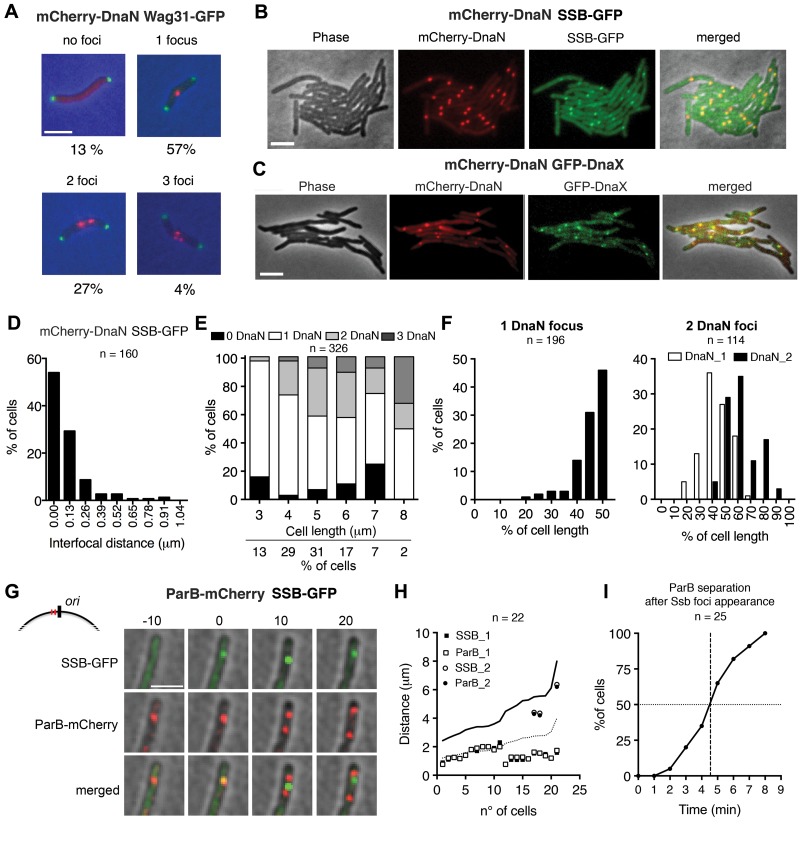
FIG 1 .
Subcellular localization of DNA replisome complexes. (A) Representative snapshots of wild-type cells with zero, one, two, or three mCherry-DnaN foci (red) and their frequencies (n = 645). Green foci, Wag31-GFP. Scale bar, 3 µm. (B) Colocalization of mCherry-DnaN foci with SSB-GFP foci. Scale bar, 3 µm. (C) Colocalization of mCherry-DnaN foci with DnaX-GFP foci. Scale bar, 3 µm. (D) Distribution of interfocal distances between mCherry-DnaN and SSB-GFP foci (n = 160). (E) Number of mCherry-DnaN foci relative to cell length (n = 326). (F) Position of mCherry-DnaN foci in cells with one (n = 196) or two (n = 114) foci. (G) Time-lapse analysis of cells expressing ParB-mCherry and SSB-GFP. Images were recorded at 10-min intervals. As shown in the schematic, ParB binds two parS sequences (red lines) located in the origin-proximal region (black line). Newly formed SSB-GFP foci colocalize with ParB-mCherry (0 min). Duplication and segregation of ParB-mCherry foci occur shortly (10 min) after replisome assembly, and segregation continues thereafter (20 min). Scale bar, 3 µm. (H) Positional correlation between ParB-mCherry and SSB-GFP foci at the first appearance of SSB-GFP foci (n = 22). DNA replication initiates prior to division in some cells. Solid line, cell length; dotted line, midcell. (I) Time-lapse analysis of cells expressing ParB-mCherry and SSB-GFP. Images were recorded at 1-min intervals. Time intervals between the first appearance of SSB-GFP foci and the separation of ParB-mCherry foci are plotted (n = 25).