Abstract
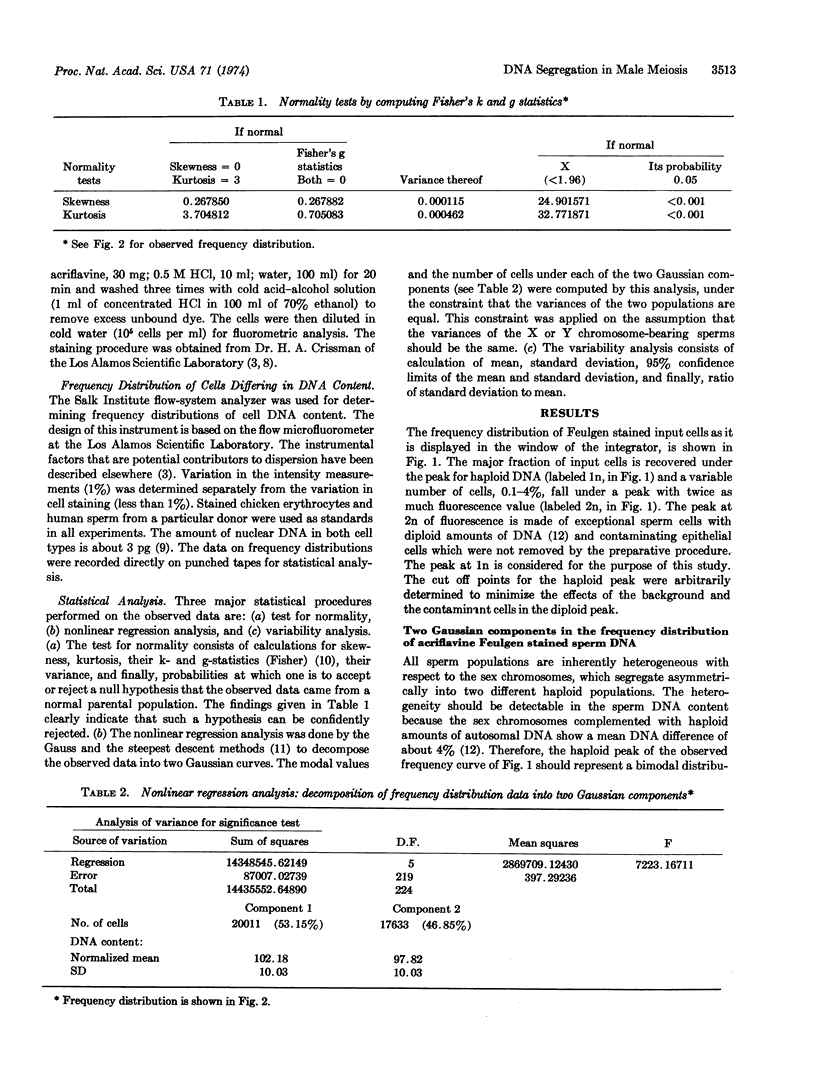
The frequency distribution of DNA content of human sperm was measured in an automated flow microfluorometer. The flow method measures the DNA content by quantifying the amount of fluorescence emitted by the fluorescent Feulgen stained DNA of single sperm cells suspended in microdroplets. The variability in the mean value for the haploid amount of DNA in sperm from 15 randomly chosen donors was less than 1%. Statistical tests on the observed frequency distribution data indicated that each sperm population probably consists of two homogenous components present in almost equal proportions but differing in mean DNA content. The difference in their modal values for DNA is within the range of known values of DNA difference between the two sex chromosomes.
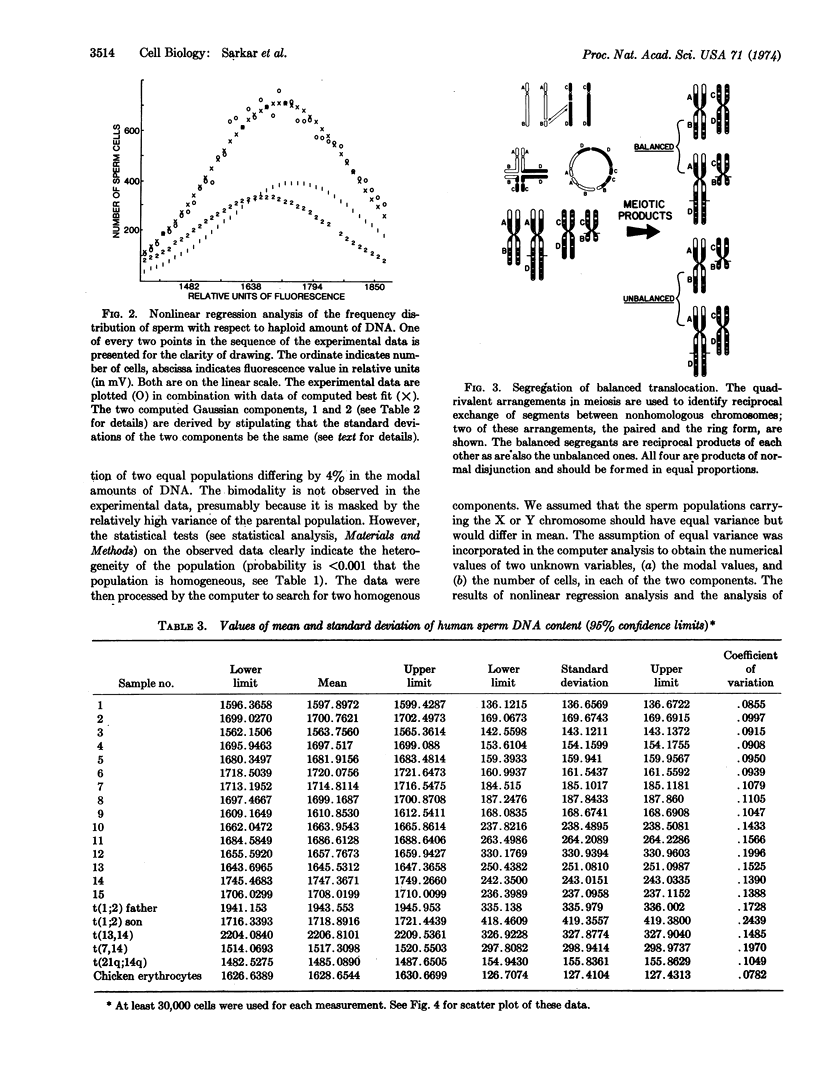
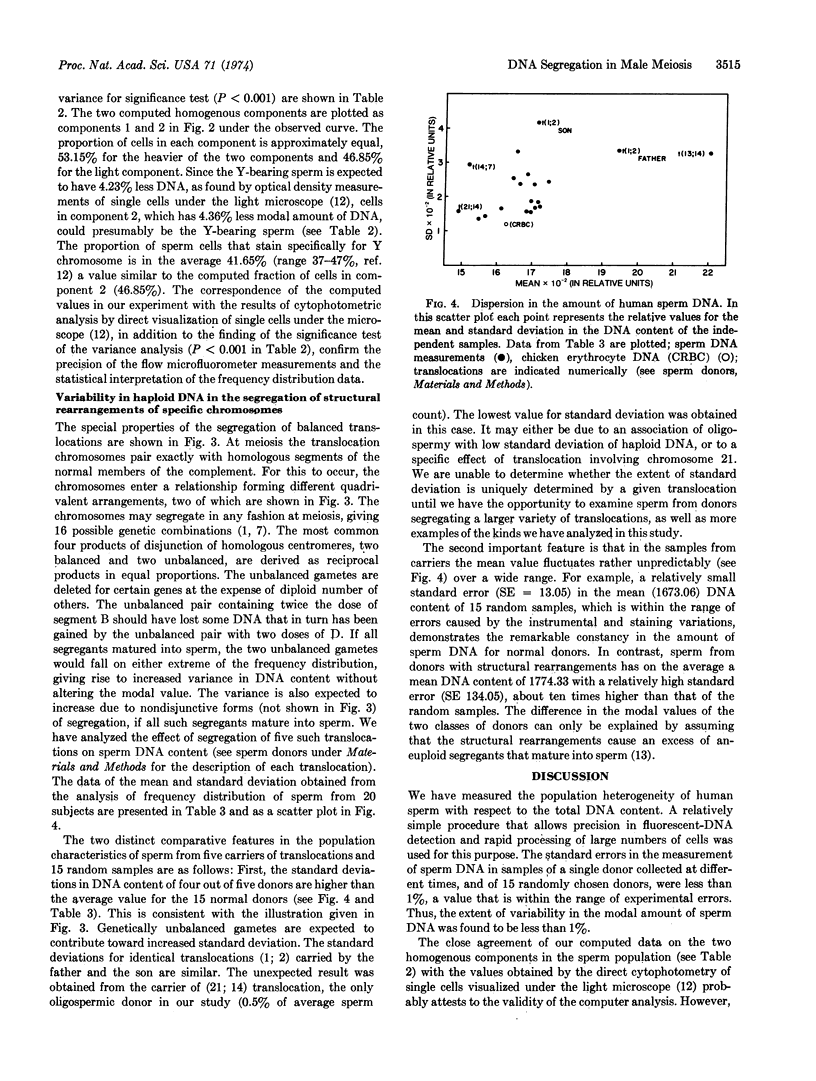
Sperm of donors segregating balanced translocations, when compared to the random samples as a class, showed greater variability in the mean DNA content.
Keywords: population heterogeneity, sex chromosomes, chromosomal translocation, fluorescent Feulgen stain, flow microfluorometer
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jacobs P. A., Aitken J., Frackiewicz A., Law P., Newton M. S., Smith P. G. The inheritance of translocations in man: data from families ascertained through a balanced heterozygote. Ann Hum Genet. 1970 Oct;34(2):119–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1970.tb00226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Frackiewicz A., Law P. Incidence and mutation rates of structural rearrangements of the autosomes in man. Ann Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;35(3):301–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1957.tb01403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley D. L., Grell E. H. Spermiogenesis without chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1969;61(1 Suppl):69–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp J. A., Fulwyler M. J., Coulter J. R., Hiebert R. D., Horney J. L., Mullancy P. F. A new multiparameter separator for microscopic particles and biological cells. Rev Sci Instrum. 1973 Sep;44(9):1301–1310. doi: 10.1063/1.1686375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Robinson J. A., Evans H. J. Distingiishing between X, Y and YY-bearing human spermatozoa by fluorescence and DNA content. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 24;229(8):231–233. doi: 10.1038/newbio229231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANAGISAWA K., DUNN L. C., BENNETT D. On the mechanism of abnormal transmission ratios at T locus in the house mouse. Genetics. 1961 Dec;46:1635–1644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.12.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]