. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212173272501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford K. C., 3rd Effectiveness of host-targeted permethrin in the control of Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) J Med Entomol. 1991 Sep;28(5):611–617. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/28.5.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Pletschette M., Flamm H., Hirschl A. M., Aberer E., Kristoferitsch W., Schmutzhard E. European Lyme borreliosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:274–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Batsford W. P., Weinberg M., Alexander J., Berger H. J., Wolfson S., Malawista S. E. Lyme carditis: cardiac abnormalities of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jul;93(1):8–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Berardi V. P., Weeks K. E., Logigian E. L., Ackermann R. Evaluation of the intrathecal antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi as a diagnostic test for Lyme neuroborreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1203–1209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Broderick T. F., Malawista S. E. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis: epidemiologic evidence for a tick vector. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):312–321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Pachner A. R., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease: successful treatment with high-dose intravenous penicillin. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):767–772. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Schoen R. T., Taylor E. The clinical evolution of Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Nov;107(5):725–731. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-5-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Taylor E., McHugh G. L., Logigian E. L. The overdiagnosis of Lyme disease. JAMA. 1993 Apr 14;269(14):1812–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Taylor E., Wilson M. L., Levine J. F., Spielman A. Longitudinal assessment of the clinical and epidemiological features of Lyme disease in a defined population. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):295–300. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A., Glass J., Patel A., Watt G., Cripps A., Clancy R. Lyme arthritis in the Hunter Valley. Med J Aust. 1982 Feb 6;1(3):139–139. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb132207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. J., Chang H. G., Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Meldrum S. C., Means R. G., Debbie J. G., Birkhead G. S., Morse D. L. The geographic spread and temporal increase of the Lyme disease epidemic. JAMA. 1991 Sep 4;266(9):1230–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. L., Telford S. R., 3rd, Piesman J., Spielman A. Reduced abundance of immature Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) following elimination of deer. J Med Entomol. 1988 Jul;25(4):224–228. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.4.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



