Abstract
Muscular contraction is essentially the shortening of the S2 subunits of heavy meromyosin, integrated to macroscopic motion by the thick and thin filaments.
Keywords: mechanochemical coupling, meromyosin subfragment 2
Full text
PDF
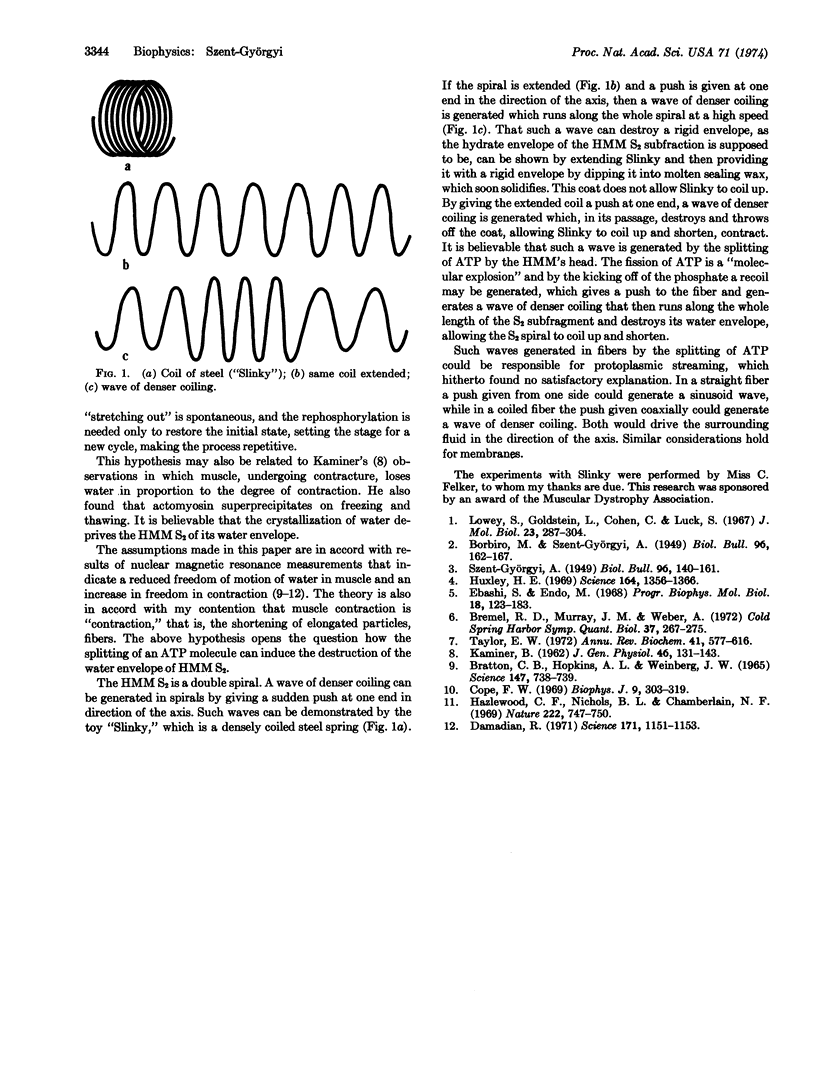
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRATTON C. B., HOPKINS A. L., WEINBERG J. W. NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE STUDIES OF LIVING MUSCLE. Science. 1965 Feb 12;147(3659):738–739. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3659.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence using D2O for structured water in muscle and brain. Biophys J. 1969 Mar;9(3):303–319. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86388-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood C. F., Nichols B. L., Chamberlain N. F. Evidence for the existence of a minimum of two phases of ordered water in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1969 May 24;222(5195):747–750. doi: 10.1038/222747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMINER B. Water loss during contracture of muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Sep;46:131–142. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Goldstein L., Cohen C., Luck S. M. Proteolytic degradation of myosin and the meromyosins by a water-insoluble polyanionic derivative of trypsin: properties of a helical subunit isolated from heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1967 Feb 14;23(3):287–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E. W. Chemistry of muscle contraction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41(10):577–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.003045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



