Abstract
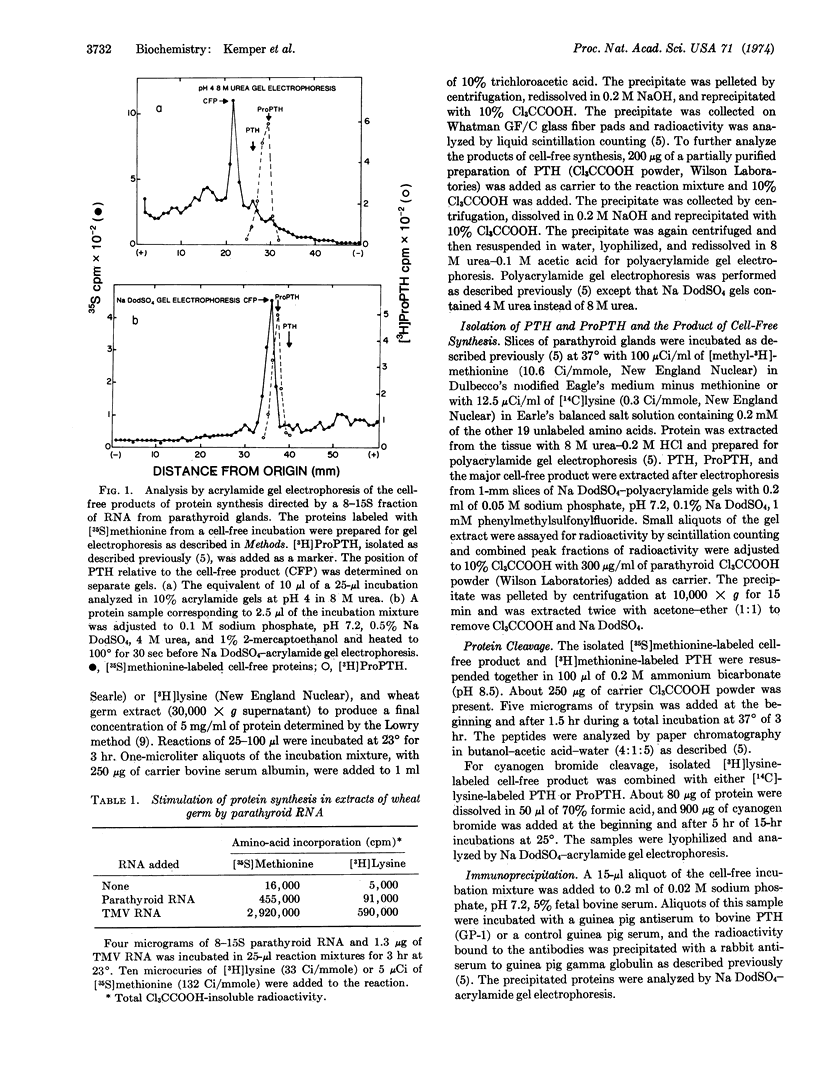
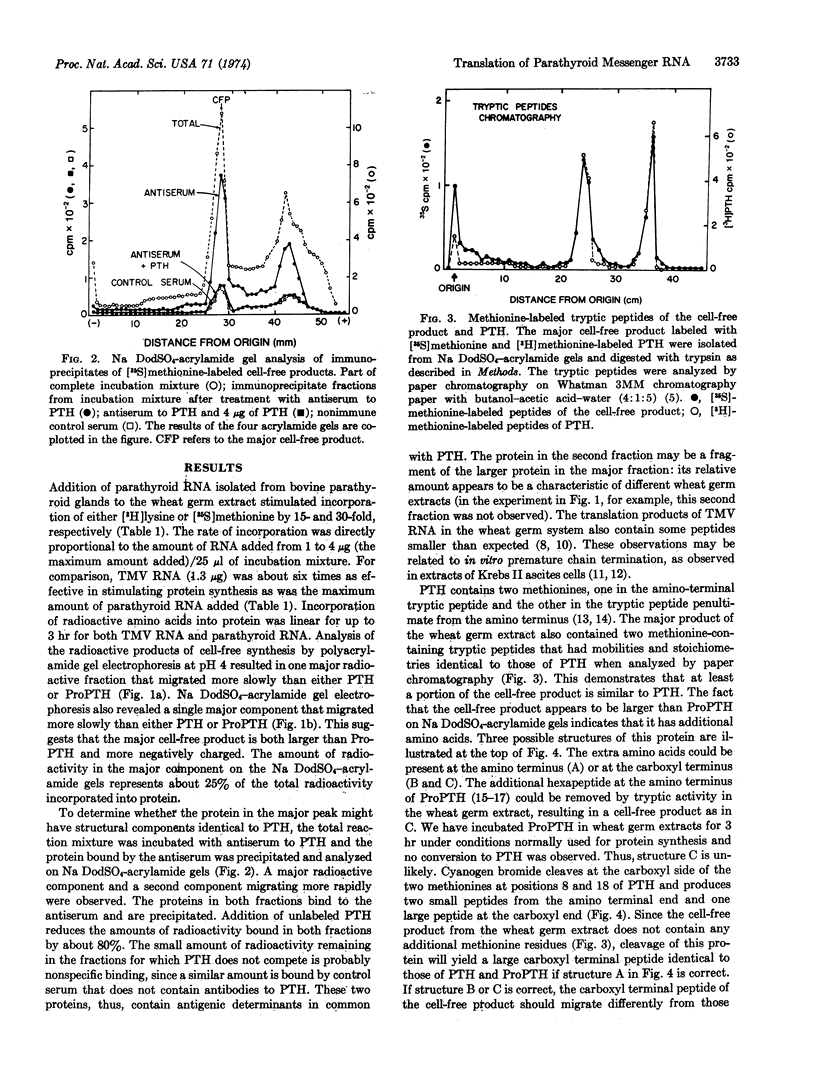
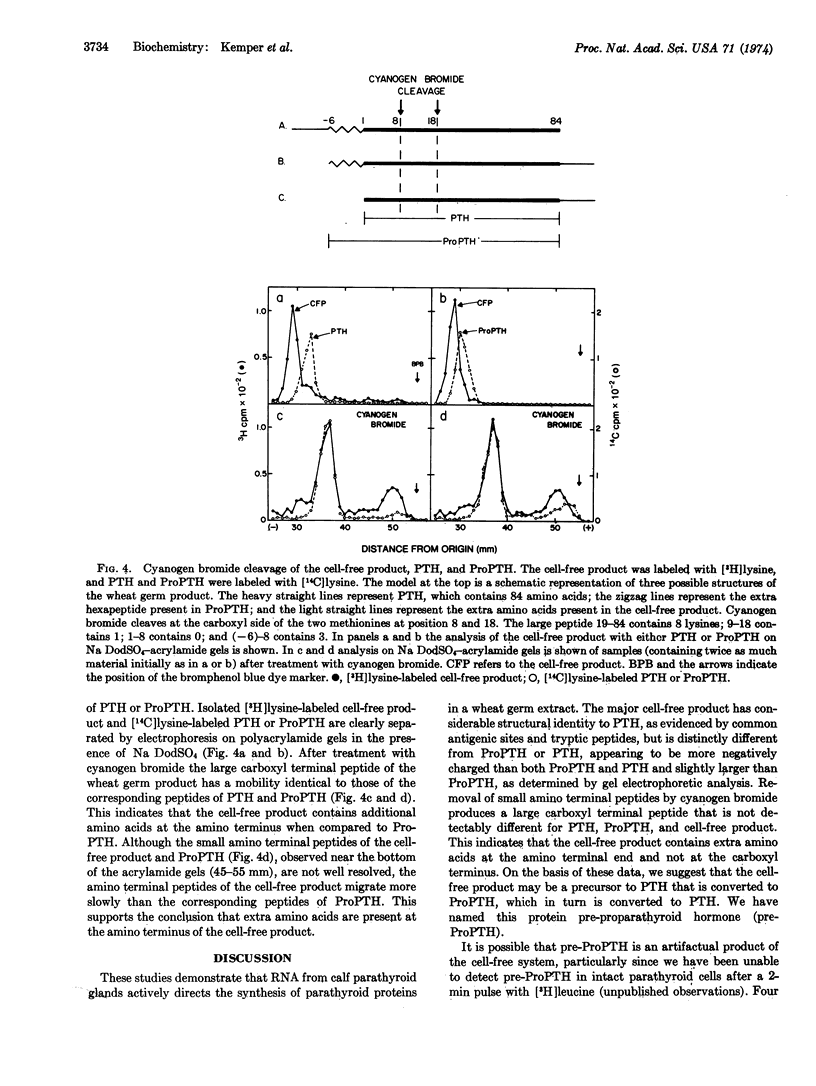
An 8-15S RNA fraction from calf parathyroid glands stimulated the incorporation of radioactive lysine and methionine into protein by 15- to 30-fold in a wheat germ extract. The major product, representing 25% of the total protein synthesized, could be bound to an antiserum to parathyroid hormone and binding was inhibited by parathyroid hormone. The chromatographic mobilities of the two tryptic peptides of the cell-free product that contained methionine were identical to the corresponding peptides of parathyroid hormone. Upon electrophoresis in acidic or sodium dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide gels, the cell-free product migrated more slowly than either parathyroid hormone or its biosynthetic precursor, proparathyroid hormone. Analysis of cyanogen bromide products indicated that the cell-free product contained an additional sequence of amino acids at the amino-terminal end. A protein corresponding to the cell-free product could not be detected in intact cells even during incubations with [3H]leucine as short as 2 min, which suggests the protein may be a transient precursor to proparathyroid hormone.
Keywords: wheat germ extract, tryptic peptides, precursor, cyanogen bromide cleavage
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson R. C., Jr, Riggs B. L., Pickard B. M., Arnaud C. D. Immunoreactive forms of circulating parathyroid hormone in primary and ectopic hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):175–181. doi: 10.1172/JCI107739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus mRNA. 3. Discrete polypeptides translated from a monocistronic messenger in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):706–713. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Ronan R. Bovine parathyroid hormone: amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Dec;67(4):1862–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.4.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Macgregor R. R., Chu L. L., Kimmel J. R., Hamilton J. W. Calcemic fraction-A: biosynthetic peptide precursor of parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1521–1525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehm P., Jimenez S. A., Olsen B. R., Prockop D. J. A transport form of collagen from embryonic tendon: electron microscopic demonstration of an NH 2 -terminal extension and evidence suggesting the presence of cystine in the molecule (chick embryo-tropocollagen-gel filtration). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):60–64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habener J. F., Kemper B., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Proparathyroid hormone: biosynthesis by human parathyroid adenomas. Science. 1972 Nov 10;178(4061):630–633. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4061.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Macgregor R. R., Chu L. L., Cohn D. V. The isolation and partial purification of a non-parathyroid hormone calcemic fraction from bovine parathyroid glands. Endocrinology. 1971 Dec;89(6):1440–1447. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-6-1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Niall H. D., Jacobs J. W., Keutmann H. T., Potts J. T., Jr, Cohn D. V. The N-terminal amino-acid sequence of bovine proparathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):653–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Spierto F. W., MacGregor R. R., Cohn D. V. Studies on the biosynthesis in vitro of parathyroid hormone. II. The effect of calcium and magnesium on synthesis of parathyroid hormone isolated from bovine parathyroid tissue and incubation medium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3224–3233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. W., Kemper B., Niall H. D., Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr Structural analysis of human proparathyroid hormone by a new microsequencing approach. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):155–157. doi: 10.1038/249155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B., Habener J. F., Potts J. T., Jr, Rich A. Proparathyroid hormone: identification of a biosynthetic precursor to parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Tovell D. R. Characterization of the polypeptides formed in response to encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system from mouse ascites tumor cells. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.73-81.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall H. D., Keutmann H., Sauer R., Hogan M., Dawson B., Aurbach G., Potts J., Jr The amino acid sequence of bovine parathyroid hormone I. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Dec;351(12):1586–1588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. L., Aviv H., Paterson B. M., Roberts B. E., Rozenblatt S., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA of simian virus 40: synthesis of the major capsid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E. Tobacco mosaic virus RNA directs the synthesis of a coat protein peptide in a cell-free system from wheat. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Clark J. L. The spontaneous reoxidation of reduced beef and rat proinsulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):622–629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. T., Lindall A. W. Preliminary evidence for a microsomal precursor to human parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2291–2294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



