Abstract
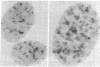
Cytological preparations of interphase nuclei and chromosomes from mouse 3T6 cells prepared at various times after infection with the murine sarcomaleukemia virus complex were hybridized with the [3H]DNA product of the viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase. While uninfected nuclei had an average of 4 autoradiographic grains, infected nuclei had 30 grains at 5 hr after infection and 63-65 grains at 11 and 25 hr. Virus-specific grains were localized in the chromocenters of interphase nuclei and were found also in the centromeric heterochromatin region of metaphase chromosomes. These findings provide evidence that the viral RNA-directed DNA polymerase functions to synthesize virus-specific DNA early after infection and that newly synthesized viral DNA rapidly becomes associated with or integrated into specific intranuclear sites.
Keywords: RNA-directed DNA polymerase, transformed cell
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Scolnick E. M. Induction of murine C-type viruses from clonal lines of virus-free BALB-3T3 cells. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):157–159. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrighi F. E., Hsu T. C., Saunders P., Saunders G. F. Localization of repetitive DNA in the chromosomes of Microtus agrestis by means of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1970;32(2):224–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00286011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrighi F. E., Saunders P. P., Saunders G. F., Hsu T. C. Distribution of repetitious DNA in human chromosomes. Experientia. 1971 Aug;27(8):964–966. doi: 10.1007/BF02135776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluda M. A., Nayak D. P. DNA complementary to viral RNA in leukemic cells induced by avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):329–336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baluda M. A. Widespread presence, in chickens, of DNA complementary to the RNA genome of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):576–580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Gene regulation for higher cells: a theory. Science. 1969 Jul 25;165(3891):349–357. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3891.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt R. A., Gall J. G. Satellite DNA associated with heterochromatin in Rhynchosciara. Chromosoma. 1971 Mar 16;32(4):407–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00285252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. Biochemical studies on adenovirus multiplication. 1. Stimulation of phosphorus incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid and ribouncleic acid. Virology. 1959 Nov;9:343–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Cohen E. H., Polan M. L. Reptitive DNA sequences in drosophila. Chromosoma. 1971;33(3):319–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00284948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Pardue M. L. Formation and detection of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):378–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb L. D., Aaronson S. A., Martin M. A. Heterogeneity of murine leukemia virus in vitro DNA; detection of viral DNA in mammalian cells. Science. 1971 Jun 25;172(3990):1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3990.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. Oncogenic viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:701–756. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Rokutanda M., Fujinaga K., Ray R. K., Rokutanda H., Gurgo C. Mechanism of carcinogenesis by RNA tumor viruses. I. An RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):385–393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel L., Harel J., Lacour F., Huppert J. Homologie entre génome du virus de la myéloblastose aviare (AMV) et génome cellulaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1966 Aug 8;263(6):616–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner R. J., Todaro G. J. Oncogenes of RNA tumor viruses as determinants of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1087–1094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John H. A., Birnstiel M. L., Jones K. W. RNA-DNA hybrids at the cytological level. Nature. 1969 Aug 9;223(5206):582–587. doi: 10.1038/223582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W. Chromosomal and nuclear location of mouse satellite DNA in individual cells. Nature. 1970 Mar 7;225(5236):912–915. doi: 10.1038/225912a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. W., Robertson F. W. Localisation of reiterated nucleotide sequences in Drosophila and mouse by in situ hybridisation of complementary RNA. Chromosoma. 1970;31(3):331–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00321229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rowe W. P., Teich N., Hartley J. W. Murine leukemia virus: high-frequency activation in vitro by 5-iododeoxyuridine and 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Science. 1971 Oct 8;174(4005):155–156. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4005.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E. Rous sarcoma virus nucleotide sequences in cellular DNA: measurement by RNA-DNA hybridization. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):750–753. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Chromosomal localization of mouse satellite DNA. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1356–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M. Chromosomal distribution of rapidly reannealing DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1018–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. N., Robinson H. L., Robinson W. S., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. DNA in uninfected and virus-infected cells complementary to avian tumor virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg S., Robin M. S., Green M. Appearance of virus-specific RNA, virus particles, and cell surface changes in cells rapidly transformed by the murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):186–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Vogt P. K. Appearance of virus-specific DNA in mammalian cells following transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):613–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Weiss R. A., Friis R. R., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. Detection of avian tumor virus-specific nucleotide sequences in avian cell DNAs (reassociation kinetics-RNA tumor viruses-gas antigen-Rous sarcoma virus, chick cells). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):20–24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A., Friis R. R., Katz E., Vogt P. K. Induction of avian tumor viruses in normal cells by physical and chemical carcinogens. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):920–938. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa-Fukada M., Ebert J. D. Hybridization of RNA from Rous sarcoma virus with cellular and viral DNA's. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):870–877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]