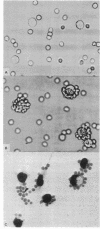
Abstract
Some clones of mouse myeloid leukemic cells (D+) can be induced to undergo cell differentiation to mature macrophages and granulocytes, and other clones (D-) could not be induced to differentiate to mature cells. Normal mature macrophages and granulocytes have surface receptors that form rosettes with erythrocytes coated with specific immunoglobulin or immunoglobulin-complement. The D+ clones were induced to form receptors by prednisolone, cytosine-arabinoside, 5-iododeoxyuridine, actinomycin D, or serum from mice injected with endotoxin. All these compounds thus induced a common change in the cell surface membrane. The induction of receptors required protein synthesis, and receptors were formed before the appearance of mature cells. There were two types of D- clones. One type was induced by these compounds to form receptors, although with a lower inducibility than D+ clones; in the other type there was no induction of receptors. The results indicate that there are different blocks in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Some leukemic cells (IR+D+) can be induced to form receptors and to differentiate to mature cells; others (IR+D-) can form receptors but not mature cells; and a third type (IR-D-) could not be induced to form receptors or mature cells.
Keywords: surface receptors for erythrocytes sensitized with antibody and with antibody and complement, rosettes with sensitized erythrocytes, macrophages, granulocytes
Full text
PDF
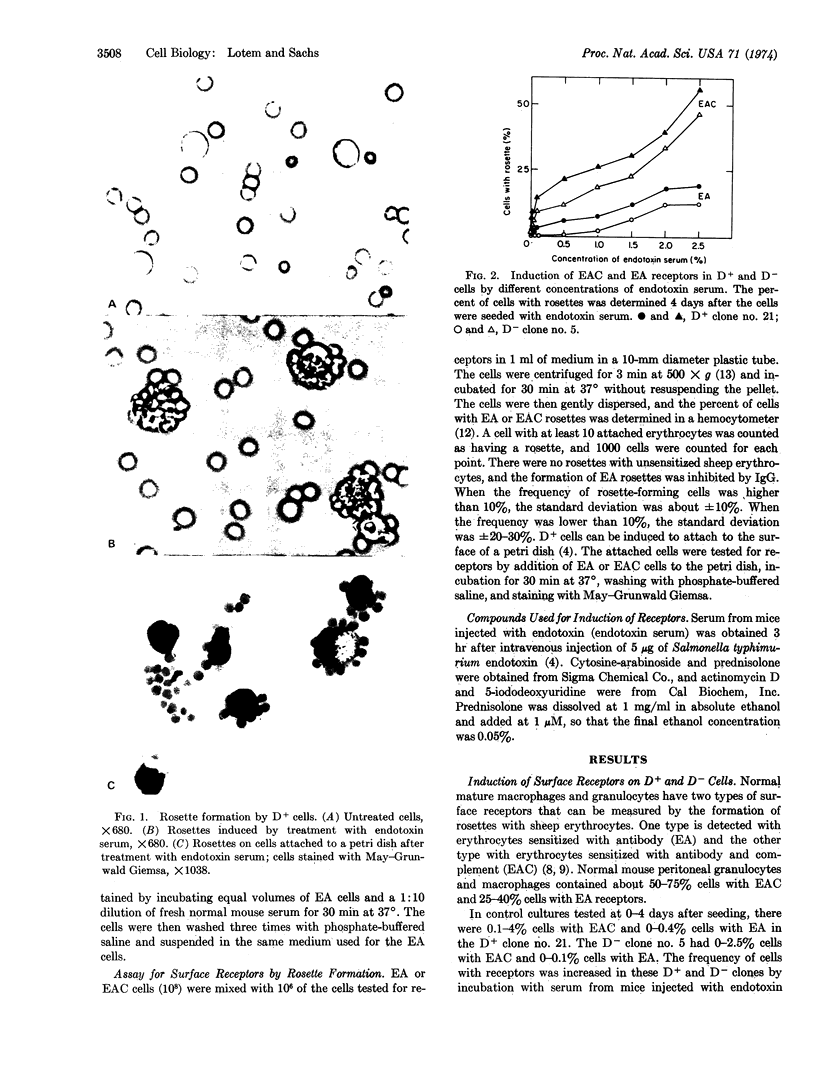

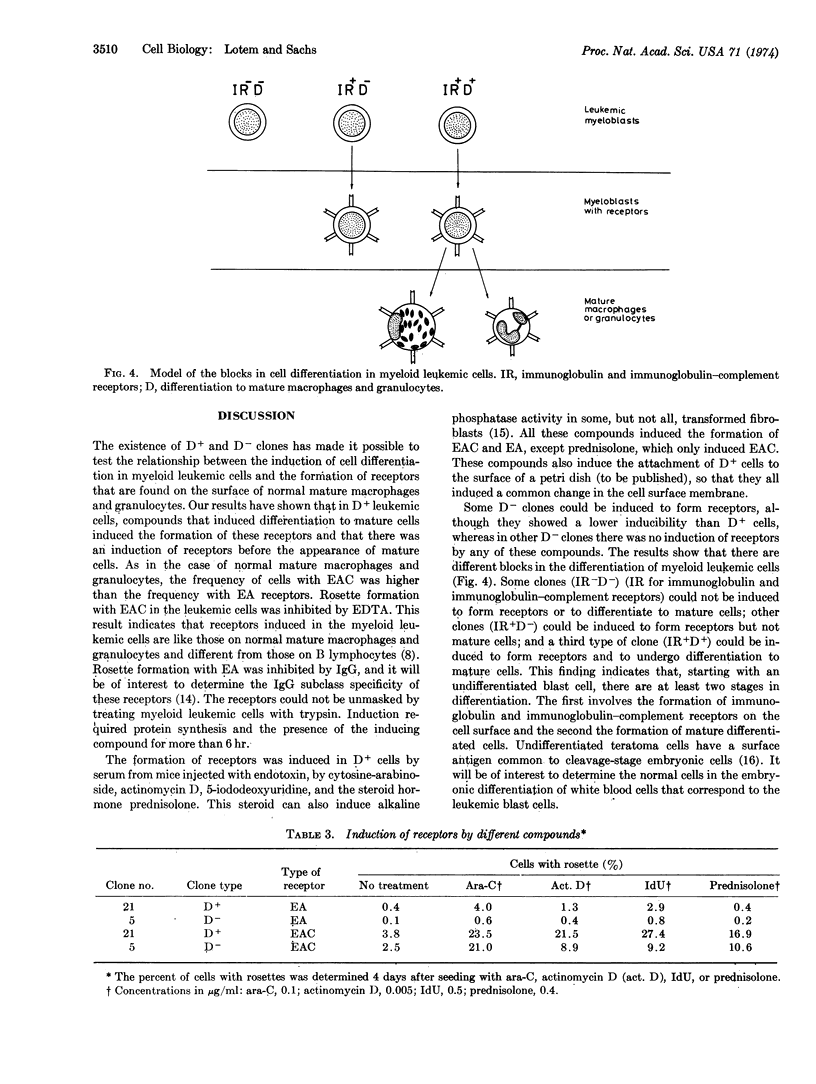
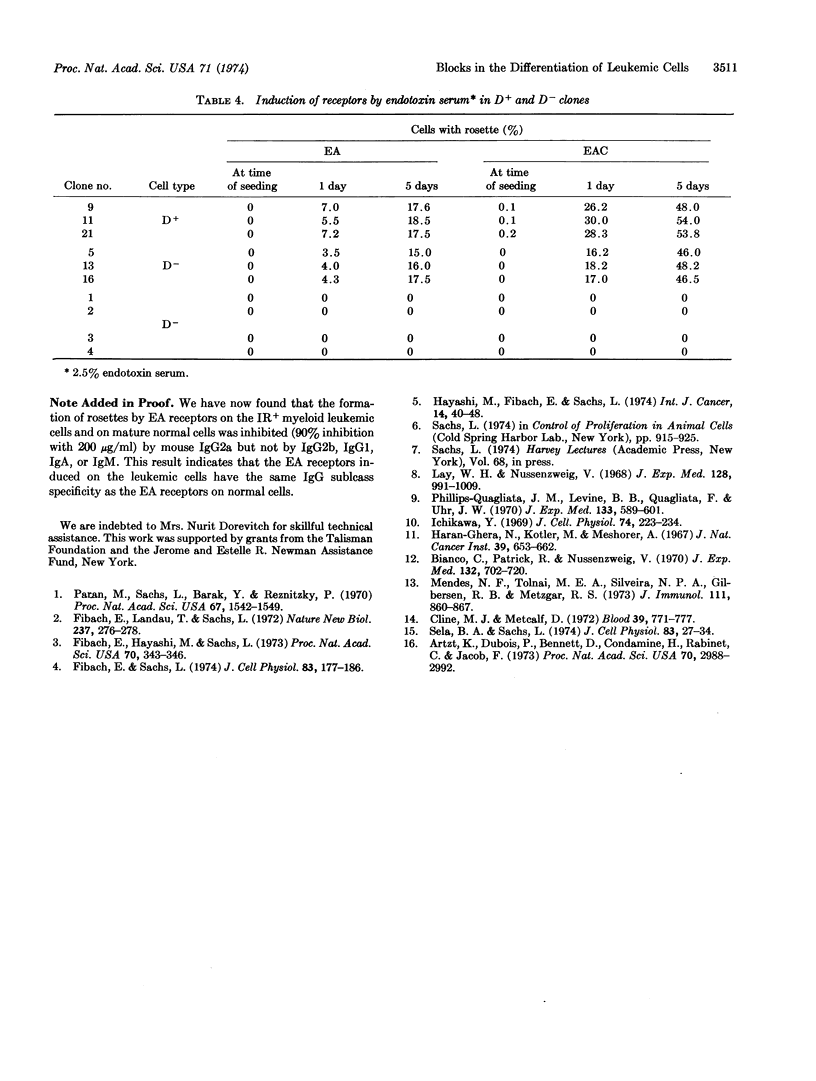
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artzt K., Dubois P., Bennett D., Condamine H., Babinet C., Jacob F. Surface antigens common to mouse cleavage embryos and primitive teratocarcinoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2988–2992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Metcalf D. Cellular differentiation in a murine myelomonocytic leukemia. Blood. 1972 Jun;39(6):771–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Hayashi M., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells to macrophages and granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):343–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Landau T., Sachs L. Normal differentiation of myeloid leukaemic cells induced by a differentiation-inducing protein. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 28;237(78):276–278. doi: 10.1038/newbio237276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. IV. Induction of differentiation by serum from endotoxin treated mice. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):177–185. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Fibach E., Sachs L. Control of normal differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. V. Normal differentiation in aneuploid leukemic cells and the chromosome banding pattern of D+ and D minus clones. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jul 15;14(1):40–48. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y. Differentiation of a cell line of myeloid leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lay W. H., Nussenzweig V. Receptors for complement of leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Nov 1;128(5):991–1009. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendes N. F., Tolnai M. E., Silveira N. P., Gilbertsen R. B., Metzgar R. S. Technical aspects of the rosette tests used to detect human complement receptor (B) and sheep erythrocyte-binding (T) lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):860–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paran M., Sachs L., Barak Y., Resnitzky P. In vitro induction of granulocyte differentiation in hematopoietic cells from leukemic and non-leukemic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1542–1549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Levine B. B., Quagliata F., Uhr J. W. Mechanisms underlying binding of immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):589–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sela B. A., Sachs L. Alkaline phosphatase activity and the regulation of growth in transformed mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Feb;83(1):27–34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]