Abstract
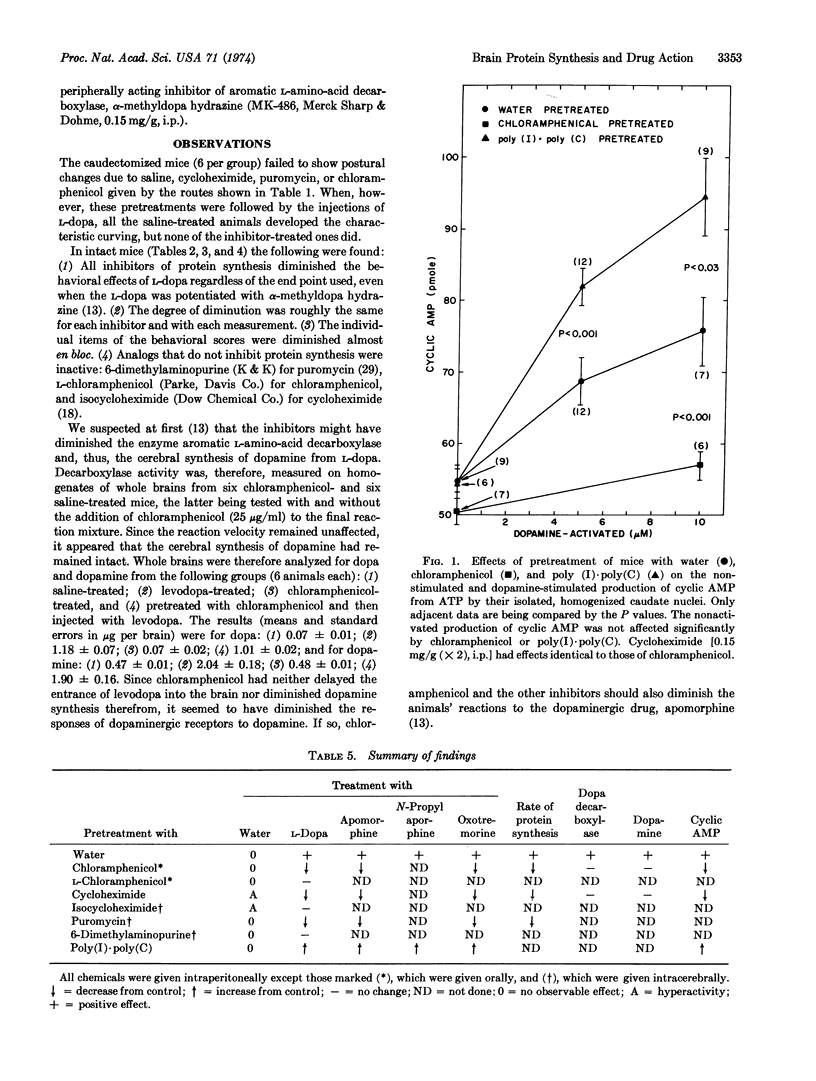
Diminution of cerebral protein synthesis diminished the cerebral responses of mice to some neuroactive drugs, while an increase in synthesis increased the responses. Protein synthesis in whole brains (tested in vitro) was diminished by giving living mice different inhibitors by different routes. The inhibitors tested (chloramphenicol, cycloheximide, and puromycin) diminished the behavioral responses of the mice to levodopa without affecting either its cerebral uptake or its conversion to dopamine. A diminution of the reactions of dopaminergic receptors was suggested by the diminished responses to the dopaminergic drug, apomorphine, while participation of cholinergic ones was suggested by experiments with oxotremorine. Proof that receptors had been specifically involved was secured on homogenized caudate nuclei from chloramphenicol-treated mice, in which the dopamine-activated production of cyclic AMP was markedly diminished. A stimulator of cerebral protein synthesis, the artificial double-stranded RNA, poly(I)·poly(C), increased the behavioral responses to these three drugs while it increased the dopamine-activated production of cyclic AMP. Since all these experimental increases or decreases in the responses to drugs required the lapse of only a few hours, proteins with rapid turnover rates must be critical in the activation of several kinds of cerebral receptors.
Keywords: L-dopa, chloramphenicol, cycloheximide, poly(I)·poly(C), cyclic AMP
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appleman M. M., Kemp R. G. Puromycin: a potent metabolic effect independent of protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 23;24(4):564–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. L., Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Sgherzi A. M. A simple and sensitive saturation assay method for the measurement of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):561–562. doi: 10.1042/bj1210561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTZIAS G. C., GREENOUGH J. J. Concomitant analysis for oxygen uptake and ammonia evolution during the monoamine oxidase reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 May;75(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90392-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. B., Hanin I., Jenden D. J. Gas chromatographic evaluation of the effects of some muscarinic and antimuscarinic drugs on acetylcholine levels in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1970 Jun;19(6):2053–2059. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(70)90302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Miller S. T., Nicholson A. R., Jr, Maston W. H., Tang L. C. Prolongation of the life-span in mice adapted to large amounts of L-dopa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2466–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Tang L. C., Miller S. T., Ginos J. Z. Melatonin and abnormal movements induced by L-dopa in mice. Science. 1971 Jul 30;173(3995):450–452. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3995.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Tang L. C., Miller S. T., Sladic-Simic D., Hurley L. S. A mutation influencing the transportation of manganese, L-dopa, and L-tryptophan. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):410–412. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Tang L., Ginos J. Z., Nicholson A. R., Papavasiliou P. S. Block of cerebral actions of L-dopa with methyl receptor substances. Nature. 1971 Jun 25;231(5304):533–535. doi: 10.1038/231533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronkite E. P. Chloramphenicol misuse. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):533–533. doi: 10.1038/227533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. C., Sells B. H. Biogenesis of 30 -S subunits during recovery from inhibition of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 24;262(3):352–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deanin G. G., Gordon M. W. Chloramphenicol- and cycloheximide-sensitive protein synthetic systems in brain mitochondrial and nerve-ending preparations. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):55–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern R. M., Chaney S. Q., Halpern B. C., Smith R. A. Nicotinamide: a natural inhibitor of tRNA methylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 19;42(4):602–607. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90530-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Colombo B., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. IV. Ribosome behaviour after puromycin release of growing peptide chains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):174–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in caudate nucleus of rat brain, and its similarity to the "dopamine receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten H. Use of inhibitors to study the structure and function of nucleic acids and ribosomes Recent advances. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jul 1;15(4):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80634-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Riley F. The effect of polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid on tumor metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):141–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotti V. J. Action of various centrally acting agents in mice with unilateral caudate brain lesions. Life Sci I. 1971 Jul 15;10(14):781–789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. S., Squire L. R., Barondes S. H. Cycloheximide: its effects on activity are dissociable from its effects on memory. Science. 1971 Apr 2;172(3978):82–84. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3978.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck A. J., Hamilton L. D. L-dopa-induced modification of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 May;140(1):172–175. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanis C. N. Chloramphenicol misuse. Nature. 1970 Aug 1;227(5257):533–533. doi: 10.1038/227533b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanis C. N., Issidorides M. Aberrant mRNA in Parkinsonism: support for hypothesis from studies with chloramphenicol. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):962–963. doi: 10.1038/225962a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strömberg U. DOPA effects on motility in mice; potentiation by MK 485 and dexchlorpheniramine. Psychopharmacologia. 1970 Aug 19;18(1):58–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00402384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISBERGER A. S., WOLFE S. EFFECT OF CHLORAMPHENICOL ON PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:976–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. F., Munro H. N., Ordonez L. A., Wurtman R. J. Dopamine: mediator of brain polysome disaggregation after L-dopa. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):613–616. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. F., Munro H. N., Wurtman R. J. L-dopa: disaggregation of brain polysomes and elevation of brain tryptophan. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):833–835. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whur P., Weatherhead B. Rates of incorporation of ( 3 H)leucine into protein of the pars intermedia of the pituitary in the amphibian Xenopus laevis after change of background colour. J Endocrinol. 1971 Nov;51(3):521–532. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0510521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



