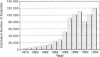
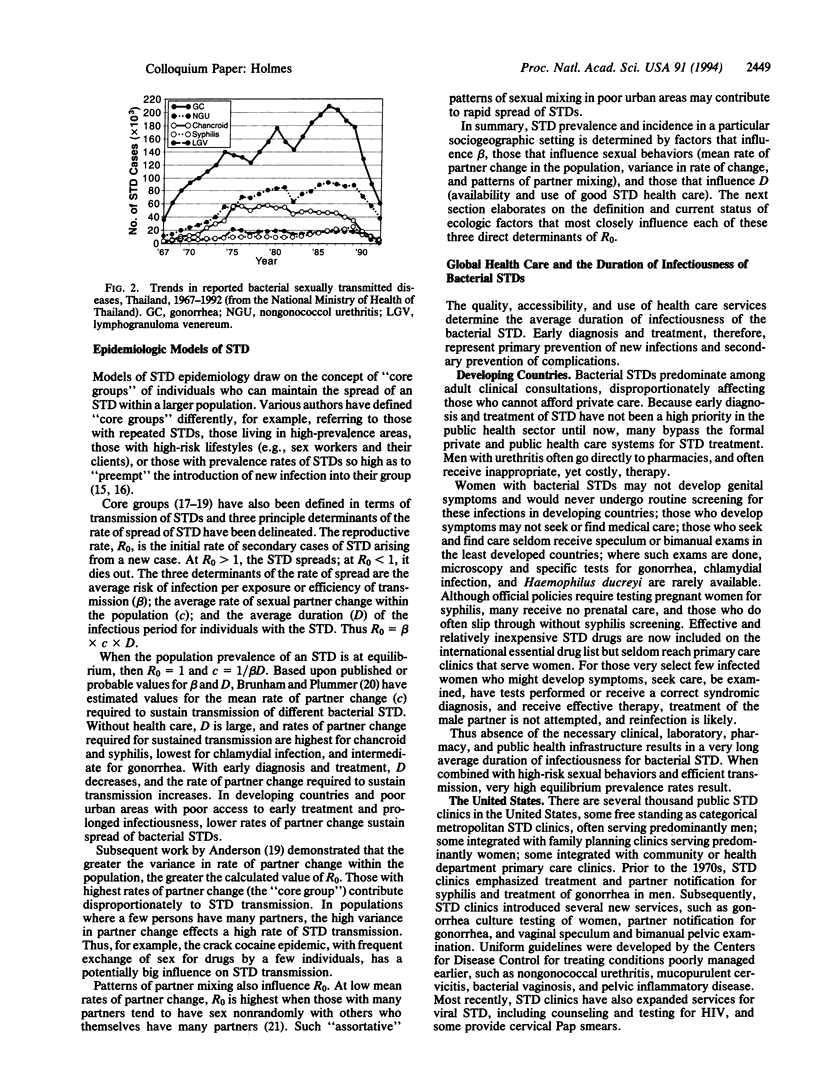
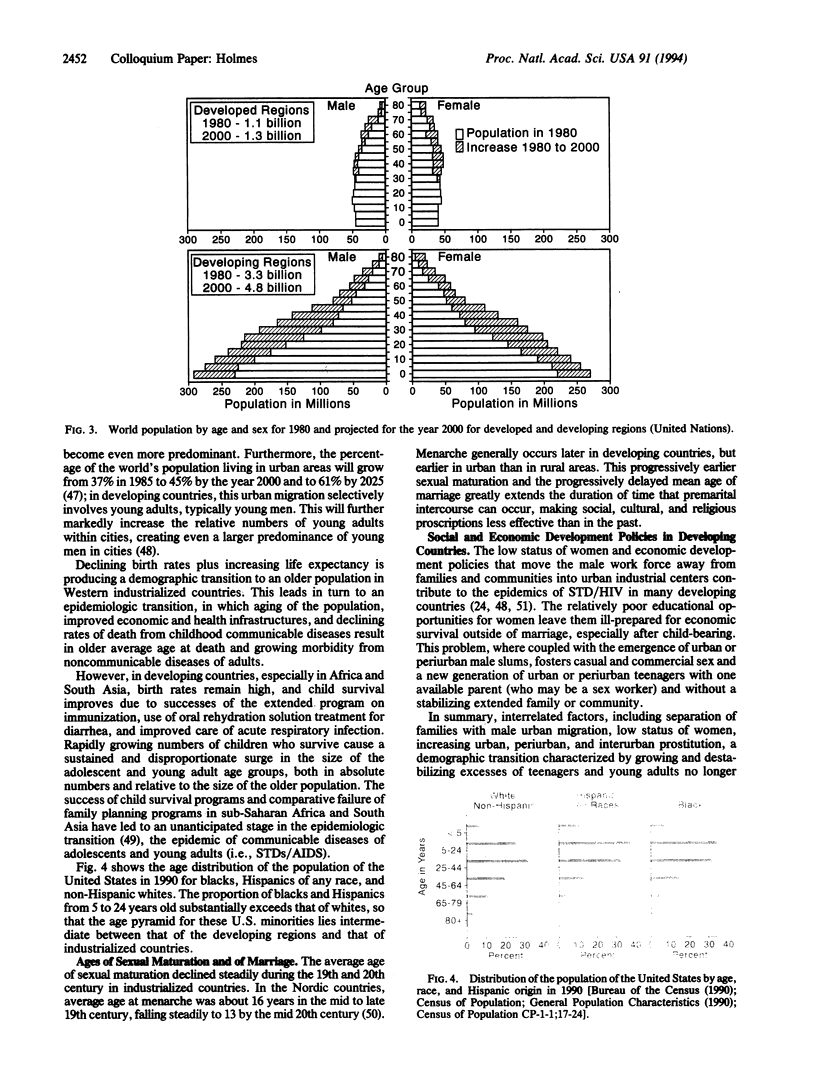
Abstract
The three direct determinants of the rate of spread of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are sexual behaviors, the mean duration of infectiousness, and the mean efficiency of sexual transmission of each STD. Underlying ecological and behavioral factors that operate through one or more of these direct determinants lie on a continuum, ranging from those most proximate back to those more remote (in time or mechanism) from the direct determinants. Most remote and least modifiable are the historical stages of economic development that even today conspicuously influence patterns of sexual behavior. Next are the distribution and changing patterns of climate, hygiene, and population density; the global population explosion and stages of the demographic transition; and ongoing changes in human physiology (e.g., menarche at younger age) and culture (e.g., later marriage). More proximate on the continuum are war, migration, and travel; and current policies for economic development and social welfare. Most recent or modifiable are technologic and commercial product development (e.g., oral contraceptives); circumcision, condom, spermicide, and contraception practices; patterns of illicit drug use that influence sexual behaviors; and the accessibility, quality, and use of STD health care. These underlying factors help explain why the curable bacterial STDs are epidemic in developing countries and why the United States is the only industrialized country that has failed to control bacterial STDs during the AIDS era.
Full text
PDF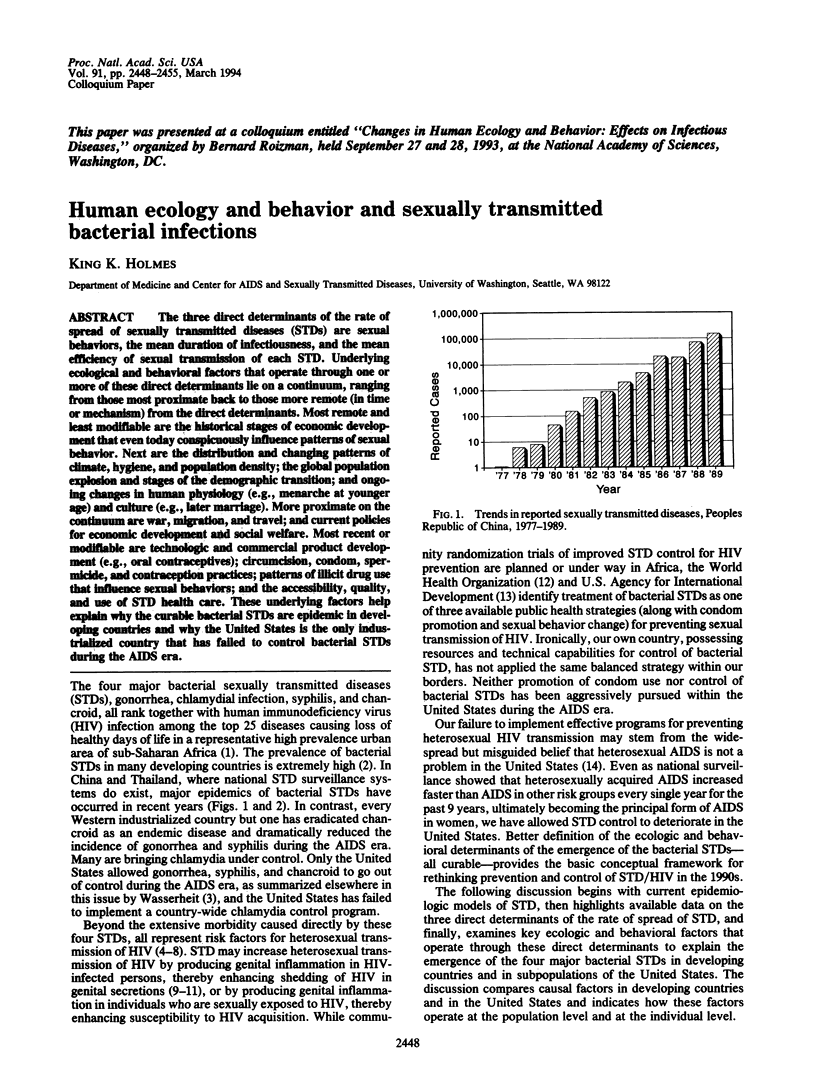





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. E., Dahlberg L. L. High-risk sexual behavior in the general population. Results from a national survey, 1988-1990. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Nov-Dec;19(6):320–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. M., May R. M. Epidemiological parameters of HIV transmission. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):514–519. doi: 10.1038/333514a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aral S. O., Holmes K. K. Sexually transmitted diseases in the AIDS era. Sci Am. 1991 Feb;264(2):62–69. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0291-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aral S. O., Mosher W. D., Cates W., Jr Vaginal douching among women of reproductive age in the United States: 1988. Am J Public Health. 1992 Feb;82(2):210–214. doi: 10.2105/ajph.82.2.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B. E., Fraiz J., Newhall W. J., Katz B. P., Jones R. B. Association of recurrent chlamydial infection with gonorrhea. J Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;159(4):661–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.4.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billy J. O., Tanfer K., Grady W. R., Klepinger D. H. The sexual behavior of men in the United States. Fam Plann Perspect. 1993 Mar-Apr;25(2):52–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Plummer F. A. A general model of sexually transmitted disease epidemiology and its implications for control. Med Clin North Am. 1990 Nov;74(6):1339–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30484-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. C., Caldwell P. High fertility in sub-Saharan Africa. Sci Am. 1990 May;262(5):118–125. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0590-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. C., Caldwell P. The demographic evidence for the incidence and cause of abnormally low fertility in tropical Africa. World Health Stat Q. 1983;36(1):2–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron D. W., Simonsen J. N., D'Costa L. J., Ronald A. R., Maitha G. M., Gakinya M. N., Cheang M., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Piot P., Brunham R. C. Female to male transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: risk factors for seroconversion in men. Lancet. 1989 Aug 19;2(8660):403–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90589-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania J. A., Coates T. J., Stall R., Turner H., Peterson J., Hearst N., Dolcini M. M., Hudes E., Gagnon J., Wiley J. Prevalence of AIDS-related risk factors and condom use in the United States. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1101–1106. doi: 10.1126/science.1439818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow W. H., Daling J. R., Weiss N. S., Moore D. E., Soderstrom R. Vaginal douching as a potential risk factor for tubal ectopic pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Dec 1;153(7):727–729. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(85)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemetson D. B., Moss G. B., Willerford D. M., Hensel M., Emonyi W., Holmes K. K., Plummer F., Ndinya-Achola J., Roberts P. L., Hillier S. Detection of HIV DNA in cervical and vaginal secretions. Prevalence and correlates among women in Nairobi, Kenya. JAMA. 1993 Jun 9;269(22):2860–2864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook L. S., Koutsky L. A., Holmes K. K. Clinical presentation of genital warts among circumcised and uncircumcised heterosexual men attending an urban STD clinic. Genitourin Med. 1993 Aug;69(4):262–264. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.4.262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronberg S. The rise and fall of sexually transmitted diseases in Sweden. Genitourin Med. 1993 Jun;69(3):184–186. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.3.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnett G. P., Anderson R. M. Contact tracing and the estimation of sexual mixing patterns: the epidemiology of gonococcal infections. Sex Transm Dis. 1993 Jul-Aug;20(4):181–191. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady W. R., Klepinger D. H., Billy J. O., Tanfer K. Condom characteristics: the perceptions and preferences of men in the United States. Fam Plann Perspect. 1993 Mar-Apr;25(2):67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J., Schnell D., Conlon R. Behaviors of crack cocaine users and their impact on early syphilis intervention. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Nov-Dec;19(6):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jekel J. F., Allen D. F., Podlewski H., Clarke N., Dean-Patterson S., Cartwright P. Epidemic free-base cocaine abuse. Case study from the Bahamas. Lancet. 1986 Mar 1;1(8479):459–462. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Wadsworth J., Wellings K., Bradshaw S., Field J. Sexual lifestyles and HIV risk. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):410–412. doi: 10.1038/360410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klepinger D. H., Billy J. O., Tanfer K., Grady W. R. Perceptions of AIDS risk and severity and their association with risk-related behavior among U.S. men. Fam Plann Perspect. 1993 Mar-Apr;25(2):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss J. K., Coombs R., Plummer F., Holmes K. K., Nikora B., Cameron W., Ngugi E., Ndinya Achola J. O., Corey L. Isolation of human immunodeficiency virus from genital ulcers in Nairobi prostitutes. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):380–384. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku L., Sonenstein F. L., Pleck J. H. Young men's risk behaviors for HIV infection and sexually transmitted diseases, 1988 through 1991. Am J Public Health. 1993 Nov;83(11):1609–1615. doi: 10.2105/ajph.83.11.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laga M., Manoka A., Kivuvu M., Malele B., Tuliza M., Nzila N., Goeman J., Behets F., Batter V., Alary M. Non-ulcerative sexually transmitted diseases as risk factors for HIV-1 transmission in women: results from a cohort study. AIDS. 1993 Jan;7(1):95–102. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199301000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson A. Social context of human immunodeficiency virus transmission in Africa: historical and cultural bases of east and central African sexual relations. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11(5):716–731. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.5.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marx R., Aral S. O., Rolfs R. T., Sterk C. E., Kahn J. G. Crack, sex, and STD. Sex Transm Dis. 1991 Apr-Jun;18(2):92–101. doi: 10.1097/00007435-199118020-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H. Slowing the spread of HIV: agenda for the 1990s. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1266–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.8493570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse S. A., Lysko P. G., McFarland L., Knapp J. S., Sandstrom E., Critchlow C., Holmes K. K. Gonococcal strains from homosexual men have outer membranes with reduced permeability to hydrophobic molecules. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.432-438.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M. Syphilis, neurosyphilis, penicillin, and AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1201–1206. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer F. A., Simonsen J. N., Cameron D. W., Ndinya-Achola J. O., Kreiss J. K., Gakinya M. N., Waiyaki P., Cheang M., Piot P., Ronald A. R. Cofactors in male-female sexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):233–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer F. A., Wainberg M. A., Plourde P., Jessamine P., D'Costa L. J., Wamola I. A., Ronald A. R. Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in genital ulcer exudate of HIV-1-infected men by culture and gene amplification. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):810–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potterat J. J., Rothenberg R. B., Woodhouse D. E., Muth J. B., Pratts C. I., Fogle J. S., 2nd Gonorrhea as a social disease. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Jan-Mar;12(1):25–32. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198501000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H. Hepatitis viruses: changing patterns of human disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2401–2406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn T. C. Population migration and the spread of types 1 and 2 human immunodeficiency viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2407–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. J., Roberts P. L., Handsfield H. H., Holmes K. K. Sociodemographic distribution of gonorrhea incidence: implications for prevention and behavioral research. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1252–1258. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers R. G., Hackenberg R. Extending epidemiologic transition theory: a new stage. Soc Biol. 1987 Fall-Winter;34(3-4):234–243. doi: 10.1080/19485565.1987.9988678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi-Espagnet A., Goldstein G. B., Tabibzadeh I. Urbanization and health in developing countries: a challenge for health for all. World Health Stat Q. 1991;44(4):185–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg R. B. The geography of gonorrhea. Empirical demonstration of core group transmission. Am J Epidemiol. 1983 Jun;117(6):688–694. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenstein F. L., Pleck J. H., Ku L. C. Sexual activity, condom use and AIDS awareness among adolescent males. Fam Plann Perspect. 1989 Jul-Aug;21(4):152–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm W. E., Handsfield H. H., Rompalo A. M., Ashley R. L., Roberts P. L., Corey L. The association between genital ulcer disease and acquisition of HIV infection in homosexual men. JAMA. 1988 Sep 9;260(10):1429–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanfer K., Grady W. R., Klepinger D. H., Billy J. O. Condom use among U.S. men, 1991. Fam Plann Perspect. 1993 Mar-Apr;25(2):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanfer K. National Survey of Men: design and execution. Fam Plann Perspect. 1993 Mar-Apr;25(2):83–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trupin E. W., Tarico V. S., Low B. P., Jemelka R., McClellan J. Children on child protective service caseloads: prevalence and nature of serious emotional disturbance. Child Abuse Negl. 1993 May-Jun;17(3):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0145-2134(93)90057-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. Social disintegration and the spread of AIDS: thresholds for propagation along 'sociogeographic' networks. Soc Sci Med. 1991;33(10):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(91)90231-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. Urban desertification, public health and public order: 'planned shrinkage', violent death, substance abuse and AIDS in the Bronx. Soc Sci Med. 1990;31(7):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(90)90175-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserheit J. N. Epidemiological synergy. Interrelationships between human immunodeficiency virus infection and other sexually transmitted diseases. Sex Transm Dis. 1992 Mar-Apr;19(2):61–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wølner-Hanssen P., Eschenbach D. A., Paavonen J., Kiviat N., Stevens C. E., Critchlow C., DeRouen T., Holmes K. K. Decreased risk of symptomatic chlamydial pelvic inflammatory disease associated with oral contraceptive use. JAMA. 1990 Jan 5;263(1):54–59. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03440010052029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wølner-Hanssen P., Eschenbach D. A., Paavonen J., Stevens C. E., Kiviat N. B., Critchlow C., DeRouen T., Koutsky L., Holmes K. K. Association between vaginal douching and acute pelvic inflammatory disease. JAMA. 1990 Apr 11;263(14):1936–1941. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03440140062032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorke J. A., Hethcote H. W., Nold A. Dynamics and control of the transmission of gonorrhea. Sex Transm Dis. 1978 Apr-Jun;5(2):51–56. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197804000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelnik M., Kantner J. F. Sexual activity, contraceptive use and pregnancy among metropolitan-area teenagers: 1971-1979. Fam Plann Perspect. 1980 Sep-Oct;12(5):230-1, 233-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]