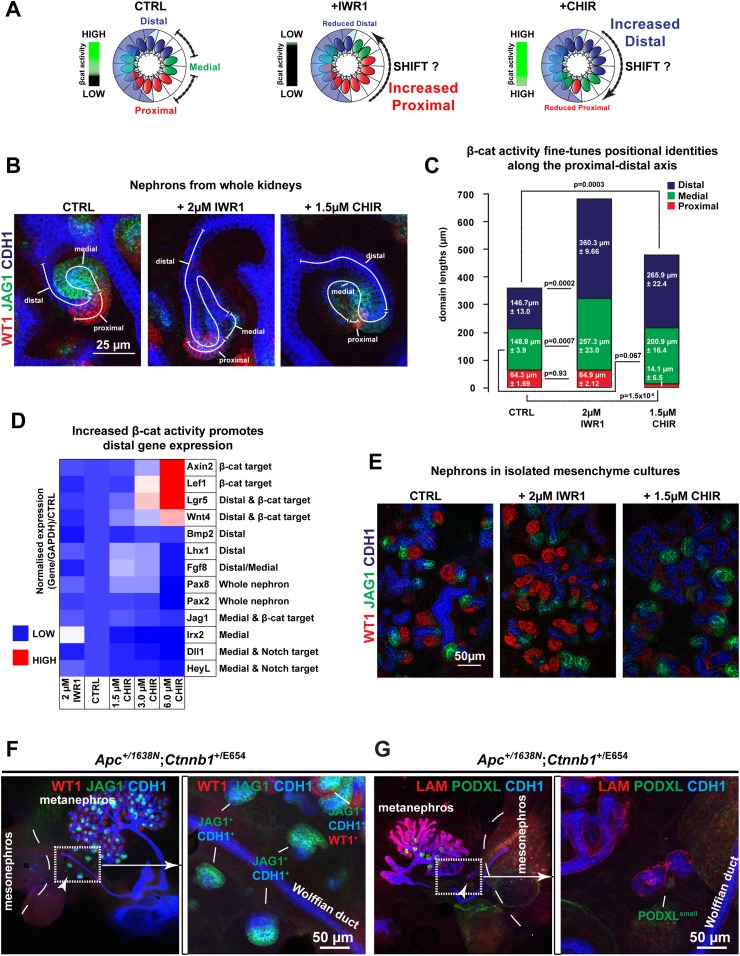
Figure 4. Shifts in positional identity by altered β-catenin activity.
(A) Model of predicted changes in segmentation if the gradient of β-catenin activity specifies positional identities in the nephron. Nephrons depicted as spheres representing renal vesicle stage. Dashed line indicates nephron segments. Gradient bar indicates β-catenin activity. (B) Antibody stains against segment specific markers in nephrons with different β-catenin signalling conditions. (C) Proximal, medial, and distal nephron domain-sizes in Control, CHIR, and IWR1 treated kidneys. Mean values and SEMs indicated within bars on graph. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of markers for nephron induction displayed as a heat-map with information displayed in figure. The RNA was isolated after 48 hr of culture from whole kidneys. (E) Antibody stains on nephrons developed in isolated mesenchyme. (F and G) Apc+/1638N Ctnnb1Y654/E654 kidneys where Ctnnb1Y654 is the wild-type allele. Kidneys characterised using anti-Wt1, Jag1, Podxl, Lam, and Cdh1. Arrowheads and boxed area indicate ectopic nephrons in E–F. Dashed lines separate metanephric and mesonephric regions in E–F.