Introduction
Despite major therapeutic advances, the public health burden associated with coronary heart disease (CHD) remains enormous with approximately 525 000 people predicted to have a new myocardial infarction (MI) in 2013, ≈15.4 million estimated to be living with CHD in 2013, and ≈1 346 000 people hospitalized in 2009 for CHD.1
There are a variety of ways to measure the population impact of a disease including prevalence, associated morbidity and mortality, quality of life, health care utilization, and economic costs, and one of the most critical is disease incidence. From a surveillance perspective in the United States, the national vital statistics data system provides information about the death rate for CHD, various national data systems provide estimates of hospitalizations for CHD and outpatient visits for CHD, and national data systems provide data about levels of risk factors for CHD. The data systems allowing for estimates of prevalent CHD are less robust as they rely primarily on self‐reported information.
A particularly glaring gap in our knowledge base has been the lack of nationally representative data to measure the incidence of CHD. Measuring incidence of a disease is particularly salient because incidence (1) is a key measure in helping to define the burden of a disease and identify high‐risk populations, (2) provides valuable information in helping decision makers set public health priorities, and (3) is a more relevant measure to assess the collective influence of risk factors in a population than prevalence. Consequently, tracking incidence of a disease in populations can: (1) yield timely data about potentially unfavorable changes in incidence that may prompt a search for explanations and corrective actions to redirect the course of a disease in a population, (2) provide valuable feedback in assessing efforts to control a disease, and (3) generate useful information for updating priorities regarding health promotion and disease prevention. The reasons why a national surveillance system to track CHD incidence in the United States has never been developed are not entirely clear but may relate to the cost and complexity of implementing such a system.
Our objective is to review the fragmented data that may have bearing on incidence of CHD in the United States. Because national data about incident CHD are not readily available, we will examine various facets of CHD epidemiology—including mortality, hospitalizations and case‐fatality, prevalence, risk factors, and predicted risk—that may provide insights about national trends in the incidence of CHD. Incidence, prevalence, and mortality are interrelated,2–3 and, hence, we will explore data for the latter two important population surveillance parameters. Declining mortality rates have been postulated as possible evidence for declining incidence rates, and, therefore, we examine published trends in mortality as well as in case‐fatality rates that have bearing on overall mortality rates from CHD. Furthermore, trends in hospitalizations for MI have often been used as a surrogate measure for trends in incidence of this condition, and consequently, we review national and regional data on this topic. Because the sum total of risk factors for CHD drive the incidence of this disease, we assess trends in individual risk factors as well as predicted risk calculated from major CHD risk factors. Finally, we review regional data about trends in CHD incidence from community surveillance and cohort studies.
Mortality
The category “diseases of the heart” has long been and continues to be the leading cause of death in the United States based on data from death certificates.4 After increasing during the first part of the 20th century, the mortality rate attributed to CHD peaked during the late 1960s and reversed course starting a prolonged and continuing decline.5–6 From 1980 through 2009, age‐adjusted CHD mortality has decreased by 66% among men and 67% among women (Figure 1). Furthermore, age‐adjusted rates decreased by 60% among African American women, 57% among African American men, 68% among white women, and 67% among white men (Figure 2). CHD mortality was defined as International Classification of Diseases (ICD)‐9 codes 410‐414 and 429.2 or ICD‐10 codes I20‐I25. Regional studies such as the Framingham Heart Study, the Minnesota Heart Survey, Honolulu Heart Program, and the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study (ARIC) also described declining rates of CHD mortality.7–11 The factors contributing to the decline have been debated, and a combination of treatment and improvements in population levels of risk factors for CHD has been credited with lowering the CHD mortality rate.12–17 The declining mortality rates raised the prospect of declining incidence rates. Because mortality rates are subject to a number of influences such as disease severity, case fatality, changes in risk factors, improved treatment, and incident or new cases,18 declining mortality rates alone cannot automatically be equated with declining incidence rates.
Figure 1.
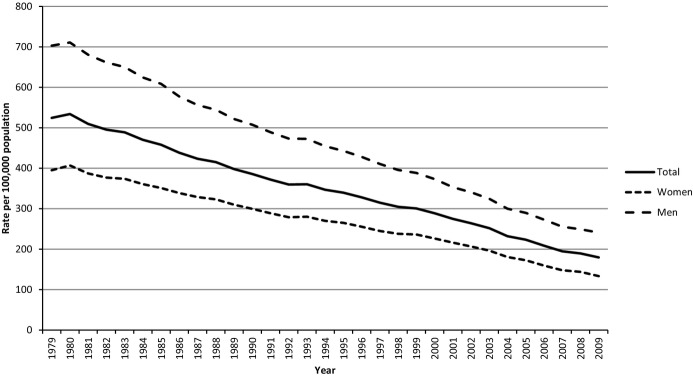
Age‐adjusted mortality rates from CHD for adults aged ≥25 years, United States. Results were generated with WONDER using the Compressed Mortality File of the National Vital Statistics System. For the period 1979–1999, International Classification of Diseases 9 codes 410‐414 and 429.2 were used. For 2000–2009, International Classification of Diseases codes I20‐O25 were used. Results were age‐adjusted to the projected year 2000 US population. CHD indicates coronary heart disease.
Figure 2.
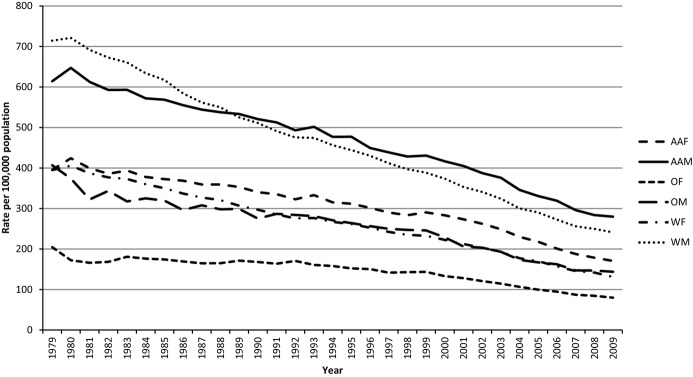
Age‐adjusted mortality rates from CHD for adults aged ≥25 years, by race and gender, United States. Results were generated with WONDER using the Compressed Mortality File of the National Vital Statistics System. For the period 1979–1999, International Classification of Diseases 9 codes 410‐414 and 429.2 were used. For 2000–2009, International Classification of Diseases codes I20‐O25 were used. Results were age‐adjusted to the projected year 2000 US population. AAF indicates African‐American females; AAM, African‐American males; CHD, coronary heart disease; OF, other females; OM, other males; WF, white females; WM, white men.
Hospitalizations
Several large data sets have provided information about trends in hospitalizations for MI (Table 1).
Table 1.
Large Studies of Trends in Hospitalization Rates for Myocardial Infarction in the United States
| Reference | Data Source | Study Period | Change in Rates (Per 100 000) | Discharge Diagnosis | Validation of Discharge Diagnoses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nallamothu19 | Acute Care Tracker Database | 2002–2005 | 309 to 266 | Principal | No |
| Fang20 | National Hospital Discharge Survey | 1979–1981 to 1985–1987 | 215 to 342 | Principal | No |
| 1985–1987 to 2003–2005 | 342 to 242 | ||||
| Chen21 | Medicare fee‐for‐service beneficiaries | 2002–2007 | 1131 to 866 | Principal | No |
| Wang22 | National inpatient sample | 2001–2007 | 314 to 222 | Principal | No |
Based on the Acute Care Tracker data base, a proprietary administrative database that included 458 US hospitals, rates of hospitalization for MI based on principal diagnosis ICD‐9 codes decreased from 309 in 2002 to 266 per 100 000 population in 2005.19 The numbers of total discharges and coronary revascularizations compared reasonably well with estimates from the National Hospital Discharge Survey, but the diagnoses of MI were not specifically validated. An analysis of data from the National Hospital Discharge Survey showed that the rate of hospitalizations for MI using the first‐listed diagnosis code increased from 215 in 1979–‐1981 to 342 per 100 000 population in 1985–‐1987, remained relatively level until 1996, and then declined to 242 per 100 000 population in 2003–‐2005.20 No validation of discharge diagnoses was done. The rate of hospitalizations for MI using principal diagnosis codes among Medicare fee‐for‐service beneficiaries dropped from 1131 in 2002 to 866 per 100 000 person‐years in 2007.21 Discharge diagnoses were not validated. An analysis of data from the National Inpatient Sample of the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project from 2001 to 2007 found that the rate of hospitalization from MI based on the principal diagnosis dropped from 314 to 222 per 100 000 population, and decreases were observed in most demographic subgroups.22 The validity of the discharge diagnoses over time remained untested in this data set. However, these studies were not able to identify incident CHD or to examine the impact of changes in diagnostic criteria for MI on hospitalization rates. Furthermore, validation of hospitalizations for MI diagnostic codes has generally not been done in these studies.
Case‐Fatality
Several measures of case‐fatality rates can be conceptualized in terms of time frame: in‐hospital mortality, 28‐ or 30‐day mortality, and 1‐, 2‐, 3‐, and 5‐year mortality (Table 2).
Table 2.
Selected Studies of Changes in Case‐Fatality Rates for Hospitalizations for Myocardial Infarction or Incident Coronary Heart Disease in the United States
| Reference | Study | CHD Event | Period | Changes in Case‐Fatality Rate (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In‐Hospital | 28‐Day | 30‐Day | 3‐Months | 1‐Year | 2‐Year | 3‐Year | 5‐Year | ||||
| Elveback7 | Rochester, MN | Incident MI | 1965–1969 to 1970–1975 | 18.0 to 9.3 | 40.0 to 34.0 | ||||||
| Gillum23 | Minnesota Heart Survey | Any MI | 1970–1980 | Men: 16.7 to 11.9 | |||||||
| Women: 16.6 to 12.2 | |||||||||||
| Pell24 | Du Pont Company | Incident MI | 1957–1959 | 30.4 | |||||||
| 1972–1974 | 34.8 | ||||||||||
| 1981–1983 | 24.3 | ||||||||||
| Goldberg25 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Any MI hospitalization | 1975–1984 | 22.2 to 15.1 | |||||||
| Incident MI | 1975–1984 | 20.1 to 12.6 | |||||||||
| Reed9 | Honolulu Heart Program | Incident CHD | 1966–1985 | ↑ | ↑ | ||||||
| Keil26 | Pee Dee, SC | Any MI | 1978–1985 | Total: 14 to 9.9 | |||||||
| WM: 12.3 to 7.4 | |||||||||||
| WW: 20.0 to 7.0 | |||||||||||
| BM: 17.7 to 17.4 | |||||||||||
| BW: 9.1 to 29.4 | |||||||||||
| McGovern18 | Minnesota Heart Survey | Incident MI hospitalization | 1985–1990 | Men: 13 to 10 | Men: 21 to 18 | ||||||
| Women: 15 to 12 | Women: 29 to 24 | ||||||||||
| Rosamond11 | Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study | Any MI hospitalization | 1987–1994 | Men: 4.1%/y ↓ | |||||||
| BM: 2% ↑ | |||||||||||
| WM: 5.1% ↓ | |||||||||||
| Women: 9.8%/y ↓ | |||||||||||
| BW: 3.1% ↓ | |||||||||||
| WW: 12.1% ↓ | |||||||||||
| Goldberg27 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Incident MI hospitalization | 1975–1978 | 17.8 | 12.0* | 17.0* | 31.0 | ||||
| 1981–1984 | 14.9 | 13.0* | 19.0* | 32.0 | |||||||
| 1986–1988 | 17.0 | 10.0* | 16.0* | 29.0 | |||||||
| 1990–1991 | 13.2 | 13.0* | 19.0* | 31.0 | |||||||
| 1993–1995 | 11.7 | 11.0* | 17.0* | ― | |||||||
| Ergin28 | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I EFS | Incident CHD | 1971–1982 | Total: 23.4; WM: 27.2; WW: 15.3; BM: 39.2; BW: 26.5 | |||||||
| 1982–1992 | Total: 16.6; WM: 19.0; WW: 14.2; BM: 10.8; BW: 16.6 | ||||||||||
| Peterson29 | National Registry of Myocardial Infarction | Any MI hospitalization | 1990–2006 | 10.4 to 6.3 | |||||||
| Any STEMI | 11.5 to 8.0 | ||||||||||
| Any NSTEMI | 7.1 to 5.2 | ||||||||||
| Wellenius30 | Medicare beneficiaries | Any MI hospitalization | 1984–2003 | WM: 22.7 to 10.1 | WM: 25.2 to 14.3 | WM: 40.3 to 28.7 | |||||
| WW: 23.1 to 10.3 | WW: 25.2 to 14.4 | WW: 39.3 to 28.8 | |||||||||
| BM: 18.6 to 11.2 | BM: 20.9 to 15.5 | BM: 37.2 to 34.8 | |||||||||
| BW: 20.0 to 11.2 | BW: 21.6 to 15.1 | BW: 38.5 to 33.8 | |||||||||
| Parikh31 | Framingham Heart Study, Framingham Heart Study Offspring | Incident MI | 1960–1969 to 1990–1999 | 73.0 ↓ | 65.0 ↓ | 64.0 ↓ | |||||
| Incident MI‐ECG | 62.0 ↓ | 58.0 ↓ | 64.0 ↓ | ||||||||
| Incident MI‐marker | 78.0 ↓ | 69.0 ↓ | 55.0 ↓ | ||||||||
| Floyd32 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Incident MI hospitalization | 1975–2005 | 19.5 to 9.5 | |||||||
| Fang20 | National Hospital Discharge Survey | Any MI hospitalization | 1979–1981 to 2003–2005 | 17.8 to 8 | |||||||
| Yeh33 | Kaiser Permanente Northern California | Incident MI hospitalization | 1999–2008 | 10.5 to 7.8 | |||||||
| Incident NSTEMI hospitalization | 10.0 to 7.6 | ||||||||||
| Roger34 | Olmsted County, MN | Incident MI hospitalization | 1987–2006 | −4.3%/y | |||||||
| McManus35 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Any STEMI hospitalization | 1997 | 11.1 | 13.2 | 10.6* | |||||
| 1999 | 9.9 | 13.0 | 14.0* | ||||||||
| 2001 | 13.5 | 15.8 | 15.4* | ||||||||
| 2003 | 8.4 | 10.0 | 8.3* | ||||||||
| 2005 | 9.7 | 11.4 | 8.4* | ||||||||
| Any NSTEMI hospitalization | 1997 | 12.9 | 16.0 | 23.1* | |||||||
| 1999 | 13.1 | 17.0 | 27.6* | ||||||||
| 2001 | 10.9 | 16.5 | 26.1* | ||||||||
| 2003 | 8.9 | 13.7 | 25.6* | ||||||||
| 2005 | 9.5 | 14.0 | 18.7* | ||||||||
| Nguyen36 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Any MI hospitalization | 1986–1988 to 2003–2005 | Men, <65 years: 7.1 to 2.2 Women, <65 years: 9.6 to 5.3 |
|||||||
| Men, age 65 to 74 years: 14.3 to 8.2 Women, age 65 to 74 years: 19.6 to 11.5 |
|||||||||||
| Men ≥75 years: 30.2 to 13.3 Women ≥75 years: 29.6 to 12.6 |
|||||||||||
| Coles37 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | Incident MI | 2001–2007 | 11.1 to 7.9* | 17.1 to 12.7* | 25.6 to 18.6* | |||||
| Rosamond38 | Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study | Incident MI hospitalizations | 1987–2008 | Men: 3.4%/y ↓, WM: 3.5%/y ↓, BM: 3.4% ↓, Women: 2.9% ↓, WW: 3.0%/y ↓, BW: 2.6% ↓ | |||||||
BM indicates black men; BW, black women; CHD, coronary heart disease; ECG, electrocardiogram; NSTEMI, non‐ST‐segment myocardial infarction; STEMI, ST‐segment elevation myocardial infarction; WM, white men; WW, white women.
Post‐discharge.
Numerous publications have documented improvements in the in‐hospital or short‐term case‐fatality rate.7,11,18,20,23–26,23–34,23–39 The first indications that CHD case‐fatality rates had improved emerged during the 1960s.7 Since then, case‐fatality rates have generally improved steadily. Fewer data are available concerning the long‐term survival of people who develop CHD. In Rochester, MN, the 5‐year mortality rate from 1965–1969 to 1970–1975 decreased from 40.0% to 34.0%.7 An early report from the Worcester Heart Attack Study failed to observe improved post‐discharge long‐term survival in patients who sustained an MI in 1975, 1978, or 1981.40 A subsequent analysis of data from this study again failed to find improvements in 1‐, 2‐, and 5‐year survival rates for patients who were discharged during 1975–1978, 1981–1984, 1986–1988, and 1990–1991.27 More recently, 1‐year survival for patients discharged with an ST‐segment elevation MI (STEMI) during 2003 and 2005 and for patients discharged with non‐ST‐segment MI (NSTEMI) during 2005 improved,35 and 1‐ and 2‐year mortality rates from 2001 to 2006 decreased from 17.1% to 12.7% and 25.6% to 18.6%, respectively.37 In the Minnesota Heart Survey, 3‐year mortality after hospitalization for MI decreased from 21% in 1985 to 18% in 1990 among men and from 29% to 24% among women.18 Among Medicare beneficiaries, 1‐year mortality after a MI decreased from 40.2% in 1984 to 34.5% in 2003.30 In the Framingham Study, 1‐ and 5‐year mortality among adults who had an MI decreased by 65% and 64%, respectively, during the period from 1960 to 1999.31
Prevalence
Broadly speaking, prevalence represents the net sum of input (incidence) and outflow (mortality). Thus, information about trends in CHD prevalence may shed light on the incidence of CHD. Information about the prevalence of CHD comes from national surveys, cohort studies, and regional surveillance systems. National surveys like the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), National Health Interview Survey (NHIS), and Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) use questionnaires to collect data to estimate the prevalence of CHD. Because these systems rely on self‐reported information, such information is particularly susceptible to various biases.
Several analyses of NHANES data have been undertaken. Among NHANES participants aged 40 to 74 years, estimates of the prevalence of self‐reported MI were 6.3% during 1971–1975, 5.6% during 1976–1980, and 5.7% during 1988–1994.41 Among adults aged 35 to 54 years who participated in NHANES, the prevalence of self‐reported MI was 2.5% during 1988–1994 and 2.2% during 1999–2004 among men and 0.7% during 1988–1994 and 1.0% during 1999–2004 among women.42 Analysis of NHANES data by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute showed that the prevalence of self‐reported MI has declined from 1971–1975 to 2005–2008 most clearly among whites and among men.6
To examine the recent trend in CHD prevalence, we used NHANES data of adults aged ≥20 years from 1999 to 2012 (Table 3).43 CHD was defined as ever having been told by a doctor or other health professional that the participant had CHD, angina pectoris, or a heart attack. The unadjusted prevalence showed little change during the 10‐year period. After adjustment for age, the prevalence of CHD increased from 6.3% during 1999–2000 to 6.9% during 2003–2004 and then decreased to 5.2% during 2009–2012, and the overall trend showed a decrease (P for linear trend=0.001). Furthermore, decreases in the age‐adjusted prevalence of self‐reported CHD were noted for men, women, whites, African Americans, adults who had not completed high school or with education beyond high school, adults without diagnosed diabetes, and adults with a body mass index <30 kg/m2.
Table 3.
Unadjusted and Age‐Adjusted Prevalence (%, SE) of Self‐Reported CHD Among Adults Aged ≥20 Years, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2012
| 1999–2000 | 2001–2002 | 2003–2004 | 2005–2006 | 2007–2008 | 2009–2010 | 2011–2012 | P Linear Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted results | ||||||||
| Total | 5.8 (0.4) | 5.9 (0.5) | 6.8 (0.8) | 6.1 (0.5) | 5.6 (0.3) | 5.5 (0.4) | 5.4 (0.4) | 0.165 |
| Age, y | ||||||||
| 20 to 44 | 1.0 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.2) | 1.0 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.3) | 0.996 |
| 45 to 54 | 4.9 (0.9) | 3.7 (0.8) | 4.3 (0.8) | 4.2 (0.6) | 3.7 (0.6) | 4.0 (0.6) | 2.9 (0.8) | 0.154 |
| 55 to 64 | 13.2 (1.5) | 11.4 (2.5) | 11.9 (1.9) | 8.9 (1.6) | 8.2 (1.1) | 9.2 (1.0) | 7.0 (0.8) | 0.001 |
| 65+ | 18.3 (1.3) | 21.6 (1.9) | 23.9 (2.2) | 20.4 (1.2) | 19.2 (1.4) | 16.3 (1.0) | 17.9 (1.1) | 0.022 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Men | 7.3 (0.8) | 6.8 (0.7) | 7.8 (1.0) | 7.1 (0.6) | 7.0 (0.5) | 7.3 (0.6) | 6.5 (0.6) | 0.529 |
| Women | 4.5 (0.5) | 5.0 (0.6) | 5.8 (0.7) | 5.1 (0.6) | 4.3 (0.3) | 3.9 (0.4) | 4.4 (0.4) | 0.105 |
| Race or ethnicity | ||||||||
| Whites | 6.7 (0.4) | 6.7 (0.6) | 7.7 (0.8) | 6.9 (0.6) | 6.1 (0.5) | 6.4 (0.5) | 6.2 (0.6) | 0.177 |
| African Americans | 4.0 (0.6) | 5.8 (0.9) | 4.7 (0.6) | 5.9 (0.7) | 4.4 (0.7) | 4.7 (0.7) | 4.4 (0.4) | 0.668 |
| Mexican Americans | 2.6 (0.3) | 2.6 (0.5) | 2.8 (0.6) | 3.1 (0.4) | 3.1 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.7) | 2.6 (0.8) | 0.414 |
| Other | 4.3 (0.5) | 2.8 (0.7) | 5.4 (1.9) | 2.3 (0.7) | 5.4 (0.8) | 3.1 (0.6) | 4.1 (0.6) | 0.991 |
| Education | ||||||||
| <High school | 8.2 (0.6) | 10.3 (1.0) | 10.8 (1.9) | 10.6 (1.1) | 8.4 (0.5) | 8.3 (1.0) | 8.0 (0.9) | 0.144 |
| High school graduate or equivalent | 7.0 (0.7) | 6.0 (0.8) | 7.1 (1.2) | 6.4 (1.1) | 6.2 (0.7) | 7.1 (0.8) | 7.0 (1.3) | 0.806 |
| >High school | 4.0 (0.5) | 4.2 (0.4) | 5.3 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.4) | 4.3 (0.3) | 4.1 (0.4) | 4.2 (0.5) | 0.733 |
| Diagnosed diabetes | ||||||||
| Yes | 21.4 (3.2) | 19.2 (3.0) | 21.4 (3.0) | 21.0 (1.8) | 20.0 (1.7) | 17.6 (1.9) | 19.3 (1.9) | 0.425 |
| No | 4.7 (0.4) | 4.9 (0.4) | 5.4 (0.5) | 4.7 (0.4) | 4.1 (0.3) | 4.3 (0.3) | 3.8 (0.4) | 0.014 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||||||
| <25 | 3.9 (0.3) | 3.3 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.8) | 3.4 (0.5) | 4.1 (0.4) | 3.5 (0.6) | 3.5 (0.6) | 0.368 |
| 25 to <30 | 6.7 (0.7) | 5.7 (0.8) | 7.2 (0.8) | 7.1 (0.7) | 5.3 (0.5) | 4.9 (0.5) | 5.2 (0.7) | 0.034 |
| ≥30 | 7.2 (0.7) | 8.0 (1.0) | 8.0 (0.9) | 7.2 (0.6) | 7.0 (0.8) | 8.0 (0.6) | 7.3 (0.5) | 0.873 |
| Age‐adjusted results | ||||||||
| Total | 6.3 (0.4) | 6.4 (0.5) | 6.9 (0.6) | 6.1 (0.3) | 5.5 (0.3) | 5.3 (0.3) | 5.2 (0.3) | 0.001 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Men | 8.4 (0.9) | 7.9 (0.7) | 8.4 (0.9) | 7.7 (0.5) | 7.4 (0.5) | 7.4 (0.4) | 6.6 (0.5) | 0.043 |
| Women | 4.6 (0.5) | 5.2 (0.5) | 5.6 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.6) | 4.0 (0.3) | 3.7 (0.4) | 4.0 (0.3) | 0.003 |
| Race or ethnicity | ||||||||
| Whites | 6.6 (0.4) | 6.5 (0.6) | 7.0 (0.7) | 6.2 (0.4) | 5.4 (0.4) | 5.5 (0.4) | 5.2 (0.4) | 0.001 |
| African Americans | 5.4 (0.9) | 7.5 (0.9) | 5.6 (0.7) | 7.1 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.7) | 4.9 (0.5) | 4.8 (0.4) | 0.037 |
| Mexican Americans | 4.6 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.7) | 5.4 (0.5) | 4.4 (0.4) | 5.2 (0.6) | 5.6 (0.7) | 4.8 (1.4) | 0.908 |
| Other | 5.5 (0.9) | 4.3 (0.8) | 7.3 (2.5) | 2.9 (0.8) | 6.1 (0.7) | 4.2 (0.8) | 4.9 (0.7) | 0.481 |
| Education | ||||||||
| <High school | 7.3 (0.7) | 9.1 (1.0) | 8.8 (1.3) | 9.1 (0.9) | 7.4 (0.6) | 7.0 (0.8) | 6.3 (0.7) | 0.040 |
| High school graduate or equivalent | 7.2 (0.7) | 6.3 (0.9) | 6.8 (1.0) | 5.6 (0.6) | 5.7 (0.5) | 6.5 (0.8) | 6.1 (1.2) | 0.404 |
| >High school | 5.5 (0.7) | 5.4 (0.4) | 6.5 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.4) | 4.8 (0.3) | 4.3 (0.3) | 4.5 (0.4) | 0.008 |
| Diagnosed diabetes | ||||||||
| Yes | 14.3 (2.8) | 13.6 (3.1) | 13.1 (2.0) | 12.0 (1.3) | 12.2 (1.4) | 9.6 (1.2) | 11.6 (1.6) | 0.150 |
| No | 5.6 (0.4) | 5.7 (0.4) | 6.0 (0.5) | 5.2 (0.4) | 4.5 (0.3) | 4.6 (0.3) | 4.1 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||||||
| <25 | 5.1 (0.4) | 4.5 (0.6) | 6.3 (0.8) | 3.7 (0.5) | 4.6 (0.4) | 3.9 (0.5) | 3.6 (0.4) | 0.003 |
| 25 to <30 | 6.8 (0.7) | 5.9 (0.7) | 6.5 (0.7) | 6.7 (0.5) | 4.9 (0.4) | 4.5 (0.4) | 4.8 (0.5) | 0.002 |
| ≥30 | 7.1 (0.8) | 8.7 (0.9) | 8.2 (0.9) | 7.1 (0.4) | 6.7 (0.8) | 7.3 (0.5) | 6.8 (0.4) | 0.151 |
Based on data from the NHIS from 1980 to 1989, the age‐adjusted prevalence of self‐reported CHD among US adults aged 45 to 84 years varied between 2.2% and 2.6% with no clear trend.44 Recent data from the BRFSS showed that the prevalence of self‐reported CHD declined from 6.7% in 2006 to 6.0% in 2010 in adult populations aged ≥18 years.45 Declines were noted in all age groups, men and women, all education groups, and among whites and Hispanics but not among blacks, Asians or Native Hawaiians/Other Pacific Islanders, and American Indians or Alaska Natives.
In several NHANES, electrocardiograms (ECGs) were administered to adults aged 40 to 74 years. However, recent NHANES have not included this component. The percentages of adults with possible or probable ECG‐defined MI were 3.6% during 1971–1975, 3.4% during 1976–1980, and 2.4% during 1988–1994.41
Among successive groups of Framingham Study participants who were aged 55 to 64 years in 1953, 1963, and 1973, the prevalence of CHD among men increased from 10.2% in 1953 to 15.9% in 1973 (P=0.003) and that among women from 5.5% in 1953 to 6.9% in 1973 (P=0.250).46 CHD was defined as MI, coronary insufficiency, angina pectoris, and sudden and non‐sudden death from CHD.
Period prevalence of MI (hospitalization for MI or an out‐of‐hospital death due to MI) in the Pee Dee area of South Carolina decreased from 642 per 100 000 population in 1978 to 469 per 100 000 population in 1985.26 This overall trend reflected a significant decrease among white men, nonsignificant decreases among black men and women, and a nonsignificant increase among white women.
A series of autopsy studies from Olmsted County, Minnesota provide an interesting perspective on the trend in the prevalence of CHD. Among adults aged >30 years, the prevalence of “significant coronary disease” increased from 23% during 1950–1954 to 51% during 1975–1979 and the prevalence of a MI scar ranged between 36% and 41%.47 A subsequent autopsy study showed that the prevalence of atherosclerosis declined among adults aged 20 to 59 years (1979–1983: 38%; 1984–1989: 36%; 1990–1994: 27%; P for trend=0.02) but not adults aged ≥60 years (1979–1983: 61%; 1984–1989: 70%; 1990–1994: 59%; P for trend=0.44) from 1979 to 1994.48 A more recent autopsy study among residents aged 16 to 64 years from 1981 to 2004 showed declines in the prevalence of any coronary artery disease and mean grade.49
Risk Factors
Impressive changes in major risk factors for CHD have occurred since the 1960s when national data about many of these risk factors first became available. The per capita cigarette consumption in the United States increased tremendously from 1900 into the 1960s. Subsequent to the first Surgeon General's Report in 1964, cigarette consumption started to decline and has reached levels last seen during the 1930s.50 In concert, the prevalence of smoking has decreased precipitously from 42.4% in 1965 to 19.3% in 2010.51 Furthermore, the exposure to second‐hand tobacco smoke has also declined.52
Concentrations of total cholesterol, non‐high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol have decreased. Among adults aged 20 to 74 years, mean concentrations of total cholesterol were 222 mg/dL during 1960–1962, 216 mg/dL during 1971–1975, 215 mg/dL during 1976–1980, 204 mg/dL during 1988–1994, and 203 mg/dL during 1999–2002.53 Among adults aged ≥20 years, mean concentrations of total cholesterol were 206 mg/dL during 1988–1994, 203 mg/dL during 1999–2002, and 196 mg/dL during 2007–2010; mean concentrations of high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol were 50.7 mg/dL during 1988–1994, 51.3 mg/dL during 1999–2002, and 52.5 mg/dL during 2007–2010; mean concentrations of non‐high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol were 155 mg/dL during 1988–1994, 152 mg/dL during 1999–2002, and 144 mg/dL during 2007–2010; and mean concentrations of low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol were 129 mg/dL during 1988–1994, 123 mg/dL during 1999–2002, and 116 mg/dL during 2007–2010.54 In addition, control of hypercholesterolemia has also improved.55
The trend in hypertension has been more complicated.56–58 Among adults aged 18 to 74 years, the age‐adjusted prevalence of hypertension was 29.7% during 1960–1962, 36.3% during 1971–1974, 31.8% during 1976–1980.56 Among adults aged ≥20 years, the age‐adjusted prevalence of hypertension was 29.6% during 1999–2000, 29.0% during 2001–2002, 30.7% during 2003–2004, 29.9% during 2005–2006, 30.6% during 2007–2008, and 29.5% during 2009–2010.58 Both publications used a similar definition of hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg, or use of antihypertensive medication). Thus, the prevalence of hypertension has shown little change since 1988–1994. However, control of hypertension is improving.57–59 Of adults with hypertension, 33.2% were controlled during 1999–2002 compared with 45.8% during 2005–2008.59
National data sets provide few insights about the long‐term changes in physical activity. Analyses of data from the NHIS show that 14.3% of adults aged ≥18 years in 1998, 15.0% in 2000, 19.1% in 2009, and 20.7% in 2010 met the 2008 Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (both aerobic activity [≥150 minutes/week of moderate‐intensity, 75 minutes/week of vigorous‐intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate‐and vigorous‐intensity aerobic activity] and muscle‐ strengthening activities [≥2 days/week of muscle‐strengthening activities involving all major muscle groups of moderate or high intensity]).60 This apparent increase in leisure‐time physical activity may have been counterbalanced by unfavorable trends in energy expenditure at work and sedentary behavior. From 1960–1962 to 2003–2006, estimated mean daily energy expenditure at work among men and women declined by more than 100 calories.61 Sedentary behavior as exemplified by screen time (the amount of time that people spend watching television and videos, playing video games, or using a computer) has increased nationally.62
Weight and height have been measured in national surveys in the United States since 1960–1962. Among adults aged 20 to 74 years, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) was 13.4% during 1960–1962, 14.5% during 1971–1974, 15.0% during 1976–1980, 23.3% during 1988–1994, and 30.9% during 1999–2000.63 Among adults aged ≥20 years, the prevalence of obesity (body mass index ≥30 kg/m2) was 30.5% during 1999–2000, 30.6% during 2001–2002, 32.2% during 2003–2004, 34.3% during 2005–2006, and 33.8% during 2007–2008, and 35.7% during 2009–2010.64–65 Abdominal obesity has also increased since 1988–1994.66–67
In the wake of the stark rise in obesity, the prevalence of diabetes has increased substantially since 1976–1980. Using 1985 WHO criteria, the prevalence of diabetes among adults aged 40 to 74 years was 11.4% during 1976–1980 and 14.3% during 1988–1994.68 Using 2008 ADA criteria, the prevalence of diabetes was 15.3% during 1988–1994 and 17.5% during 2005–2006.69
Predicted CHD Risk
Starting with the Framingham Risk Score,70 multiple CHD risk equations have been developed to estimate the risk of developing incident CHD over a defined period, generally 10 years. Because these risk equations integrate the effects of key risk factors for CHD, trends in the predicted risk for CHD may correlate with trends in incident CHD. Using risk equations contained in the Adult Treatment Panel III report, little change in predicted 10‐year risk for CHD was observed from the period 1988–1994 to 1999–2002 among US adults.71 During 1988–1994, 76.5% of adults had a predicted 10‐year risk of <10%, 11.2% had a predicted 10‐year risk of 10% to 20%, and 12.3% had a predicted 10‐year risk of >20%. During 1999–2002, these percentages were 75.6%, 11.4%, and 13.0%, respectively. A subsequent analysis of national data showed that mean predicted 10‐year risk calculated using the Framingham Risk Score for CHD decreased from 10.0% during 1976–1980 to 7.9% during 1988‐1994 (P<0.001) and decreased from 7.9% during 1988–1994 to 7.4% during 1999‐2004 (P<0.001).72 The results from the latter study support the thesis of a decline in the incidence of CHD. A more recent analysis of NHANES data showed a continuing decline in predicted 10‐year risk from 1999–2000 to 2009–2010.73
Incidence
Because incident CHD can manifest itself in different clinical presentations, measuring incident CHD can be challenging. A person may experience the first signs of CHD as angina pectoris and be treated on an outpatient basis. Another person may experience an MI as the first sign of CHD and be hospitalized. Someone else may die of sudden cardiac death. Thus, providing an integrated picture of all these possible first occurrences of CHD would require a system that is able to capture the spectrum of disease expression. However, such a system does not currently exist at the national level. Because national data about incident CHD are not available, our current knowledge of the true incidence of CHD in the United States comes from an amalgam of community surveillance (Table 4), cohort studies (Table 5), and health care delivery systems. Each of these sources of information has, to a variable degree, limitations that may include time frames, geographic coverage, and generalizability of the study populations.
Table 4.
Community Studies of Incident Coronary Heart Disease or Sudden Death in the United States
| Reference | Study | CHD Event | Period | Group | Rates or Percent Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elveback7,74 | Rochester, Minnesota | Incident CHD (angina, MI, sudden unexpected death): medical, hospital, and autopsy records | 1950–1954 to 1955–1959 to 1979–1982 | Total | 589 to 699 to 559/100 000 population* |
| Gillum23 | Minnesota Heart Survey | Sudden death: death certificates | 1970–1978 | Men | 311 to 244/100 000 population* |
| Women | 96 to 70/100 000 population* | ||||
| Goldberg25 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | MI. Review of medical records: history, enzymes, ECG. Autopsy records | 1975–1984 | Total | 255 to 186/100 000 population* |
| Goldberg75 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | MI. Review of medical records: history, enzymes, ECG. Autopsy records | 1975–1988 | Men | 323 to 240/100 000 population* |
| Women | 176 to 137/100 000 population* | ||||
| McGovern18 | Minnesota Heart Survey | Acute CHD: ICD‐9 410‐411. Hospital records were abstracted; computer‐based algorithm | 1985 to 1990 | Men | 315 to 298/100 000 population* |
| Women | 111 to 107/100 000 population* | ||||
| Goff76 | Corpus Christi Heart Project | MI hospitalizations. Review of medical records: ECG, enzymes, cardiac pain | 1988–1989 to 1991–1992 | Mexican American women | 353.5 to 205.3/100 000 population* |
| Non‐Hispanic White women | 224.3 to 150.0/100 000 population* | ||||
| Mexican American men | 485.8 to 367.4/100 000 population* | ||||
| Non‐Hispanic White men | 345.9 to 342.2/100 000 population* | ||||
| Rosamond11 | Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study | MI hospitalizations. Hospital records were abstracted (symptoms, history, enzymes, ECG); computer‐based algorithm | 1987–1994 | Women | 1.9 to 1.8/1000 persons* |
| Men | 4.1 to 4.1/1000 persons* | ||||
| Cobb77 | Seattle, Washington | Cardiac arrests receiving advanced life support. Medical incident reports supplemented with information from death certificates and hospital admissions | 1979–1980 to 1999–2000 | Total | 1.39 to 0.91/1000 population* |
| Men | 2.15 to 1.24/1000 population* | ||||
| Women | 0.68 to 0.61/1000 population* | ||||
| Cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation as first recorded rhythm | Total | 0.85 to 0.38/1000 population* | |||
| Men | 1.39 to 0.60/1000 population* | ||||
| Women | 0.35 to 0.17/1000 population* | ||||
| Polentini78 | Milwaukee, Wisconsin | Emergency medical services database | 1992–2002 | Total | 37.1 to 19.4/100 000 population* |
| Floyd32 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | MI. Review of medical records: history, enzymes, ECG | 1975 to 1981 to 2005 | Total | 277 to 320 to 209/100 000 population* |
| Roger34 | Olmsted County, Minnesota | MI. Review of medical records: cardiac pain, biomarkers (CK, CK‐MB, troponin), ECG. Computer‐based algorithm | 1987–2006 | All MI | 186 to 180/100 000 population* |
| CK/CK‐MB MI | 186 to 141/100 000 population* | ||||
| McManus35 | Worcester Heart Attack Study | MI hospitalizations. Review of medical records: history, enzymes, ECG | 1997–2005 | STEMI | 121 to 77/100 000 population* |
| NSTEMI | 126 to 132/100 000 population* | ||||
| Rosamond38 | Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study | MI hospitalizations. Hospital records were abstracted: chest pain, biomarkers, ECG. Computer‐based algorithm | 1987–2008 | All MI | |
| Men | 3.8%/year ↓* | ||||
| Women | 3.5%/year ↓* | ||||
| White men | 4.3%/year ↓* | ||||
| White women | 3.8%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black men | 1.5%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black women | 2.9%/year ↓* | ||||
| STEMI | |||||
| Men | 4.8%/year ↓* | ||||
| Women | 4.1%/year ↓* | ||||
| White men | 5.4%/year ↓* | ||||
| White women | 4.4%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black men | 2.2%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black women | 3.3%/year ↓* | ||||
| NSTEMI | |||||
| Men | 4.3%/year ↓* | ||||
| Women | 4.2%/year ↓* | ||||
| White men | 4.8%/year ↓* | ||||
| White women | 4.5%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black men | 2.0%/year ↓* | ||||
| Black women | 3.9%/year ↓* |
ECG indicates electrocardiograms; MI, myocardial infarction; NSTEMI, non ST‐segment elevation myocardial infarction; STEMI, ST‐segment elevation myocardial infarction.
Statistically significant change.
Change was not statistically significant.
Statistical significance of change was not reported.
Table 5.
Cohort Studies Reporting on Incidence of Coronary Heart Disease in Selected Locations in the United States
| Reference | Study | CHD Event | Period | No. of Incident Events | Sample Size, Gender | Age at Baseline | Group | Change in Rates or Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pell24 | Du Pont Company | M; review of medical records, ECG | 1957–1959 to 1981–1983 | 6286 MI | Men: 2 304 958 PY | 25 to 64 | Total | 3.19 to 2.29 per 1000* |
| 1957–1963 to 1978–1983 | 150 MI | Women: 426 150 PY | 0.37 to 0.32 per 1000* | |||||
| Reed9 | Honolulu Heart Program | CHD: Medical review of hospital discharge and mortality records | 1966–1984 | 674 CHD, 327 CHD deaths | 7681 men | 45 to 68 | Men | 6.1 to 5.7/1000 PY* |
| D'Agostino46 | Framingham Heart Study | CHD: Medical review of MI, angina, sudden and nonsudden death from CHD, coronary insufficiency | 1953–1963, 1963–1973, 1973–1983 | ― | 526, 535, 581 men | 55 to 64 | Men | 187 to 208/1000* |
| 689, 782, 812 women | Women | 131 to 110/1000* | ||||||
| Sytkowski10 | Framingham Heart Study | CHD: Medical review of MI, angina, sudden and nonsudden coronary death, coronary insufficiency | 1950–1960–1970 | 928 CHD | 618, 586, 598 men | 50 to 59 | Men | 354 to 346/1000* |
| 757, 816, 834 women | Women | 218 to 175/1000* | ||||||
| Hu79 | Nurses' Health Study | Nonfatal MI or fatal coronary disease. Review of medical records. Deaths from state vital records, National Death Index, reports by next of kin or postal system | 1980–1982 to 1992–1994 | 946 nonfatal MI, 358 fatal CD | 85 941 women | 34 to 59 | ≤49 years | 25 to 13/100 000 PY* |
| 50 to 54 years | 103 to 53/100 000 PY* | |||||||
| 55 to 59 years | 177 to 149/100 000 PY* | |||||||
| Total | 31% ↓* | |||||||
| Ergin28 | National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I EFS | CHD: Hospital and nursing home discharge records, death certificate records. No review | 1971–1975 to 1982–1984, 1982–1984 to 1992 | 1501, 778 CHD | 10 869 men, women (1971–1982), 9774 men, women (1982–1992) | 35 to 74 | Total | 133.3 to 113.5/10 000 PY* |
| MI: Hospital and nursing home discharge records, death certificate records. No review | 583, 358 MI | Total | 49.7 to 49.2/10 000 PY* | |||||
| Parikh31 | Framingham Heart Study, Framingham Heart Study Offspring | MI‐ECG: Ischemic chest discomfort with diagnostic ECG changes, ±biomarker changes | 1960s–1990s | 639 MI‐ECG | 9824 men, women | 40 to 89 | Total | ≈50% ↓* |
| MI‐biomarker: Ischemic chest discomfort with diagnostic biomarkers but no ECG changes | 302 MI‐biomarker | Total | ≈100% ↑* |
ECG indicates electrocardiograms; MI, myocardial infarction.
Statistically significant change.
Change was not statistically significant.
Statistical significance of change was not reported.
Community surveillance
One of the earliest studies to examine trends in the incidence of CHD emanated from Rochester, Minnesota.7,74 The age‐ and sex‐adjusted rates (per 100 000) of CHD incidence comprising angina pectoris, MI, and sudden unexpected death were 589 during 1950–1954, 699 during 1955–1959, 589 during 1960–1964, 571 during 1965–1969, and 572 during 1970–1974, 538 during 1975–1978, and 559 during 1979–1982. The rate among men generally decreased, whereas the rate among women increased slightly. The age‐adjusted rate (per 100 000) of sudden unexpected death decreased from 126 during 1950–1954 to 73 during 1979–1982. Rates of angina pectoris decreased from 240 to 213, whereas rates of MI increased from 222 to 255 during the same period.
A more recent study from Olmsted County, Minnesota showed that the age‐ and sex‐adjusted rate (per 100 000) of hospitalizations for incident MI from 1987 to 2006 changed from 186 to 180 (P=0.171).34 When MI hospitalizations were restricted to those that used creatine kinase/creatine kinase‐MB but not troponin for the diagnosis of MI, a significant decrease in the rate from 186 to 141 was observed. Furthermore, rates of STEMI declined significantly by 41% when troponin was considered or 44% when troponin was excluded. However, rates of incident NSTEMI increased by 49%. An interesting aspect of this study is that measurements of creatine kinase/creatine kinase‐MB continued to be administered from 2000 on as troponin was being ushered in, thus allowing an evaluation of the impact of changing diagnostic criteria on trends in MI incidence.
From 1970 to 1978, out‐of‐hospital mortality rates from CHD in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota declined by 43% among men and by 40% among women.23 Another study in Minneapolis and St. Paul found that the age‐adjusted hospitalization rates for first MI declined by 5% among men and 4% among women from 1985 to 1990 based on ICD‐9‐CM codes of 410 and 411 obtained from 31 hospitals in 1985 and 25 hospitals in 1990 among patients aged 30 to 74 years.18 These changes were not statistically significant.
From 1988 to 1992, the age‐adjusted incidence rates of hospitalized MI in the Corpus Christi Heart Project decreased significantly among Mexican‐American women.76 Nonsignificant reductions were reported for white women and Mexican‐American men, and little change was reported for white men.
In Seattle, the age‐ and sex‐adjusted incidence rates of cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation from 1980 to 2000 declined by 56%, and the incidence of all treated arrests declined by 34%.77 Declines in the incidence rates of cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation were similar for men and women, but the decline in the incidence rates of all treated arrests in men exceeded that in women.
As part of the ARIC study, surveillance of hospital admissions for MI among residents aged 35 to 74 years was conducted among adults aged 35‐74 years in 4 communities (Forsyth County, NC; Jackson, MS; Minneapolis suburbs, MN; Washington County, MD) from 1987 to 1994.11 Hospital discharges meeting certain ICD‐9‐CM codes from 28 hospitals were reviewed, and a computerized algorithm assigned a diagnosis using information on symptoms, cardiac enzymes, and ECGs collected by study personnel from medical records. A total of 11 869 hospitalizations for MI were estimated. The age‐adjusted rate of hospitalizations for incident MI in women was 1.9 per 1000 population in 1987 and 1.8 per 1000 population in 1994, whereas the rate in men remained unchanged at 4.1 per 1000 population. The average annual rate of change during the study period was +2.9% among black men, +7.4% among black women, −2.5% among white women, and −0.3% among white men. Out‐of‐hospital mortality attributed to CHD declined by 3.6% per year.
More recently, updated results of this surveillance system in these 4 communities from 1987 to 2008 showed that the age‐adjusted rate of hospitalizations for incident MI declined.38 The basic surveillance methodology remained largely the same. Because this study covered a period that saw profound changes in the use of diagnostic biomarkers (the advent of troponin), the study authors made a number of adjustments in their analytic strategy to account for these changes. For this study, 30 985 hospitalizations for MI were estimated. The age‐ and biomarker adjusted rate of hospitalization for a first MI changed by −4.3% (95% CI: −4.7, −3.8) among white men, −3.8% (95% CI: −4.5, −3.1) among white women, −1.5% (95% CI: −2.7, −0.4) among black men, and −2.9% (95% CI: −4.2, −1.5) among black women. Compared to the period 1987–1996, the decline in the rates of combined hospitalization for incident MI or fatal CHD during 1997–2008 accelerated. Declines were observed in the age‐ and biomarker‐adjusted rate of hospitalization for both STEMI and NSTEMI. The authors noted that the patterns in rates based only on ECG criteria and clinical history mirrored rates that included biomarker data. Out‐of‐hospital mortality attributed to CHD declined by 5.6% per year among white men, 4.4% per year among white women, 2.7% among black men, and 2.6% among black women. Declines in both sexes during the period 1997–2008 far exceeded the declines during the period from 1987 to 1996.
Surveillance of MI among residents of Worcester, Massachusetts as part of the Worcester Heart Attack Study has been conducted since 1975.25,27,32,75 Hospitalizations for MI were identified, and medical records for these hospitalizations were reviewed. Information about the clinical history, ECG changes, and biomarker changes was abstracted to make a determination of MI. Although the age‐adjusted hospitalization rates (per 100 000) for incident MI dropped from 277 in 1975 to 209 in 2005, the rates during intervening years varied considerably.32 A subsequent investigation of trends in incident hospitalizations for MI from 1997 to 2005 showed that the incidence rate for STEMI was 121 in 1997, peaked in 1999 and then declined progressively to 77 through 2005.35 In contrast, the incidence rate of NSTEMI spiked in 2001 and then declined reaching a level in 2005 (132) that was similar to that in 1997 (126). From 1975 to 1988, out‐of‐hospital mortality rates attributed to CHD declined by 60% among men and 69% among women.75
In Milwaukee, the incidence (per 100 000) of treated cardiac arrest with ventricular fibrillation or tachycardia as the first recorded rhythm declined from 37.1 in 1992 to 19.4 in 2002.78 The incidence of all treated arrests was 82.8 in 1992 and 82.3 in 2002.
These community surveillance studies provide strong evidence that incidence has decreased in those areas although the onset of the decline varied by geographical location with the earliest decline being observed in Olmsted County, Minnesota. These well‐conducted studies employed standardized case‐definitions for MI. Two of these studies also carefully navigated the changing currents in diagnostic criteria for MI. Nevertheless, a drawback of these studies remains their narrow geographic focus.
Cohort studies
A study of male employees of Du Pont Company showed that the age‐adjusted incidence rate (per 1000) of first MI decreased steadily from 3.19 during 1957–1959 to 2.29 during 1981–1983.24 Events were identified from insurance claims and death certificates, and medical records were reviewed.
In a cohort of 8006 men of Japanese ancestry living on Oahu, the incidence of CHD increased from 1966 to 1978 and then decreased through 1984.9 For the entire study period, the estimated annual change in incidence was −0.4% (95% CI: −2.6%, +1.8%). Incident CHD events included CHD deaths (ICD‐8 codes 410‐414 as the underlying or contributing cause of death or sudden unexplained deaths within 1 hour of being well) and nonfatal MI (ECG evidence and/or cardiac enzyme changes).
An early analysis of data from the Framingham Heart Study found that the incidence of CHD among 3 successive cohorts of men and women aged 55‐64 years did not change significantly from 1953–1963 to 1973–1983.46 For men, incidence rates (per 1,000) for CHD were 187 during 1953–1963, 210 during 1963–1973, and 208 during 1973–1983 (P trend=0.41), and incidence rates for MI were 103 during 1953–1963, 116 during 1963–1973, and 120 during 1973–1983 (P trend=0.42). For women, incidence rates for CHD were 131 during 1953–1963, 132 during 1963–1973, and 110 during 1973–1983 (P trend=0.41), and incidence rates for MI were 38 during 1953–1963, 50 during 1963–1973, and 45 during 1973–1983 (P trend=0.38). CHD was defined as MI, coronary insufficiency, angina pectoris, and sudden and non‐sudden death from CHD. MI was determined from serial ECG changes and cardiac enzymes when they became available.
In a subsequent analysis of data from the Framingham Heart Study, 20‐year incidence of CHD in 3 consecutive cohorts of adults aged 50 to 59 years was examined.10 CHD included MI, angina, sudden and non‐sudden coronary death, and coronary insufficiency. Among women, the incidence (per 1000) of CHD decreased significantly from 218 events in the 1950 cohort to 175 events in the 1970 cohort (P<0.05). In contrast, the rate among men was 354 in the 1950 cohort and 346 in the 1970 cohort.
Another analysis of data from the Framingham Heart Study and Framingham Heart Study Offspring Cohort found that the risk of sudden coronary death in adults without CHD or congestive heart failure decreased by 39% from 1950–1969 to 1990–1999.80
More recently, data from the Framingham Heart Study and Framingham Heart Study Offspring Cohort showed that the incidence of MI had declined during successive decades starting with 1960–1969 and ending with 1990–1999.31 Among 9824 participants aged 40 to 89 years, 941 MIs were recorded of which 639 were defined on the basis of ECG changes and 302 on the basis of biomarker changes. MIs were identified by information obtained from study participants during follow‐up examinations or mailings of update questionnaires and evaluated with medical records. MIs were divided into 2 groups: those with ischemic chest discomfort and diagnostic ECG changes irrespective of diagnostic biomarker changes (MI‐ECG) and those with ischemic chest discomfort and diagnostic biomarker changes without diagnostic ECG changes (MI‐marker). Rates of incident MI‐ECG dropped by about half, whereas rates of incident MI‐marker doubled. Significant decreases in MI‐ECG were noted for men aged 50 to 59 years and 70 to 79 years as well as women aged 70 to 79 years. In contrast, significant increases in ECG‐marker were noted for men aged 50 to 59 years and 70 to 79 years as well as women aged 70 to 79 years. The authors concluded that much of the uncertainty in trends in the incidence of MI may have been attributable to changes in diagnostic criteria for MI.
Data from the Nurses' Health Study that included 85 941 participants aged 34 to 59 years showed that the incidence of CHD declined by 31% from 1980–1982 to 1992–1994.79 CHD was defined as nonfatal MI or fatal coronary disease. The former was determined from medical record review of MIs reported by the study participants, and MI was defined using World Health Organization criteria. Deaths were determined from state vital records, the National Death Index, reports by next of kin, and the postal system. In all, 946 participants had a nonfatal MI and 358 experienced death attributable to coronary disease.
An analysis of data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey I Epidemiologic Follow‐up Study from 1971 to 1992 showed that the age‐adjusted incidence (per 10 000) declined from 133.3 from 1971–1975 to 1982–1984 to 113.5 from 1982–1984 to 1992 for CHD and from 49.7 to 49.2, respectively, for MI.28 The incidence of CHD declined significantly among white men (−14.6%) and women (−11.4%). The relative decrease among black men (−18.5%) was the largest of the 4 groups but failed to reach statistical significance. The decrease among black women (−3.8%) was the smallest of any of the 4 groups. The baseline cohort included 10 869 participants aged 35 to 74 years, and the follow‐up cohort included 9774 participants aged 35 to 74. Incident CHD was defined as a death from CHD, a hospitalization for CHD, or a nursing home stay with the ICD‐9 codes of 410‐414. Prevalent CHD was excluded from the baseline cohort on the basis of self‐reported heart attack, heart failure, or stroke as well as the use of medications used to treat heart disease.
The cohort studies provide valuable insights into trends of incident CHD in their study populations, which range from relatively specific populations such as employees of a company to near representative samples of US adults. Thus, generalizability of their findings to the national level is a prime limitation. Also, the age range of participants of many cohort studies is limited precluding an examination of trends in incidence across the full adult lifespan. By examining the experience of the participants who have been repeatedly examined, a Hawthorne‐type of effect could be introduced into studies in that study participants may alter their behaviors in response to their study participation. On the other hand, cohort studies often use some of the best‐validated measures of incident CHD and yield information over some of the longest time frames.
Health care delivery systems
The large health care delivery systems potentially represent an important opportunity for conducting surveillance of CHD in large segments of the US population. Drawing from the administrative systems of Kaiser Permanente Northern California, investigators identified hospitalizations for MI from 1999 to 2008 using the ICD‐9‐CM code of 410 and divided these into hospitalizations for STEMI (ICD‐9‐CM codes 410.0‐410.6, 410.8) and NSTEMI (410.7, 410.9).33 A total of 46 086 hospitalizations for incident MI among adults aged ≥30 years were included in the analyses. The age‐ and sex‐adjusted rate (per 100 000 person‐years) of hospitalizations for incident MI were 274 in 1999 and 287 in 2000 and then progressively declined to 208 through 2008. Rates of STEMI decreased steadily throughout the study period from 133 to 50, but the rates of NSTEMI increased until 2004 and began to decrease in subsequent years. Validation studies were performed to show that the positive predictive value for the STEMI and NSTEMI coding algorithm did not materially change during the study period.
Because health care delivery systems represent an important source of health care and coverage, the databases and expanding rich electronic medical records of these health systems contain potentially valuable information about trends in the incidence of CHD of their memberships. However, information from these data systems is subject to several considerations: data from these plans generally may not reach back far in time, the need to validate electronic data sources deserves careful consideration, and health care delivery systems may not be fully representative of all relevant populations (eg, uninsured persons).
Population surveys
Data from the National Health Interview Survey have been analyzed to examine trends in the incidence of CHD.44 Participants who reported that they had CHD, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, or heart attack with an onset during the 12 months prior to their interview were considered to have had an incident event. From 1980 to 1989, the age‐adjusted incidence per 1000 population ranged between 2.2 and 3.2 with no significant linear trend. Among white men, a nonlinear trend was described with decreasing rates from 1986 to 1989. Among white women, a significant increase in the incidence rate was observed.
Unrecognized MI
Some percentage of MIs are not diagnosed because patients are asymptomatic, experience symptoms that do not prompt them to seek medical care, or experience symptoms that may be insufficiently characteristic of an MI and do not result in a diagnostic evaluation.81 Thus, these MIs are typically recognized when patients receive an ECG examination subsequent to the MI. Such MIs are also referred to as silent, asymptomatic, or undiagnosed MIs. The prevalence of unrecognized MIs has been reported to range from 4.3% to 44%,81–82 and factors like the age and gender distribution of study participants account in part for the wide range in estimates. Little about possible trends in unrecognized MI is known, and the impact of this category of MI on the trends in incidence of MI is unclear. Despite clinical impressions that persons with diabetes experience more painless MIs, it remains uncertain whether the increased prevalence of diabetes may have affected trends in unrecognized MI because diabetes has not been shown to be an independent predictor of unrecognized MI.81 For cohort studies such as the Framingham Heart Study that administer periodic ECGs, unrecognized MIs should have been captured, and the trends in incident CHD reported from such cohort studies should not be biased by the exclusion of unrecognized MIs, although Framingham included a selected patient sample that may not be representative of the broader US population. The results from other studies that rely on identifying patients with MI who present for medical care could be biased depending on the direction and strength of the trends in unrecognized MI.
Severity of MI
Successful primary prevention that reduces the incidence of CHD may favorably shift the distribution of severity of MI. Consequently, evidence of a change in the severity of MI may provide indirect support for a reduction in the incidence of CHD. Data from several studies suggest that the severity of MIs has lessened.34–35,34–88 Initial reports from Worcester, Massachusetts found that the incidence of cardiogenic shock complicating an MI did not change significantly from 1975 to 1988 or from 1975 to 1997.83–84 A more recent report noted that there was evidence of a decline in cardiogenic shock from the late 1990s to 2005.87 A decline in the incidence of STEMI but not NSTEMI in Worcester also suggests that the severity of MI declined in that area.35 An initial report from ARIC investigators yielded inconsistent evidence that the severity of MIs had decreased from 1987 to 1994.85 However, a subsequent report covering the period from 1987 to 2002 noted that the severity of MI had declined.88 An investigation conducted in Olmsted County, Minnesota showed that the severity of MI had decreased from 1983 to 1994.86 A more recent study from 1987 to 2006 noted declines in the proportion of MIs with Killip class 2‐4 and with ST‐segment elevation.34 Furthermore, the decline in hospitalizations for incident STEMI not paralleled by a similar decline in NSTEMI in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system argues for a decline in the severity of MI.33 Because severity of an MI reflects a complex mix of pathophysiologic underpinnings, patient behavior in seeking medical care, comorbidities, and medical care, studying temporal trends in severity is a complicated endeavor.89–90 Nevertheless, the available evidence suggests some degree of concordance between improving trends in MI severity and incident CHD.
Summary and Closing Thoughts
Although a complete picture of the national trend in CHD incidence in the United States remains elusive, the findings from community‐based studies, prospective studies, and health care delivery systems reporting decreases in incidence of CHD provide the most convincing evidence that the national incidence of CHD may have declined. These findings are buttressed by data showing declines in national rates of death attributed to CHD, studies showing decreases in sudden death and out‐of hospital mortality associated with MI, declines in hospitalizations for CHD, improving MI severity, possible recent declines in prevalence of CHD, declines in predicted 10‐year risk, and favorable improvements in the prevalence and control of some major CHD risk factors. Although each of these pieces of information is an imperfect reflection of incident CHD, in the aggregate they tell an increasingly compelling story of the evolution of CHD incidence in the United States. Declines in death from CHD are potentially suggestive of declining CHD incidence if the declines in case‐fatality rates do not account for the entire decrease in mortality.
Because the studies examining trends in CHD incidence covered different time frames and were conducted in different areas of the United States, pinpointing the exact time when incidence started to decrease is difficult because the onset of the start of any declines may have varied geographically. Community surveillance studies have reported decreases in incidence as early as the 1960s (Rochester, MN),7 during the late 1980s (Corpus Christi Heart Project),76 1990s (ARIC),38 and 2000s (Worcester Heart Attack Study).32 Other studies suggest that decreases in incidence occurred during the 1960s (Framingham Heart Study, the Du Pont Company),10,24 1970s (Framingham Heart Study),31 1980s (Nurses' Health Study, NHANES Epidemiologic Follow‐up Study, Framingham Heart Study),28,31,79 1990s (Framingham Heart Study, Nurses' Health Study),31,79 and 2000s (Kaiser Permanente Northern California).33
Three of the studies illustrate the difficulty in interpreting surveillance data over long periods of time particularly when changes in diagnostic criteria occur.31,34,38 The introduction of troponin testing around the turn of the century marked an important change in the diagnostic criteria for MI91 and coincided with a shift in the ratio of STEMI to NSTEMI with decreases in rates of STEMI and increases in rates of NSTEMI. Furthermore, the advent of electron‐beam computed tomography and multi‐detector computed tomography to detect calcium in the walls of coronary arteries has led to earlier identification of CHD.92 From a surveillance point of view, these disruptive changes in diagnostic criteria emphasize the importance of being able to disentangle the effects on such changes on trend analyses.
Validation of incident CHD events enhances the credibility of trends in CHD incidence. The majority of community surveillance, cohort, and health care delivery system‐based studies included reviews of medical records searching for clinical presentation, electrographic criteria, and cardiac biomarkers to confirm the presence of CHD, although these validation efforts differed across studies and across time periods as diagnostic criteria were also evolving.
Furthermore, observational studies suggest that an enormous amount of CHD can yet be prevented by adopting healthy behaviors or by optimizing behavioral and clinical risk factors as exemplified by the AHA's 7 cardiovascular health metrics.93–99 In addition, initiatives such as the Million Hearts Initiative, which aims to prevent 1 million heart attacks and strokes by 2017 through a combination of clinical and community actions, will, if successful, potentially hasten the decline in the incidence of CHD.100–101
The data sources opening a window into race or ethnicity‐specific trends of CHD incidence are few. Data from the ARIC study suggest that African‐American men and women did enjoy declining CHD incidence, but the decline among African Americans manifested itself later than among whites and the size of the decline was smaller than that of whites. These results are corroborated by Medicare data and data from the NIS also showing that the hospitalization rate for MI declined more slowly among African Americans than among whites.21–22 Gaps in evidence exist about the trends in CHD incidence among other racial or ethnic groups such as Hispanics and Asians. Given the rapidly evolving demographic composition of the US population, data collection efforts to shed light on the evolution of CHD in major and growing racial and ethnic groups are needed. Perhaps, large health care delivery systems and growing health system‐based networks are best suited to provide such results if their expanding electronic medical record and other data systems capture valid racial and ethnic designations and relevant clinical outcomes of their memberships.
Efforts to establish community surveillance for CHD harken back decades.102–103 A national system to monitor CHD incidence has never been established, however, and this gap has not gone unnoticed.104–107 As part of its recommendations, the Institute of Medicine highlighted the critical importance of having data on the incidence of CVD and the need for a system that would collect such data. The report cited potential avenues such as the establishment of registries, the use of cohort studies, and the use of claims and electronic medical record data to accomplish such a goal. The development of a national system to monitor the trend in the incidence of CHD would help to fill this current void in the knowledge base of the epidemiology of CHD and provide critical data to improve cardiovascular health of the US population.
In conclusion, definitive data about national trends of incident CHD in the United States currently are not available, and, therefore, clues about these trends must be gleaned from a variety of auxiliary data sources. Studies in different parts of the country demonstrate improvements in the incidence of CHD that may have commenced several decades ago in some parts of the country, and an increasing number of recent studies have described favorable trends during the first decade of the 21st century. Taken together, these studies yield encouraging but tentative signals that the incidence of CHD in the United States may be waning. Bringing greater clarity to this important topic of cardiovascular epidemiology poses a pressing public health need.
Disclosures
None.
References
- 1.Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER, III, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB. Heart disease and stroke statistics–2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014; 129:e28-e292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Podgor MJ, Leske MC. Estimating incidence from age‐specific prevalence for irreversible diseases with differential mortality. Stat Med. 1986; 5:573-578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Davies AR, Smeeth L, Grundy EM. Contribution of changes in incidence and mortality to trends in the prevalence of coronary heart disease in the UK: 1996 2005. Eur Heart J. 2007; 28:2142-2147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Murphy SL, Xu J, Kochanek KD. Deaths: Preliminary Data for 2010 Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr60/nvsr60_04.pdf. Accessed November 12, 2014.
- 5.Higgins M, Thom T. Trends in CHD in the United States. Int J Epidemiol. 1989; 18:S58-S66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.National Institutes of Health, National Heart LaBI. Morbidity & Mortality: 2012 Chartbook on Cardiovascular, Lung, and Blood Diseases Available at: http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/resources/docs/2012_ChartBook_508.pdf. Accessed November 16, 2012.
- 7.Elveback LR, Connolly DC, Kurland LT. Coronary heart disease in residents of Rochester, Minnesota. II. Mortality, incidence, and survivorship, 1950–1975. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981; 56:665-672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gillum RF, Hannan PJ, Prineas RJ, Jacobs DR, Jr, Gomez‐Marin O, Luepker RV, Baxter J, Kottke TE, Blackburn H. Coronary heart disease mortality trends in Minnesota, 1960–80: the Minnesota Heart Survey. Am J Public Health. 1984; 74:360-362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reed D, Maclean C. The nineteen‐year trends in CHD in the Honolulu Heart Program. Int J Epidemiol. 1989; 18:S82-S87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sytkowski PA, D'Agostino RB, Belanger A, Kannel WB. Sex and time trends in cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality: the Framingham Heart Study, 1950–1989. Am J Epidemiol. 1996; 143:338-350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rosamond WD, Chambless LE, Folsom AR, Cooper LS, Conwill DE, Clegg L, Wang CH, Heiss G. Trends in the incidence of myocardial infarction and in mortality due to coronary heart disease, 1987 to 1994. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:861-867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Walker WJ. Changing United States life‐style and declining vascular mortality: cause or coincidence? N Engl J Med. 1977; 297:163-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Stern MP. The recent decline in ischemic heart disease mortality. Ann Intern Med. 1979; 91:630-640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Goldman L, Cook EF. The decline in ischemic heart disease mortality rates. An analysis of the comparative effects of medical interventions and changes in lifestyle. Ann Intern Med. 1984; 101:825-836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sytkowski PA, Kannel WB, D'Agostino RB. Changes in risk factors and the decline in mortality from cardiovascular disease. The Framingham Heart Study. N Engl J Med. 1990; 322:1635-1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hunink MG, Goldman L, Tosteson AN, Mittleman MA, Goldman PA, Williams LW, Tsevat J, Weinstein MC. The recent decline in mortality from coronary heart disease, 1980–1990. The effect of secular trends in risk factors and treatment. JAMA. 1997; 277:535-542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, Critchley JA, Labarthe DR, Kottke TE, Giles WH, Capewell S. Explaining the decrease in U.S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980–2000. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:2388-2398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.McGovern PG, Pankow JS, Shahar E, Doliszny KM, Folsom AR, Blackburn H, Luepker RV. Recent trends in acute coronary heart disease—mortality, morbidity, medical care, and risk factors. The Minnesota Heart Survey Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:884-890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nallamothu BK, Young J, Gurm HS, Pickens G, Safavi K. Recent trends in hospital utilization for acute myocardial infarction and coronary revascularization in the United States. Am J Cardiol. 2007; 99:749-753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fang J, Alderman MH, Keenan NL, Ayala C. Acute myocardial infarction hospitalization in the United States, 1979 to 2005. Am J Med. 2010; 123:259-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chen J, Normand SL, Wang Y, Drye EE, Schreiner GC, Krumholz HM. Recent declines in hospitalizations for acute myocardial infarction for Medicare fee‐for‐service beneficiaries: progress and continuing challenges. Circulation. 2010; 121:1322-1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang OJ, Wang Y, Chen J, Krumholz HM. Recent trends in hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2012; 109:1589-1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gillum RF, Folsom A, Luepker RV, Jacobs DR, Jr, Kottke TE, Gomez‐Marin O, Prineas RJ, Taylor HL, Blackburn H. Sudden death and acute myocardial infarction in a metropolitan area, 1970–1980. The Minnesota Heart Survey. N Engl J Med. 1983; 309:1353-1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pell S, Fayerweather WE. Trends in the incidence of myocardial infarction and in associated mortality and morbidity in a large employed population, 1957–1983. N Engl J Med. 1985; 312:1005-1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Goldberg RJ, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Dalen JE. Incidence and case fatality rates of acute myocardial infarction (1975–1984): the Worcester Heart Attack Study. Am Heart J. 1988; 115:761-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Keil JE, Gazes PC, Litaker MS, Saunders DE, Jr, Weinrich MC, Baroody NB, Jr, Lackland DT, Hudson MB. Changing patterns of acute myocardial infarction: decline in period prevalence and delay in onset. Am Heart J. 1989; 117:1022-1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Goldberg RJ, Yarzebski J, Lessard D, Gore JM. A two‐decades (1975 to 1995) long experience in the incidence, in‐hospital and long‐term case‐fatality rates of acute myocardial infarction: a community‐wide perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999; 33:1533-1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ergin A, Muntner P, Sherwin R, He J. Secular trends in cardiovascular disease mortality, incidence, and case fatality rates in adults in the United States. Am J Med. 2004; 117:219-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Peterson ED, Shah BR, Parsons L, Pollack CV, Jr, French WJ, Canto JG, Gibson CM, Rogers WJ. Trends in quality of care for patients with acute myocardial infarction in the National Registry of Myocardial Infarction from 1990 to 2006. Am Heart J. 2008; 156:1045-1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wellenius GA, Mittleman MA. Disparities in myocardial infarction case fatality rates among the elderly: the 20‐year Medicare experience. Am Heart J. 2008; 156:483-490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Parikh NI, Gona P, Larson MG, Fox CS, Benjamin EJ, Murabito JM, O'Donnell CJ, Vasan RS, Levy D. Long‐term trends in myocardial infarction incidence and case fatality in the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute's Framingham Heart study. Circulation. 2009; 119:1203-1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Floyd KC, Yarzebski J, Spencer FA, Lessard D, Dalen JE, Alpert JS, Gore JM, Goldberg RJ. A 30‐year perspective (1975–2005) into the changing landscape of patients hospitalized with initial acute myocardial infarction: Worcester Heart Attack Study. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2009; 2:88-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yeh RW, Sidney S, Chandra M, Sorel M, Selby JV, Go AS. Population trends in the incidence and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:2155-2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Roger VL, Weston SA, Gerber Y, Killian JM, Dunlay SM, Jaffe AS, Bell MR, Kors J, Yawn BP, Jacobsen SJ. Trends in incidence, severity, and outcome of hospitalized myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2010; 121:863-869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McManus DD, Gore J, Yarzebski J, Spencer F, Lessard D, Goldberg RJ. Recent trends in the incidence, treatment, and outcomes of patients with STEMI and NSTEMI. Am J Med. 2011; 124:40-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nguyen HL, Saczynski JS, Gore JM, Waring ME, Lessard D, Yarzebski J, Reed G, Spencer FA, Li SX, Goldberg RJ. Long‐term trends in short‐term outcomes in acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 2011; 124:939-946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Coles AH, Fisher KA, Darling C, McManus D, Maitas O, Yarzebski J, Gore JM, Lessard D, Goldberg RJ. Recent trends in post‐discharge mortality among patients with an initial acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2012; 110:1073-1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rosamond WD, Chambless LE, Heiss G, Mosley TH, Coresh J, Whitsel E, Wagenknecht L, Ni H, Folsom AR. Twenty‐two‐year trends in incidence of myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease mortality, and case fatality in 4 US communities, 1987–2008. Circulation. 2012; 125:1848-1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.McManus DD, Piacentine SM, Lessard D, Gore JM, Yarzebski J, Spencer FA, Goldberg RJ. Thirty‐year (1975 to 2005) trends in the incidence rates, clinical features, treatment practices, and short‐term outcomes of patients <55 years of age hospitalized with an initial acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2011; 108:477-482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Goldberg RJ, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Dalen JE. Recent changes in attack and survival rates of acute myocardial infarction (1975 through 1981). The Worcester Heart Attack Study. JAMA. 1986; 255:2774-2779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ford ES, Giles WH. Changes in prevalence of nonfatal coronary heart disease in the United States from 1971‐1994. Ethn Dis. 2003; 13:85-93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Towfighi A, Zheng L, Ovbiagele B. Sex‐specific trends in midlife coronary heart disease risk and prevalence. Arch Intern Med. 2009; 169:1762-1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm. Accessed July 11, 2013.
- 44.DeStefano F, Merritt RK, Anda RF, Casper ML, Eaker ED. Trends in nonfatal coronary heart disease in the United States, 1980 through 1989. Arch Intern Med. 1993; 153:2489-2494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence of coronary heart disease–United States, 2006–2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011; 60:1377-1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.D'Agostino RB, Kannel WB, Belanger AJ, Sytkowski PA. Trends in CHD and risk factors at age 55–64 in the Framingham Study. Int J Epidemiol. 1989; 18:S67-S72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Elveback L, Lie JT. Continued high incidence of coronary artery disease at autopsy in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1950 to 1979. Circulation. 1984; 70:345-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Roger VL, Weston SA, Killian JM, Pfeifer EA, Belau PG, Kottke TE, Frye RL, Bailey KR, Jacobsen SJ. Time trends in the prevalence of atherosclerosis: a population‐based autopsy study. Am J Med. 2001; 110:267-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nemetz PN, Roger VL, Ransom JE, Bailey KR, Edwards WD, Leibson CL. Recent trends in the prevalence of coronary disease: a population‐based autopsy study of nonnatural deaths. Arch Intern Med. 2008; 168:264-270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.U.S.Public Health Service. Smoking and health. Report of the Advisory Committee to the Surgeon General of the Public Health Service. PHS Publication No. 1103; 1964.
- 51.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Trends in Current Cigarette Smoking Among High School Students and Adults, United States, 1965–2010 Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/tables/trends/cig_smoking/index.htm. Accessed November 29, 2012.
- 52.Pirkle JL, Bernert JT, Caudill SP, Sosnoff CS, Pechacek TF. Trends in the exposure of nonsmokers in the U.S. population to secondhand smoke: 1988–2002. Environ Health Perspect. 2006; 114:853-858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Carroll MD, Lacher DA, Sorlie PD, Cleeman JI, Gordon DJ, Wolz M, Grundy SM, Johnson CL. Trends in serum lipids and lipoproteins of adults, 1960–2002. JAMA. 2005; 294:1773-1781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Carroll MD, Kit BK, Lacher DA, Shero ST, Mussolino ME. Trends in lipids and lipoproteins in US adults, 1988–2010. JAMA. 2012; 308:1545-1554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital signs: prevalence, treatment, and control of high levels of low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol–United States, 1999–2002 and 2005‐200. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011; 60:109-114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Burt VL, Cutler JA, Higgins M, Horan MJ, Labarthe D, Whelton P, Brown C, Roccella EJ. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population. Data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991. Hypertension. 1995; 26:60-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA. 2010; 303:2043-2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Guo F, He D, Zhang W, Walton RG. Trends in prevalence, awareness, management, and control of hypertension among United States adults, 1999 to 2010. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 60:599-606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Vital signs: prevalence, treatment, and control of hypertension–United States, 1999–2002 and 2005–2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011; 60:103-108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2011: With Special Feature on Socioeconomic Status and Health; 2012. [PubMed]
- 61.Church TS, Thomas DM, Tudor‐Locke C, Katzmarzyk PT, Earnest CP, Rodarte RQ, Martin CK, Blair SN, Bouchard C. Trends over 5 decades in U.S. occupation‐related physical activity and their associations with obesity. PLoS ONE. 2011; 6:e19657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Brownson RC, Boehmer TK, Luke DA. Declining rates of physical activity in the United States: what are the contributors? Annu Rev Public Health. 2005; 26:421-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA. 2002; 288:1723-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA. 2010; 303:235-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA. 2012; 307:491-497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ford ES, Mokdad AH, Giles WH. Trends in waist circumference among U.S. adults. Obes Res. 2003; 11:1223-1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ford ES, Li C, Zhao G, Tsai J. Trends in obesity and abdominal obesity among adults in the United States from 1999–2008. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011; 35:736-743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Harris MI, Flegal KM, Cowie CC, Eberhardt MS, Goldstein DE, Little RR, Wiedmeyer HM, Byrd‐Holt DD. Prevalence of diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance in U.S. adults. The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:518-524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Cowie CC, Rust KF, Ford ES, Eberhardt MS, Byrd‐Holt DD, Li C, Williams DE, Gregg EW, Bainbridge KE, Saydah SH, Geiss LS. Full accounting of diabetes and pre‐diabetes in the U.S. population in 1988–1994 and 2005–2006. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:287-294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Kannel WB, McGee D, Gordon T. A general cardiovascular risk profile: the Framingham Study. Am J Cardiol. 1976; 38:46-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ajani UA, Ford ES. Has the risk for coronary heart disease changed among U.S. adults? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006; 48:1177-1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Lopez‐Jimenez F, Batsis JA, Roger VL, Brekke L, Ting HH, Somers VK. Trends in 10‐year predicted risk of cardiovascular disease in the United States, 1976 to 2004. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2009; 2:443-450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Ford ES. Trends in predicted 10‐year risk of coronary heart disease and cardiovascular disease among U.S. adults from 1999 to 2010. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013; 61:2249-2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Elveback LR, Connolly DC, Melton LJ., III Coronary heart disease in residents of Rochester, Minnesota. VII. Incidence, 1950 through 1982. Mayo Clin Proc. 1986; 61:896-900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Goldberg RJ, Gorak EJ, Yarzebski J, Hosmer DW, Jr, Dalen P, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Dalen JE. A communitywide perspective of sex differences and temporal trends in the incidence and survival rates after acute myocardial infarction and out‐of‐hospital deaths caused by coronary heart disease. Circulation. 1993; 87:1947-1953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Goff DC, Nichaman MZ, Chan W, Ramsey DJ, Labarthe DR, Ortiz C. Greater incidence of hospitalized myocardial infarction among Mexican Americans than non‐Hispanic whites. The Corpus Christi Heart Project, 1988–1992. Circulation. 1997; 95:1433-1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Cobb LA, Fahrenbruch CE, Olsufka M, Copass MK. Changing incidence of out‐of‐hospital ventricular fibrillation, 1980–2000. JAMA. 2002; 288:3008-3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Polentini MS, Pirrallo RG, McGill W. The changing incidence of ventricular fibrillation in Milwaukee, Wisconsin (1992–2002). Prehosp Emerg Care. 2006; 10:52-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Manson JE, Grodstein F, Colditz GA, Speizer FE, Willett WC. Trends in the incidence of coronary heart disease and changes in diet and lifestyle in women. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:530-537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Fox CS, Evans JC, Larson MG, Kannel WB, Levy D. Temporal trends in coronary heart disease mortality and sudden cardiac death from 1950 to 1999: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2004; 110:522-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Sheifer SE, Manolio TA, Gersh BJ. Unrecognized myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:801-811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Ammar KA, Kors JA, Yawn BP, Rodeheffer RJ. Defining unrecognized myocardial infarction: a call for standardized electrocardiographic diagnostic criteria. Am Heart J. 2004; 148:277-284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Goldberg RJ, Gore JM, Alpert JS, Osganian V, de Groot J, Bade J, Chen Z, Frid D, Dalen JE. Cardiogenic shock after acute myocardial infarction. Incidence and mortality from a community‐wide perspective, 1975 to 1988. N Engl J Med. 1991; 325:1117-1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Goldberg RJ, Samad NA, Yarzebski J, Gurwitz J, Bigelow C, Gore JM. Temporal trends in cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1999; 340:1162-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Goff DC, Jr, Howard G, Wang CH, Folsom AR, Rosamond WD, Cooper LS, Chambless LE. Trends in severity of hospitalized myocardial infarction: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study, 1987–1994. Am Heart J. 2000; 139:874-880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hellermann JP, Reeder GS, Jacobsen SJ, Weston SA, Killian JM, Roger VL. Longitudinal trends in the severity of acute myocardial infarction: a population study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Am J Epidemiol. 2002; 156:246-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Goldberg RJ, Spencer FA, Gore JM, Lessard D, Yarzebski J. Thirty‐year trends (1975 to 2005) in the magnitude of, management of, and hospital death rates associated with cardiogenic shock in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a population‐based perspective. Circulation. 2009; 119:1211-1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Myerson M, Coady S, Taylor H, Rosamond WD, Goff DC., Jr Declining severity of myocardial infarction from 1987 to 2002: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation. 2009; 119:503-514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Goldberg RJ. Monitoring trends in severity of acute myocardial infarction: challenges for the next millennium. Am Heart J. 2000; 139:767-770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Roger VL. Severity of myocardial infarction: new insights on an elusive construct. Circulation. 2009; 119:489-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Myocardial infarction redefined—a consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 36:959-969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Greenland P, Alpert JS, Beller GA, Benjamin EJ, Budoff MJ, Fayad ZA, Foster E, Hlatky MA, Hodgson JM, Kushner FG, Lauer MS, Shaw LJ, Smith SC, Jr, Taylor AJ, Weintraub WS, Wenger NK, Jacobs AK, Smith SC, Jr, Anderson JL, Albert N, Buller CE, Creager MA, Ettinger SM, Guyton RA, Halperin JL, Hochman JS, Kushner FG, Nishimura R, Ohman EM, Page RL, Stevenson WG, Tarkington LG, Yancy CW. 2010 ACCF/AHA guideline for assessment of cardiovascular risk in asymptomatic adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010; 56:e50-e103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Folsom AR, Yatsuya H, Nettleton JA, Lutsey PL, Cushman M, Rosamond WD. Community prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health, by the American Heart Association definition, and relationship with cardiovascular disease incidence. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:1690-1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ford ES, Zhao G, Tsai J, Li C. Low‐risk lifestyle behaviors and all‐cause mortality: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Mortality Study. Am J Public Health. 2011; 101:1922-1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ford ES, Greenlund KJ, Hong Y. Ideal cardiovascular health and mortality from all causes and diseases of the circulatory system among adults in the United States. Circulation. 2012; 125:987-995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Yang Q, Cogswell ME, Flanders WD, Hong Y, Zhang Z, Loustalot F, Gillespie C, Merritt R, Hu FB. Trends in cardiovascular health metrics and associations with all‐cause and CVD mortality among US adults. JAMA. 2012; 307:1273-1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Artero EG, Espana‐Romero V, Lee DC, Sui X, Church TS, Lavie CJ, Blair SN. Ideal cardiovascular health and mortality: Aerobics Center Longitudinal Study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012; 87:944-952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Dong C, Rundek T, Wright CB, Anwar Z, Elkind MS, Sacco RL. Ideal cardiovascular health predicts lower risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and vascular death across whites, blacks, and hispanics: the northern Manhattan study. Circulation. 2012; 125:2975-2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Wu S, Huang Z, Yang X, Zhou Y, Wang A, Chen L, Zhao H, Ruan C, Wu Y, Xin A, Li K, Jin C, Cai J. Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health and its relationship with the 4‐year cardiovascular events in a northern Chinese industrial city. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012; 5:487-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Frieden TR, Berwick DM. The “Million Hearts” initiative–preventing heart attacks and strokes. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:e27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Tomaselli GF, Harty MB, Horton K, Schoeberl M. The American Heart Association and the Million Hearts Initiative: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011; 124:1795-1799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Fortmann SP, Haskell WL, Williams PT, Varady AN, Hulley SB, Farquhar JW. Community surveillance of cardiovascular diseases in the Stanford Five‐City Project. Methods and initial experience. Am J Epidemiol. 1986; 123:656-669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.White AD, Folsom AR, Chambless LE, Sharret AR, Yang K, Conwill D, Higgins M, Williams OD, Tyroler HA. Community surveillance of coronary heart disease in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study: methods and initial two years' experience. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996; 49:223-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.U.S.Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A Public Health Action Plan to Prevent Heart Disease and Stroke Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/action_plan/index.htm. Accessed November 29, 2012.
- 105.Goff DC, Jr, Brass L, Braun LT, Croft JB, Flesch JD, Fowkes FG, Hong Y, Howard V, Huston S, Jencks SF, Luepker R, Manolio T, O'Donnell C, Robertson RM, Rosamond W, Rumsfeld J, Sidney S, Zheng ZJ. Essential features of a surveillance system to support the prevention and management of heart disease and stroke: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Councils on Epidemiology and Prevention, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Nursing and the Interdisciplinary Working Groups on Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease. Circulation. 2007; 115:127-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Institute of Medicine. A Nationwide Framework for Surveillance of Cardiovascular and Chronic Lung Diseases. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press, 2011:1–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Sidney S, Rosamond WD, Howard VJ, Luepker RV. The “Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics–2013 Update” and the Need for a National Cardiovascular Surveillance System. Circulation. 2013; 127:21-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


